1 3 Divided By 6
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
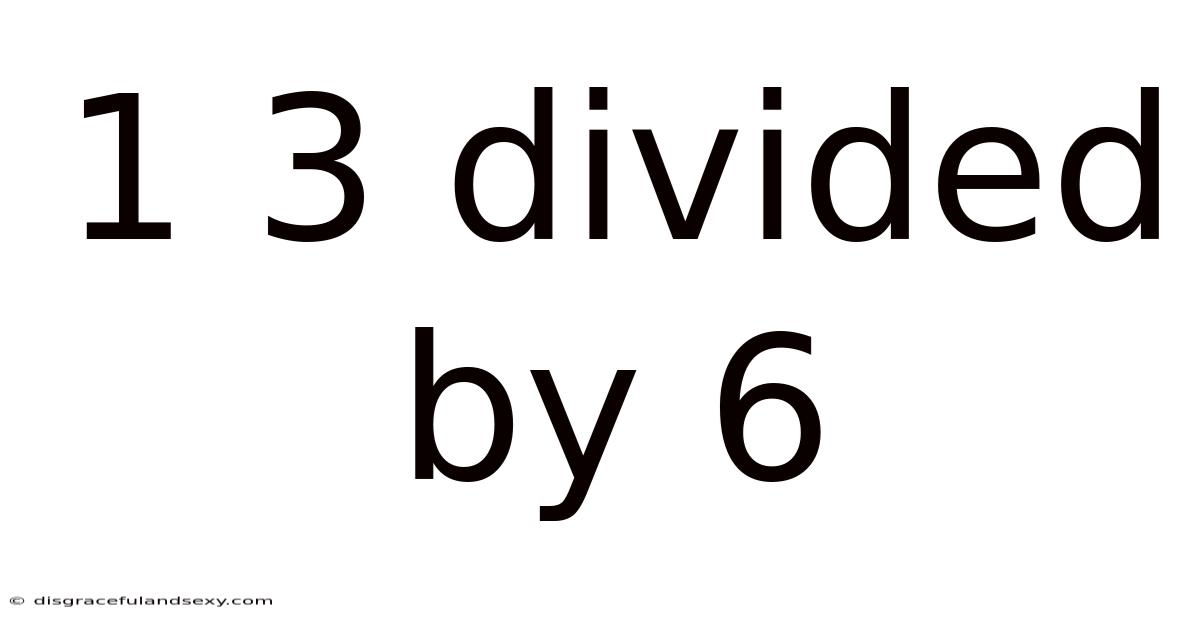
Table of Contents
Unpacking the Mystery: 1/3 Divided by 6
Understanding fractions and division can feel like navigating a mathematical maze, especially when faced with a problem like 1/3 divided by 6. This seemingly simple equation can be surprisingly tricky, but fear not! This comprehensive guide will break down the process step-by-step, providing you not only with the answer but also a deep understanding of the underlying principles involved. We’ll explore various methods of solving this problem, delve into the mathematical rationale behind each step, and address frequently asked questions to solidify your grasp of fraction division.
Understanding the Basics: Fractions and Division
Before diving into the specific problem of 1/3 divided by 6, let's review the fundamental concepts of fractions and division. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts you have, while the denominator shows how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
Division, on the other hand, is the process of splitting a quantity into equal groups. When we divide a whole number by another whole number, we're essentially asking how many times the second number fits into the first. But what happens when we introduce fractions into the mix?
Method 1: The Reciprocal Approach
The most common method for dividing fractions involves using reciprocals. A reciprocal is simply a fraction flipped upside down. For example, the reciprocal of 2/3 is 3/2. The key rule to remember is: dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
Let's apply this to our problem: 1/3 divided by 6.
-
Rewrite the whole number as a fraction: We can rewrite 6 as 6/1. This makes it easier to work with the fraction 1/3.
-
Change division to multiplication: Replace the division symbol with a multiplication symbol, and flip the second fraction (the divisor) to its reciprocal.
1/3 ÷ 6/1 becomes 1/3 x 1/6
-
Multiply the numerators and denominators: Multiply the numerators together and the denominators together.
(1 x 1) / (3 x 6) = 1/18
Therefore, 1/3 divided by 6 equals 1/18.
Method 2: Visual Representation
While the reciprocal method is efficient, visualizing the problem can enhance understanding, particularly for beginners. Imagine you have one-third of a pizza. You want to divide this one-third into six equal shares. How big is each share?
To visualize this, consider the original one-third. Dividing it into six equal pieces means you're creating eighteen equal pieces out of a whole pizza (because 3 x 6 = 18). Your original one-third represents just one of those eighteen pieces. Therefore, each share is 1/18 of the whole pizza.
This visual approach reinforces the answer obtained using the reciprocal method.
Method 3: Using Decimals (for Enhanced Understanding)
Converting fractions to decimals can sometimes aid comprehension. Let's convert 1/3 to a decimal: 1/3 ≈ 0.333... (the 3s repeat infinitely).
Now, we have 0.333... divided by 6. Performing this division gives us approximately 0.0555... This decimal is also approximately equal to 1/18. Note that using decimals might introduce slight inaccuracies due to rounding off repeating decimals. This method is best used for conceptual clarity rather than precise calculation.
The Mathematical Rationale: Why Reciprocals Work
The reciprocal method isn't just a trick; it's rooted in sound mathematical principles. Consider the general rule for dividing fractions:
a/b ÷ c/d = (a/b) x (d/c)
This rule is derived from the definition of division. When you divide a by b, you're essentially asking "how many times does b fit into a?". The same logic applies when dividing fractions. The reciprocal effectively "flips" the division process, allowing for straightforward multiplication. It's a powerful technique that simplifies complex fraction divisions.
Expanding the Concept: Dividing Fractions by Other Fractions
The principles discussed above extend beyond dividing a fraction by a whole number. Let’s consider an example of dividing a fraction by another fraction:
2/5 ÷ 3/4
-
Rewrite the problem as multiplication using reciprocals:
2/5 x 4/3
-
Multiply numerators and denominators:
(2 x 4) / (5 x 3) = 8/15
Therefore, 2/5 divided by 3/4 equals 8/15. The same process – converting division into multiplication by using the reciprocal of the divisor – remains consistent regardless of whether you’re dividing by a whole number or another fraction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why can't I just divide the numerators and denominators directly when dividing fractions?
A: Unlike multiplication, where you can multiply numerators and denominators directly, division requires the use of reciprocals. Direct division of numerators and denominators would not yield the correct result.
-
Q: What if the divisor is a decimal instead of a fraction or whole number?
A: Convert the decimal to a fraction first. For instance, if you have 1/3 divided by 0.5, convert 0.5 to 1/2 and then proceed with the reciprocal method.
-
Q: Can I simplify the fraction before or after multiplying?
A: You can simplify the fraction either before or after multiplying. Simplifying before multiplying (canceling common factors) can often make the calculation easier.
-
Q: Is there a way to check my answer?
A: Yes! You can always check your answer by performing the inverse operation: multiplication. Multiply your answer (1/18) by the original divisor (6). If you get the original dividend (1/3), your answer is correct. (1/18 x 6 = 6/18 = 1/3)
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Division
Dividing fractions, even seemingly simple ones like 1/3 divided by 6, requires a systematic approach and a firm understanding of the underlying concepts. The reciprocal method, explained and illustrated in this article, provides a clear and efficient way to solve such problems. Remember to practice regularly, using both the numerical and visual approaches to solidify your understanding and build confidence in handling fraction division. The key takeaway is to view this not merely as a calculation but as a process of logical deduction and manipulation of mathematical tools, making you a more confident and adept problem-solver. By mastering this concept, you build a strong foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts in the future.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 3 Divided By 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.