1 4 9 16 25
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
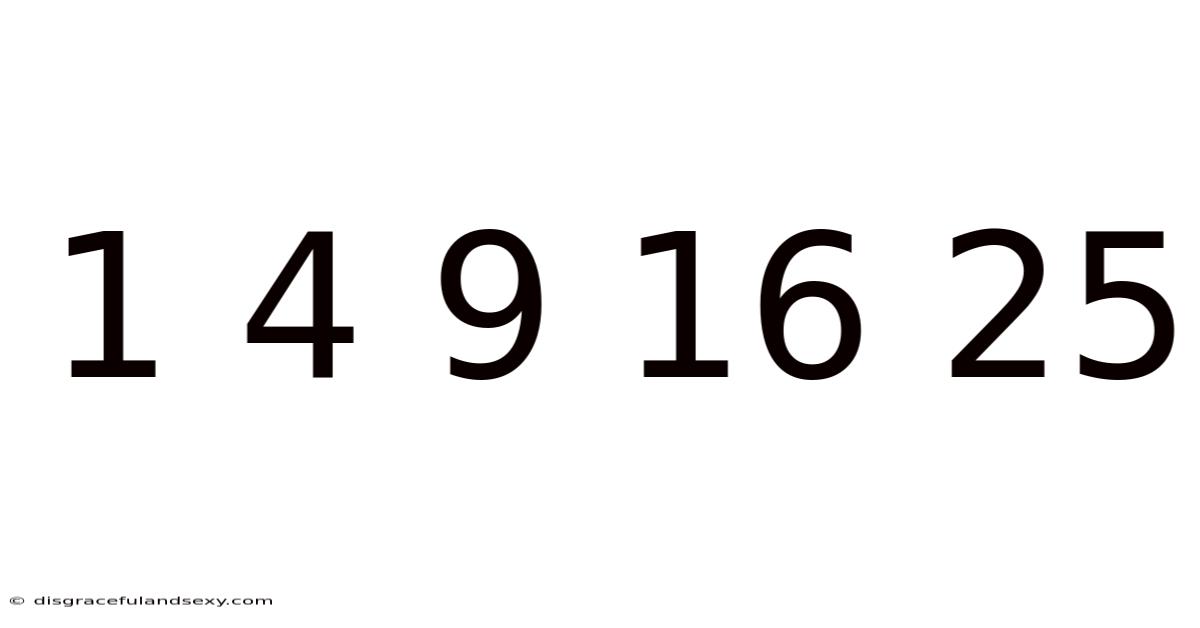
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Mystery: The Sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 25... and Beyond
The seemingly simple sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 25... holds a wealth of mathematical beauty and significance. At first glance, it might appear unremarkable, but a deeper dive reveals connections to fundamental mathematical concepts, geometric patterns, and even practical applications. This article will explore this sequence, delving into its underlying patterns, exploring its connections to other mathematical concepts, and examining its broader implications. Understanding this sequence provides a strong foundation for exploring more complex mathematical ideas.
Introduction: Recognizing the Pattern
The sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 25... is instantly recognizable to anyone familiar with basic arithmetic. Each number is a perfect square: the product of a whole number multiplied by itself. More formally, the nth term of this sequence is given by n². Therefore, the first five terms are:
- 1² = 1
- 2² = 4
- 3² = 9
- 4² = 16
- 5² = 25
This simple observation forms the bedrock of understanding this seemingly straightforward sequence. However, the beauty lies in how this simple pattern connects to much broader mathematical ideas.
Exploring the Sequence: Visual and Numerical Representations
The sequence of perfect squares can be visualized in several interesting ways. One powerful visual representation is through square numbers. Imagine drawing squares with sides of length 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 units. The number of unit squares in each larger square corresponds precisely to the terms in our sequence: 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25. This visual representation reinforces the concept of perfect squares and provides a concrete, intuitive understanding.
Furthermore, the differences between consecutive terms also reveal an interesting pattern. Subtracting consecutive terms yields the following sequence:
- 4 - 1 = 3
- 9 - 4 = 5
- 16 - 9 = 7
- 25 - 16 = 9
Notice that the differences form the sequence of odd numbers (3, 5, 7, 9...). This connection between the sequence of perfect squares and the sequence of odd numbers provides another insightful perspective on the underlying structure. This observation can be used to derive a formula for the sum of the first n odd numbers, which interestingly equals n².
The Mathematical Foundation: Connecting to Series and Sums
The sequence of perfect squares is intimately related to the concept of series in mathematics. A series is simply the sum of the terms in a sequence. The sum of the first n perfect squares is given by the following formula:
∑ᵢ₌₁ⁿ i² = n(n+1)(2n+1) / 6
This formula allows us to calculate the sum of the first n terms efficiently. For instance, the sum of the first 5 perfect squares (1 + 4 + 9 + 16 + 25) is:
5(5+1)(2*5+1) / 6 = 5(6)(11) / 6 = 55
This formula is a significant result in mathematics and has various applications in different fields. Understanding its derivation requires a deeper exploration into mathematical induction or other proof techniques. However, the fact that such a concise and elegant formula exists highlights the mathematical significance of the sequence of perfect squares.
Beyond the Basics: Extensions and Related Sequences
The sequence of perfect squares is just one instance of a larger family of sequences. We can explore variations and extensions:
-
Cubes: Instead of squares, we can consider cubes (1³, 2³, 3³, 4³, 5³...). This yields the sequence 1, 8, 27, 64, 125... Similar to perfect squares, this sequence also has interesting properties and formulas related to their sums.
-
Higher Powers: We can generalize this concept to higher powers (1⁴, 2⁴, 3⁴,...), 1, 16, 81, 256... The mathematical complexity increases with the power, but the underlying principles remain similar.
-
Sequences of Differences: As demonstrated earlier, the differences between consecutive terms in the perfect square sequence produce the sequence of odd numbers. Examining the differences of differences, or even higher-order differences, can reveal further patterns and relationships.
These extensions demonstrate that the sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 25... is not isolated but a part of a broader mathematical landscape. Exploring these extensions reveals deeper connections within mathematics.
Applications in Various Fields: From Physics to Computer Science
While seemingly abstract, the sequence of perfect squares and related concepts have practical applications in various fields:
-
Physics: In physics, particularly in kinematics (the study of motion), the concept of squared terms is frequently encountered. For example, the distance traveled by an object under constant acceleration is proportional to the square of the time elapsed. This directly relates to the sequence of perfect squares.
-
Computer Science: In algorithm analysis, the concept of time complexity is crucial. Many algorithms have a time complexity that grows quadratically (proportional to n²), reflecting the growth pattern of the perfect square sequence. Understanding this helps in predicting the performance of algorithms as the input size increases.
-
Statistics and Probability: Perfect squares appear in various statistical formulas and probability distributions. For instance, the variance of a data set is calculated using squared differences, highlighting the significance of squares in data analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there a formula to find the nth term of the sequence?
A: Yes, the nth term is simply n².
Q: How can I calculate the sum of the first 10 perfect squares?
A: Use the formula: n(n+1)(2n+1)/6. Substituting n=10, you get 10(11)(21)/6 = 385.
Q: Are there other sequences with similar properties?
A: Yes, sequences of cubes, higher powers, and various other sequences share similar characteristics and possess interesting properties. The study of number sequences is a rich area of mathematics.
Q: What are some resources to learn more about sequences and series?
A: Numerous textbooks and online resources are available covering sequences and series, ranging from introductory levels to advanced topics in calculus and analysis.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of a Simple Sequence
The sequence 1, 4, 9, 16, 25... might seem deceptively simple at first glance. However, a closer examination reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical connections, visual representations, and practical applications. From its basic representation as perfect squares to its connections with series, sums, and even applications in various scientific and computational fields, this sequence embodies the elegance and power of fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding this simple sequence serves as a gateway to appreciating the deeper beauty and interconnectedness of mathematics. The seemingly simple can often hold profound and far-reaching implications, and the sequence of perfect squares is a testament to this truth. Further exploration of this and related sequences will undoubtedly reveal even more fascinating aspects of the mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 4 9 16 25 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.