1 5 8 X 2
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
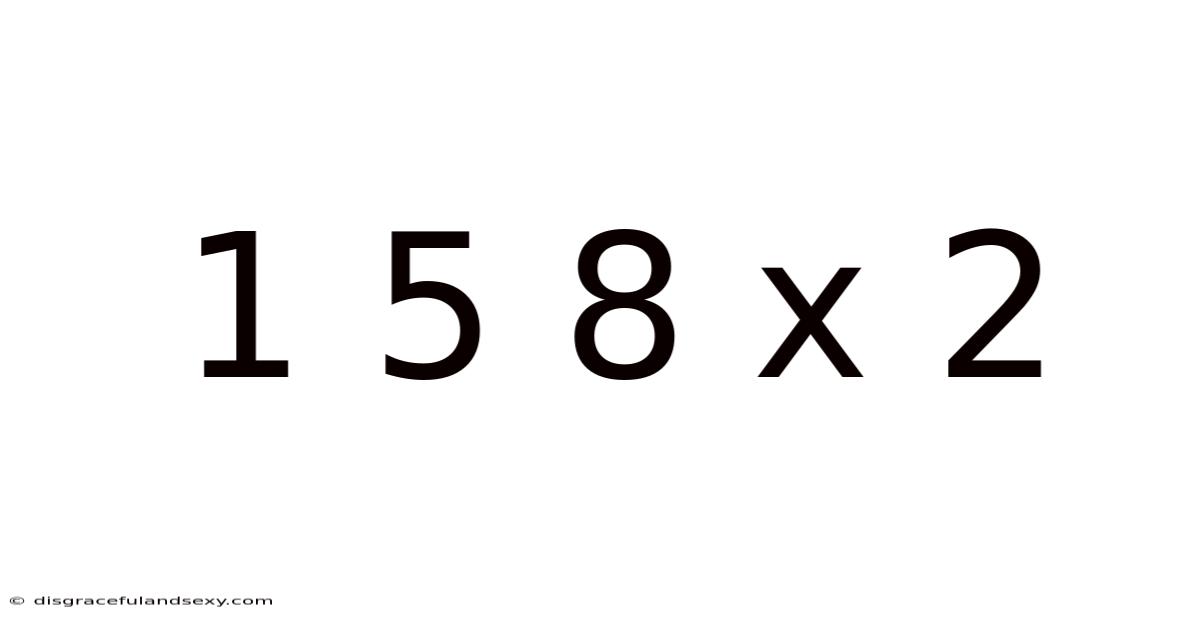
Table of Contents
Decoding 1 5 8 x 2: A Deep Dive into Number Patterns, Multiplicative Properties, and Practical Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "1 5 8 x 2," delving beyond the immediate calculation to uncover underlying patterns, explore the mathematical principles involved, and reveal its relevance in various fields. We'll examine the multiplicative properties of this specific sequence, discuss related number patterns, and illustrate its practical applications in areas like coding, data analysis, and even music. This comprehensive guide is designed for anyone interested in mathematics, from beginners curious about number sequences to those seeking a deeper understanding of multiplicative operations.
Understanding the Basics: The Calculation and Initial Observations
The most straightforward interpretation of "1 5 8 x 2" involves treating "1 5 8" as a single number, a concatenated value of 158. In this case, the calculation is simply:
158 x 2 = 316
This is a basic multiplication problem, easily solved using standard arithmetic. However, the true value of exploring this expression lies in analyzing the underlying mathematical structures and patterns, moving beyond the immediate solution.
Exploring Number Patterns: Sequences and Series
The sequence "1 5 8" itself can be seen as a short numerical sequence. While it doesn't immediately fit into a well-known mathematical sequence like Fibonacci or arithmetic progressions, we can consider it in the context of generating potential series. We could speculate about various ways to extend this sequence, each leading to different results and underlying rules:
-
Scenario 1: Arbitrary Sequence: This sequence could simply be an arbitrary selection of numbers with no inherent mathematical relationship. This is a valid possibility; not every sequence needs to follow a defined rule.
-
Scenario 2: Difference Sequence: Let's analyze the differences between consecutive numbers: 5 - 1 = 4 and 8 - 5 = 3. There isn't a consistent difference, suggesting a non-arithmetic progression.
-
Scenario 3: Exploring Quadratic Relationships: A more sophisticated approach involves investigating if a quadratic equation could generate this sequence. However, finding such an equation that fits perfectly requires more data points. With only three numbers, this approach yields multiple possible quadratic solutions, making it inconclusive.
These explorations highlight that, while simple, the sequence itself opens doors to exploring concepts like sequence generation, pattern recognition, and the limitations of determining patterns from limited data.
Multiplicative Properties: Examining the Impact of 'x 2'
The multiplication by 2 ("x 2") is a significant operation. Multiplying by 2 is equivalent to doubling. This simple action has profound implications in various fields:
-
Computer Science: In binary systems, multiplying by 2 is equivalent to a left bit shift. This is a highly efficient operation used extensively in computer programming and digital signal processing. Understanding this connection is crucial for optimizing algorithms and managing data efficiently.
-
Data Analysis and Scaling: Doubling data points in a dataset is a common scenario in scaling experiments or simulating growth. For instance, in population modeling, the growth rate often involves doubling times. The operation "x 2" directly reflects this process.
-
Finance and Economics: Compound interest calculations utilize multiplication. While "x 2" might not directly represent annual interest, understanding the multiplicative nature of growth, as represented by this simple operation, is foundational to understanding financial models and investment growth.
Extending the Exploration: Variations and Generalizations
Let’s consider variations of the initial problem and generalize the concept:
-
Multiplying by other numbers: Instead of multiplying by 2, we could explore the result of multiplying 158 by other integers (3, 4, 5, etc.), or even by decimal numbers and fractions. This allows for a broader understanding of scaling and its impact on the original number.
-
Different concatenated numbers: What if we change the initial sequence? We could explore different three-digit concatenated numbers (e.g., 246 x 2, 917 x 2) and analyze their properties. This allows for a comparative study of multiplicative effects on different numbers.
-
Sequences of different lengths: Instead of a three-digit number, what if we use four-digit concatenated numbers? How do the patterns and multiplicative effects change?
Practical Applications Across Disciplines
The core mathematical principles involved – multiplication, pattern recognition, and sequence analysis – extend far beyond this seemingly simple expression:
-
Computer Programming: As mentioned earlier, bitwise operations and efficient algorithms are crucial in computer science. Understanding how multiplication impacts binary numbers is essential for optimizing code. This includes efficient multiplication algorithms, which are fundamental to computer graphics, cryptography, and various simulations.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Scaling data involves multiplying data points by a constant factor. This is fundamental to normalization, standardization, and scaling datasets for various statistical analyses. The principle underlying "158 x 2" is relevant in scenarios ranging from image processing to economic modeling.
-
Music Theory: Musical intervals and ratios often involve multiplication. Understanding multiplicative relationships between frequencies is crucial in harmony, counterpoint, and music composition. Although the specific numbers (1, 5, 8) might not have direct musical significance, the principle of multiplication applies.
-
Engineering and Physics: Many engineering and physics problems involve scaling, proportionality, and ratios. Understanding multiplicative relationships is fundamental to calculating forces, stresses, and other physical quantities.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are there any special mathematical properties of the number 316 (158 x 2)?
A1: While 316 itself isn't a particularly special number in the realm of prime numbers or other well-known mathematical concepts, its relevance comes from its derivation through the multiplication process. The focus should be less on the final result and more on the process and implications of the multiplication.
Q2: How does this relate to more complex mathematical concepts?
A2: This simple example provides a foundation for understanding more advanced topics: Linear algebra (scalar multiplication), abstract algebra (group theory), and number theory (prime factorization, modular arithmetic). The underlying principles of multiplication and pattern recognition are fundamental to these advanced concepts.
Q3: Is there a pattern to extending the sequence 1, 5, 8?
A3: No readily apparent pattern exists. Many sequences are possible. Extending a sequence requires a defined rule or generating function. Without such a rule, multiple extensions are valid, highlighting the ambiguity in inferring patterns from limited data.
Q4: What if the spaces between the numbers in "1 5 8" are significant?
A4: If the spaces are significant, it suggests a different interpretation, potentially involving a code or a more abstract representation. Without additional context, we can only address the most likely interpretation (treating "1 5 8" as a single number).
Conclusion: Beyond the Calculation
The expression "1 5 8 x 2" might seem trivial at first glance. However, a thorough exploration reveals its value lies not just in the calculation itself (resulting in 316), but in the broader implications of the underlying mathematical concepts. This simple problem offers a gateway to explore number patterns, multiplicative properties, and the pervasive use of multiplication in various fields. By understanding the principles involved, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their far-reaching applications. It's a reminder that even the simplest mathematical expressions can lead to insightful discoveries when examined closely and thoughtfully. This exploration should encourage a deeper curiosity about the world of numbers and the beauty of mathematical relationships.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 5 8 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.