1 8 X 2 3
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
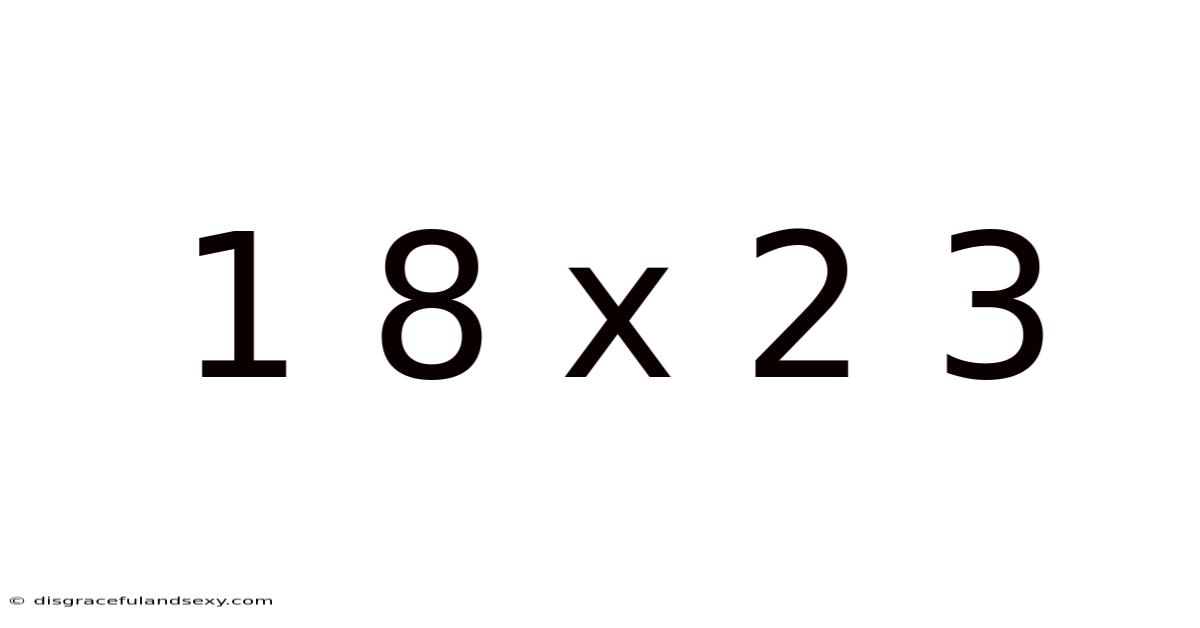
Table of Contents
Decoding 18 x 23: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and Beyond
This article explores the seemingly simple multiplication problem, 18 x 23, as a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts. We'll move beyond the simple answer to delve into various methods of calculation, the underlying principles, and the broader applications of multiplication in everyday life and advanced mathematics. This comprehensive guide is suitable for students of all levels, from elementary school to those refreshing their mathematical skills. We'll cover different approaches to solving this problem, explore the properties of numbers involved, and even touch upon the historical context of multiplication.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is Multiplication?
Before diving into 18 x 23, let's establish a solid foundation. Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. When we say 18 x 23, we are essentially asking: "What is the result of adding 18 to itself 23 times?" While this method is conceptually sound, it's not the most efficient approach for larger numbers.
Multiplication represents the scaling of a number. In this case, 18 is scaled by a factor of 23. This concept extends beyond simple whole numbers to fractions, decimals, and even complex numbers. Understanding this scaling aspect is crucial for grasping the power and versatility of multiplication.
Methods for Solving 18 x 23
There are several ways to solve 18 x 23, each offering a different perspective on the underlying mathematical principles.
1. The Standard Algorithm (Long Multiplication)
This is the method most commonly taught in schools. It involves breaking down the multiplication into smaller, manageable steps:
- Step 1: Multiply 18 by 3 (the units digit of 23): 18 x 3 = 54. Write down '4' and carry-over '5'.
- Step 2: Multiply 18 by 2 (the tens digit of 23): 18 x 2 = 36. Add the carry-over '5': 36 + 5 = 41. Write down '41' to the left of the '4'.
- Step 3: Add the results: 414.
Therefore, 18 x 23 = 414. This method utilizes the distributive property of multiplication over addition, breaking down the problem into simpler multiplications and additions.
2. The Distributive Property Method
This method explicitly uses the distributive property, a(b + c) = ab + ac. We can rewrite 23 as 20 + 3:
- 18 x (20 + 3) = (18 x 20) + (18 x 3)
- 18 x 20 = 360
- 18 x 3 = 54
- 360 + 54 = 414
This approach highlights the underlying mathematical principle behind the standard algorithm.
3. Lattice Multiplication
This less common method is visually appealing and can be helpful for understanding place value. It uses a grid to break down the multiplication into smaller parts.
- Create a grid with two rows (for the digits of 18) and two columns (for the digits of 23).
- Multiply each digit combination (1 x 2, 1 x 3, 8 x 2, 8 x 3) and write the result in the corresponding cell, separating the tens and units digits diagonally.
- Add the numbers along the diagonals, carrying over as needed. The final answer is obtained by reading the sums along the diagonals.
4. Mental Math Techniques
With practice, you can perform this calculation mentally. One approach involves using the distributive property and rounding:
- Approximate 18 as 20: 20 x 23 = 460
- Subtract the excess: (20 - 18) x 23 = 2 x 23 = 46
- 460 - 46 = 414
This method requires estimation and subtraction skills, but it's very useful for quick calculations.
Exploring the Numbers: Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Let's analyze the numbers 18 and 23 themselves.
- 18: The prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3 (or 2 x 3²). This means 18 is divisible by 2, 3, 6, and 9.
- 23: 23 is a prime number, meaning it's only divisible by 1 and itself.
Understanding the prime factorization of numbers helps in simplifying calculations, finding common factors, and working with fractions and ratios.
Applications of Multiplication: Real-World Examples
Multiplication is not just an abstract mathematical concept; it's a fundamental tool used in countless everyday situations:
- Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items.
- Cooking: Doubling or tripling recipes.
- Travel: Determining distances and travel times.
- Finance: Calculating interest and taxes.
- Construction: Measuring areas and volumes.
- Data analysis: Scaling data sets and calculating averages.
The ability to perform multiplication efficiently and accurately is essential for navigating many aspects of life.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Mathematical Concepts
The seemingly simple 18 x 23 problem opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Algebra: Multiplication is a fundamental operation in algebra, used in solving equations and manipulating expressions. Think of 18x + 23y = ...
- Calculus: Derivatives and integrals, the cornerstones of calculus, involve multiplication and its inverse, division.
- Linear Algebra: Matrix multiplication, a cornerstone of linear algebra, extends the concept of multiplication to arrays of numbers.
- Number Theory: Exploring the properties of numbers like prime factorization and divisibility is a core part of number theory.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are some common mistakes students make when multiplying?
A: Common mistakes include errors in carrying over digits, misplacing digits in the product, and forgetting to multiply by each digit in the second number. Practicing regularly and carefully checking work are crucial for avoiding these mistakes.
Q: Are there any alternative methods for multiplication beyond those mentioned?
A: Yes, there are other methods, including Napier's bones (a historical calculation device), the Russian peasant multiplication method, and various abacus-based techniques.
Q: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A: Consistent practice, using a variety of methods, and focusing on understanding the underlying principles are key to improving multiplication skills. Online resources, educational games, and working with a tutor can also be beneficial.
Q: Why is multiplication important?
A: Multiplication is a fundamental building block of mathematics and has wide-ranging applications in various fields, including science, engineering, finance, and everyday life. Mastering multiplication is essential for academic success and problem-solving abilities.
Conclusion: More Than Just Numbers
The seemingly simple equation 18 x 23 is far more than just a calculation. It serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts, various calculation methods, and the diverse applications of multiplication in the real world. Through exploration, practice, and a deeper understanding of the underlying principles, you can enhance your mathematical skills and appreciate the elegance and power of this core operation. This journey beyond the simple answer of 414 demonstrates how even basic arithmetic can unlock a world of mathematical possibilities. Keep exploring, keep learning, and keep enjoying the beauty of numbers!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 8 X 2 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.