11 3/4 Divided By 2
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
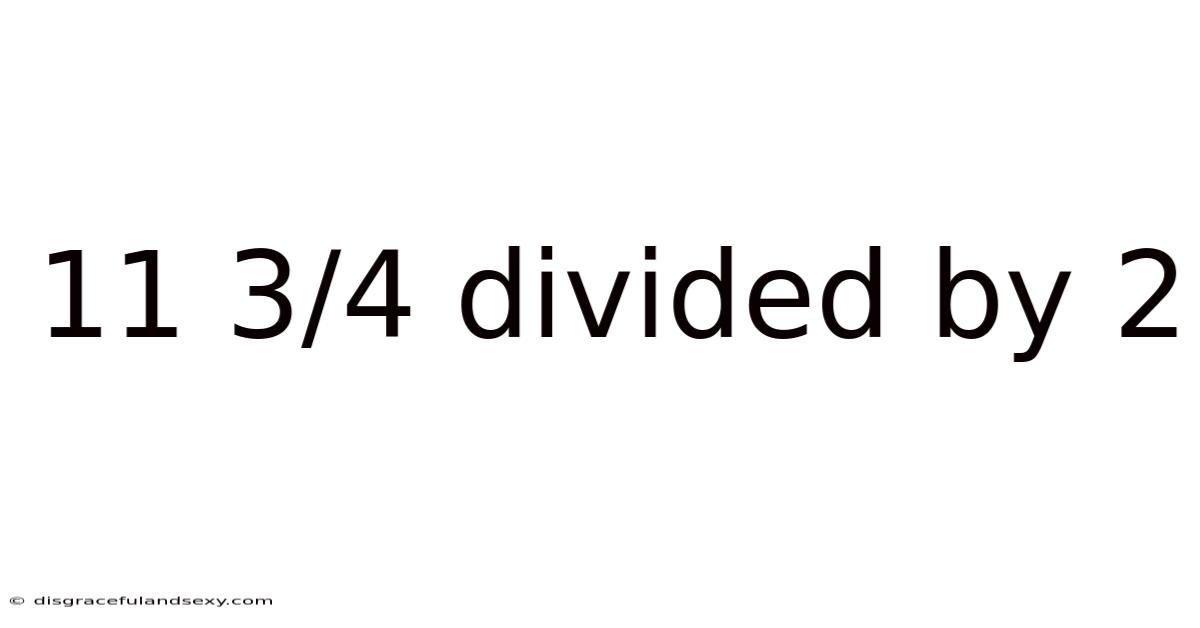
Table of Contents
Diving Deep into Division: Solving 11 3/4 Divided by 2
This article will comprehensively explore the solution to the mathematical problem: 11 3/4 divided by 2. We'll move beyond simply providing the answer, delving into the underlying concepts, various solution methods, and practical applications to solidify your understanding of division with mixed numbers. This exploration will be suitable for learners of all levels, from those brushing up on basic arithmetic to those seeking a deeper understanding of fractional division. We'll cover different approaches, ensuring you grasp the fundamental principles and can confidently tackle similar problems in the future.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Division
Before we dive into solving 11 3/4 divided by 2, let's refresh our understanding of key concepts. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 11 3/4. Division, in its essence, is the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts. When dividing with fractions or mixed numbers, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of these fundamentals.
Method 1: Converting to Improper Fractions
This is a widely used and highly effective method. The first step involves converting the mixed number, 11 3/4, into an improper fraction. An improper fraction has a numerator (top number) larger than or equal to its denominator (bottom number).
To convert 11 3/4 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 11 * 4 = 44
- Add the numerator: 44 + 3 = 47
- Keep the same denominator: The improper fraction is 47/4.
Now, our problem becomes: 47/4 ÷ 2. Remember that dividing by a whole number is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal. The reciprocal of 2 is 1/2. Therefore:
47/4 ÷ 2 = 47/4 * 1/2 = 47/8
This improper fraction, 47/8, can be converted back into a mixed number:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator: 47 ÷ 8 = 5 with a remainder of 7
- The quotient becomes the whole number: 5
- The remainder becomes the numerator, and the denominator stays the same: 7/8
Therefore, 11 3/4 ÷ 2 = 5 7/8
Method 2: Dividing the Whole Number and Fraction Separately
This method offers a more intuitive approach for some learners. We can divide the whole number and the fractional part separately and then combine the results.
- Divide the whole number: 11 ÷ 2 = 5 with a remainder of 1. This means we have 5 wholes.
- Convert the remainder to a fraction: The remainder 1 is equivalent to 4/4 (since our original fraction's denominator is 4). We now have 1 3/4 remaining.
- Add the fractional part: 1 3/4 ÷ 2 = (4/4 + 3/4) ÷ 2 = 7/4 ÷ 2 = 7/4 * 1/2 = 7/8
- Combine the results: 5 + 7/8 = 5 7/8
This method might seem longer, but it highlights the underlying principle of distributing the division across the whole and fractional components.
Method 3: Decimal Conversion
This method involves converting the mixed number into a decimal and then performing the division.
- Convert the fraction to a decimal: 3/4 = 0.75
- Combine with the whole number: 11 + 0.75 = 11.75
- Divide by 2: 11.75 ÷ 2 = 5.875
This decimal, 5.875, can be converted back into a mixed number:
- The whole number is 5.
- The decimal part, 0.875, represents 875/1000, which simplifies to 7/8.
Therefore, 11.75 ÷ 2 = 5 7/8
A Deeper Dive into the Mathematical Principles
The core principle behind dividing fractions and mixed numbers involves understanding reciprocals and the commutative property of multiplication. When we divide by a fraction, we multiply by its reciprocal. The reciprocal of a fraction is obtained by switching the numerator and the denominator. For example, the reciprocal of 2/3 is 3/2. The commutative property states that the order of multiplication doesn't change the result (a x b = b x a).
These principles are at the heart of all the methods shown above. Whether we convert to improper fractions or divide the whole and fractional parts separately, we're implicitly using these fundamental mathematical properties.
Practical Applications
Understanding division with mixed numbers has a wide range of practical applications in everyday life:
- Cooking and Baking: Scaling recipes up or down often requires dividing mixed number quantities (e.g., dividing a recipe that calls for 2 1/2 cups of flour by 2 to make a smaller batch).
- Construction and Measurement: Dividing lengths or quantities of materials frequently involves mixed numbers (e.g., dividing a 12 3/4-foot beam into three equal sections).
- Sewing and Crafting: Calculating fabric requirements or dividing patterns often involves working with mixed numbers.
- Financial Calculations: Dividing expenses or shares among multiple people might require dividing mixed number amounts.
Mastering this skill allows you to tackle these real-world problems confidently and accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why are there multiple methods to solve this problem? Different methods cater to different learning styles and preferences. Some find converting to improper fractions easier, while others prefer the separate division approach. The choice depends on your comfort level and understanding.
-
Can I use a calculator? While calculators can provide a quick answer, it's essential to understand the underlying mathematical principles. Using a calculator without understanding the process limits your ability to solve similar problems without assistance.
-
What if I get a different answer using a different method? If you obtain a different answer using a different method, double-check each step carefully. Errors in calculation are common, especially when working with fractions. Review the steps in each method to identify any mistakes.
-
How can I improve my skills in fractional division? Practice is key! Work through various problems with different mixed numbers and divisors. Focus on understanding the underlying principles rather than just memorizing steps. Start with simpler problems and gradually increase the complexity.
Conclusion
Solving 11 3/4 divided by 2, which equals 5 7/8, involves a deeper understanding of fractional arithmetic. We explored three different methods – converting to improper fractions, dividing the whole number and fraction separately, and decimal conversion – all leading to the same correct answer. Understanding these methods and the underlying mathematical principles enhances problem-solving skills and opens up a world of practical applications across various fields. Remember to practice regularly to build confidence and mastery in working with mixed numbers and fractions. The more you practice, the more intuitive these calculations will become. Don't be afraid to explore different approaches until you find the method that best suits your learning style. Consistent effort and a solid grasp of the fundamentals will make you a confident problem-solver.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 11 3/4 Divided By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.