12 Square Root Of 3
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
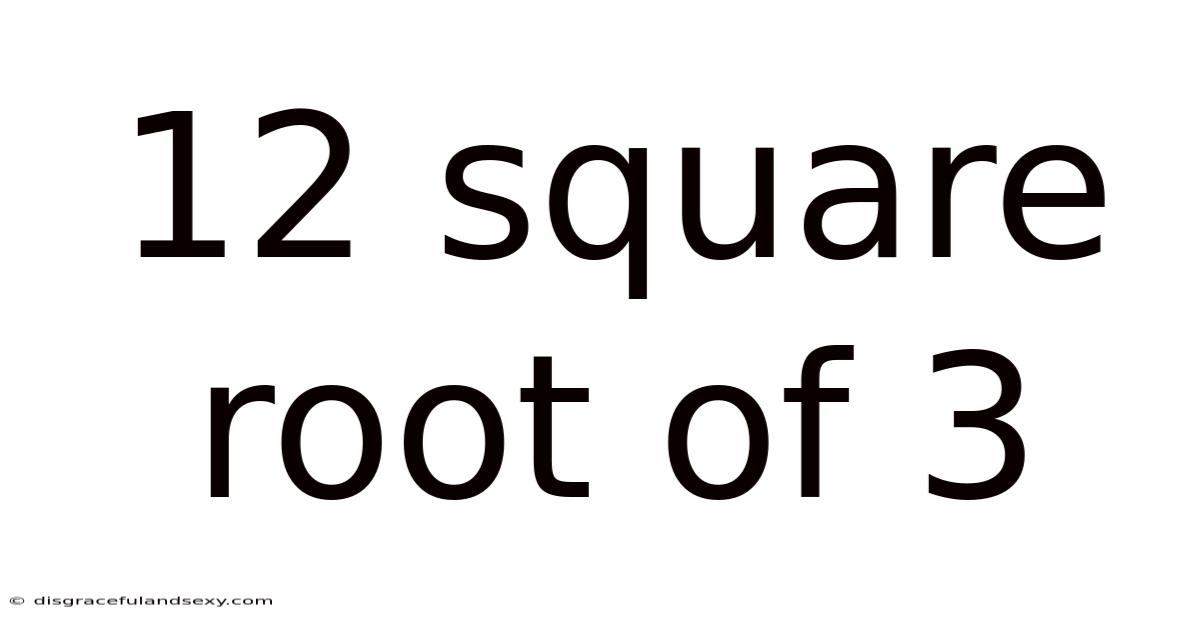
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into 12√3
The expression "12√3" might seem intimidating at first glance, conjuring images of complex mathematical formulas and endless calculations. However, understanding this seemingly simple expression unlocks a deeper appreciation of fundamental mathematical concepts, particularly in geometry and trigonometry. This article will explore the meaning of 12√3, its applications, and how to approach similar expressions, providing a comprehensive guide suitable for students and anyone interested in deepening their mathematical understanding. We'll delve into its geometrical significance, explore its simplification, and even tackle some common misconceptions.
Understanding the Basics: What does 12√3 mean?
At its core, 12√3 represents a number. Let's break down its components:
- 12: This is a whole number, a simple and straightforward coefficient.
- √: This symbol denotes a square root. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9.
- 3: This is the radicand, the number under the square root symbol. In this case, we're looking for the square root of 3.
Therefore, 12√3 signifies 12 times the square root of 3. The square root of 3 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. Its approximate value is 1.732. So, 12√3 is approximately 12 * 1.732 = 20.784.
Geometrical Significance: The Ubiquitous 30-60-90 Triangle
The expression 12√3 frequently appears in problems involving 30-60-90 triangles. These are right-angled triangles with angles measuring 30, 60, and 90 degrees. The sides of a 30-60-90 triangle have a specific ratio:
- Shortest side (opposite the 30° angle): x
- Longer leg (opposite the 60° angle): x√3
- Hypotenuse (opposite the 90° angle): 2x
Understanding this ratio is crucial for solving many geometry problems. If the shortest side of a 30-60-90 triangle is 6, then the longer leg will be 6√3 and the hypotenuse will be 12. Now, consider a scenario where the hypotenuse of a 30-60-90 triangle is 12. Using the ratio, we can determine the lengths of the other sides:
- Hypotenuse: 12 (given)
- Shortest side: 12/2 = 6
- Longer leg: 6√3
Here's where 12√3 comes into play. This value directly represents the length of the longer leg of a 30-60-90 triangle with a hypotenuse of 12.
Applications in Various Fields
The number 12√3 isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications across diverse fields:
- Engineering: Calculations involving structures, forces, and angles frequently utilize trigonometry, making 12√3 a valuable component in various engineering designs. For instance, calculating stress on a structural member at an angle.
- Physics: Problems dealing with vectors, projectile motion, and other mechanics often involve the manipulation of trigonometric functions and right-angled triangles, leading to expressions like 12√3.
- Architecture: Architectural designs frequently incorporate angles and geometric shapes. Understanding the properties of 30-60-90 triangles, and hence numbers like 12√3, is vital for accurate planning and construction.
- Surveying: Land surveying techniques heavily rely on trigonometry to measure distances and angles. Determining the precise dimensions of a land parcel often involves calculating values similar to 12√3.
Simplifying and Approximating 12√3
While leaving the expression as 12√3 is often preferred for its exactness, knowing how to approximate its value can be beneficial in practical situations. As mentioned earlier, √3 is approximately 1.732. Therefore, 12√3 is approximately 12 * 1.732 = 20.784.
This approximation is useful for quick estimations, but it's vital to remember that it's not perfectly precise. For precise calculations, always use the exact form, 12√3.
Advanced Concepts: Rationalizing the Denominator
While not directly related to 12√3 itself, understanding the concept of rationalizing the denominator is crucial when dealing with more complex expressions involving square roots. Rationalizing the denominator involves removing any radicals from the denominator of a fraction. For instance, if you had an expression like 1/(√3), you would rationalize it by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by √3, resulting in √3/3. This simplifies calculations and presents a cleaner, more manageable expression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is 12√3 a rational or irrational number?
A: It's an irrational number. While 12 is rational, the multiplication of a rational number (12) by an irrational number (√3) results in an irrational number.
Q: How can I calculate 12√3 without a calculator?
A: You can't calculate it precisely without a calculator because √3 is irrational. You can only obtain an approximation using methods like the Babylonian method for approximating square roots. However, leaving the expression as 12√3 preserves its exact value.
Q: What are some common mistakes when working with expressions like 12√3?
A: A common mistake is incorrectly assuming that √3 is simply 1.7. Remember to use a sufficiently accurate approximation or to keep the expression in its exact form for precise calculations. Another common error is misapplying the rules of exponents when simplifying expressions involving square roots.
Q: Can 12√3 be simplified further?
A: No, 12√3 is already in its simplest form. You can't simplify it any further unless you approximate the value of √3.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
Understanding 12√3 goes beyond simply knowing its approximate numerical value. It's about grasping the underlying mathematical concepts—the properties of irrational numbers, the relationships in 30-60-90 triangles, and the principles of trigonometry. By mastering these fundamentals, you equip yourself with the tools to tackle more complex mathematical problems and appreciate the elegance and practicality of mathematical principles in diverse fields. This deep understanding isn't just about memorizing formulas; it's about developing a robust intuition for how mathematical concepts interact and apply to real-world scenarios. The seemingly simple expression 12√3 serves as a gateway to a much wider and fascinating world of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 12 Square Root Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.