13 40 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
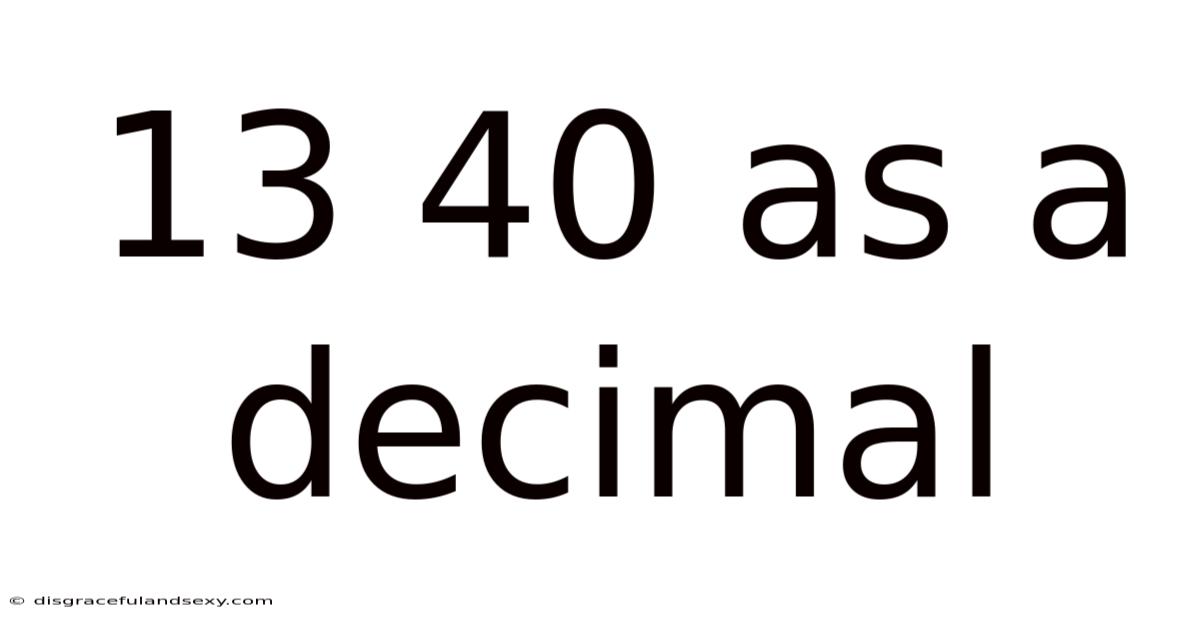
Table of Contents
13/40 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide to Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of converting the fraction 13/40 into its decimal equivalent, explaining the method in detail and exploring related concepts. We'll delve into different approaches, address potential difficulties, and provide you with the tools to confidently tackle similar conversions. This guide will cover not only the basic calculation but also the underlying mathematical principles and practical applications. Let's dive in!
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we begin converting 13/40, let's refresh our understanding of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The denominator indicates the number of equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered.
A decimal, on the other hand, is a way of expressing a number using a base-ten system. The digits to the left of the decimal point represent whole numbers, while the digits to the right represent fractions of a whole, with each place value representing a power of ten (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on).
The conversion between fractions and decimals involves finding the equivalent representation of the same value using a different notation.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting a fraction to a decimal is through long division. To convert 13/40 to a decimal, we divide the numerator (13) by the denominator (40):
-
Set up the long division: Write 13 as the dividend (inside the division symbol) and 40 as the divisor (outside the division symbol).
-
Add a decimal point and zeros: Since 13 is smaller than 40, we add a decimal point after 13 and add zeros as needed. This doesn't change the value of 13, but allows us to continue the division process.
-
Perform the division: Now, perform the long division. 40 goes into 130 three times (3 x 40 = 120). Subtract 120 from 130, leaving a remainder of 10.
-
Bring down the next zero: Bring down the next zero to make 100. 40 goes into 100 two times (2 x 40 = 80). Subtract 80 from 100, leaving a remainder of 20.
-
Continue the process: Bring down another zero to make 200. 40 goes into 200 five times (5 x 40 = 200). The remainder is 0, indicating that the division is complete.
Therefore, 13/40 = 0.325
Method 2: Converting to an Equivalent Fraction with a Denominator of 10, 100, or 1000
This method involves finding an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). This equivalent fraction can then be easily converted to a decimal.
However, in the case of 13/40, finding a direct equivalent fraction with a denominator of 10, 100, or 1000 is not straightforward. 40 does not divide evenly into any of these numbers. This method works best when the denominator of the fraction has prime factors of only 2 and/or 5. Since 40 = 2³ x 5, this method is technically possible but not as efficient as long division in this specific case.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
The simplest and quickest method is to use a calculator. Simply enter 13 ÷ 40 and the calculator will display the decimal equivalent, which is 0.325. While this is the easiest approach, understanding the underlying mathematical processes is crucial for developing a deeper understanding of fractions and decimals.
Understanding the Decimal Value: Significance and Interpretation
The decimal value 0.325 represents 325 thousandths. This means that if we divide a whole into 1000 equal parts, 0.325 represents 325 of those parts. This decimal can be expressed as a fraction: 325/1000. This fraction can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 25, resulting in 13/40, demonstrating that our conversion was correct.
Practical Applications of Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert fractions to decimals is essential in many real-world applications:
- Finance: Calculating interest rates, discounts, and proportions.
- Engineering: Precision measurements and calculations involving ratios.
- Science: Data analysis, experimental results, and scientific notation.
- Everyday Life: Calculating percentages, splitting bills, and measuring quantities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
A: No. Only fractions whose denominators have only 2 and/or 5 as prime factors can be converted to terminating decimals. Fractions with denominators containing other prime factors will result in repeating decimals.
Q: What is a repeating decimal?
A: A repeating decimal is a decimal that has a sequence of digits that repeat infinitely. For example, 1/3 = 0.3333... The three dots indicate that the 3 repeats indefinitely.
Q: How do I convert a repeating decimal back to a fraction?
A: Converting a repeating decimal back to a fraction requires algebraic manipulation. This process involves setting up an equation and solving for the unknown fraction.
Q: Are there online tools or calculators that can help with this conversion?
A: Yes, many online tools and calculators are available to assist with fraction-to-decimal conversions. However, it is important to understand the underlying principles of the conversion process.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
Converting fractions to decimals is a crucial skill with wide-ranging applications. This guide has demonstrated three different methods for converting 13/40 to its decimal equivalent (0.325), emphasizing the long division method as the most fundamental and broadly applicable approach. Remember, mastering this conversion involves not only understanding the mechanics but also appreciating the underlying mathematical concepts and their significance in various fields. Whether you use long division, an equivalent fraction method, or a calculator, the ability to accurately convert fractions to decimals is a valuable asset in both academic and practical contexts. Continue practicing, and you'll soon become proficient in this important mathematical skill. Understanding the why behind the how will further enhance your comprehension and problem-solving capabilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 13 40 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.