14 20 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
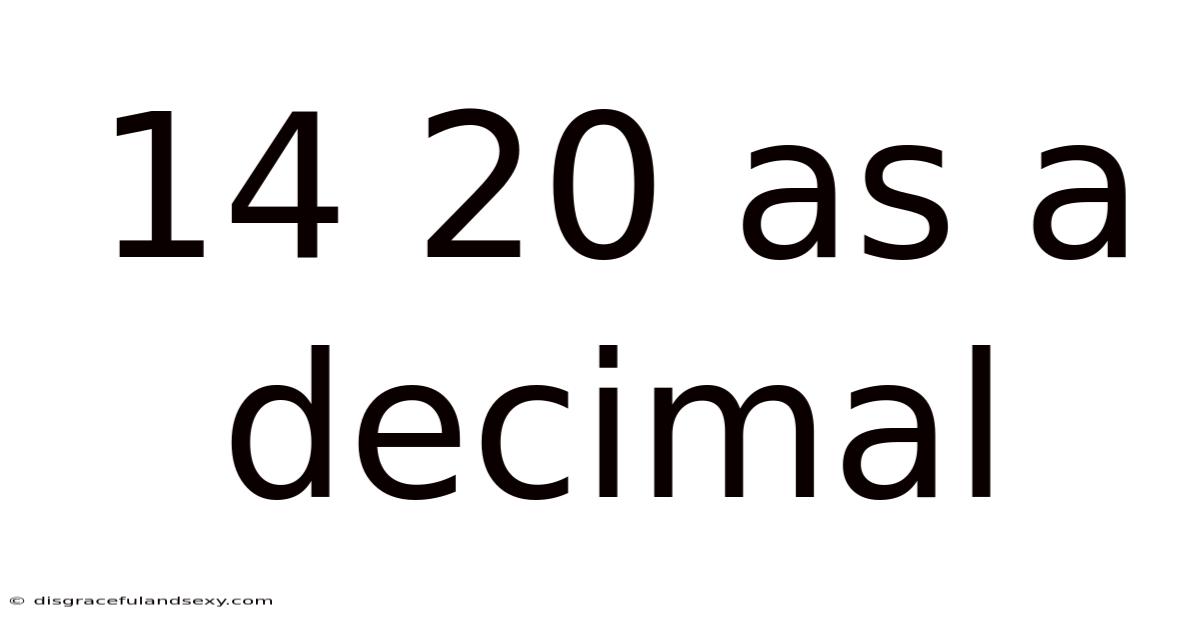
Table of Contents
Understanding 14/20 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, applicable across various fields from everyday calculations to advanced scientific applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting the fraction 14/20 into its decimal equivalent, exploring different methods, clarifying underlying concepts, and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We will also address common misconceptions and frequently asked questions to ensure a complete and thorough grasp of this mathematical operation.
What is a Fraction? A Quick Refresher
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly revisit the concept of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two parts: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts we have, while the denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into. In the fraction 14/20, 14 is the numerator and 20 is the denominator. This means we have 14 parts out of a possible 20 equal parts.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method to convert a fraction to a decimal is through long division. We simply divide the numerator (14) by the denominator (20).
-
Set up the division: Write 14 as the dividend (inside the division symbol) and 20 as the divisor (outside the division symbol).
-
Add a decimal point and zeros: Since 14 is smaller than 20, we add a decimal point after 14 and append zeros as needed. This doesn't change the value of the number; it simply allows us to continue the division process.
-
Perform the division: Now, perform the long division. 20 goes into 140 seven times (20 x 7 = 140). This gives us a remainder of 0.
Therefore, 14/20 = 0.7
Step-by-step illustration:
0.7
20 | 14.0
14.0
-----
0.0
Method 2: Simplifying the Fraction First
Often, simplifying the fraction before converting to a decimal can make the long division easier. We can simplify 14/20 by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 14 and 20. The GCD of 14 and 20 is 2. We divide both the numerator and denominator by 2:
14 ÷ 2 = 7 20 ÷ 2 = 10
This simplifies the fraction to 7/10. Now, converting 7/10 to a decimal is much simpler:
7 divided by 10 is 0.7
This method highlights that simplifying a fraction doesn't change its value, only its representation. Both 14/20 and 7/10 represent the same quantity.
Method 3: Using Decimal Equivalents of Common Fractions
Knowing the decimal equivalents of some common fractions can be a helpful shortcut. For example, we know that 1/10 = 0.1, 1/2 = 0.5, 1/4 = 0.25, and so on. While 14/20 isn't directly one of these common fractions, we can express it in terms of them after simplification:
As we showed earlier, 14/20 simplifies to 7/10. Since 1/10 = 0.1, then 7/10 = 7 * 0.1 = 0.7
Understanding the Decimal Result: 0.7
The decimal 0.7 represents seventy hundredths (70/100). This is equivalent to seven tenths (7/10), confirming our conversion from the fraction. Understanding this relationship between fractions and decimals is crucial for interpreting and using the results accurately.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversion
Converting fractions to decimals is widely used in various real-world scenarios:
-
Financial Calculations: Calculating percentages, discounts, interest rates, and profit margins often involve converting fractions to decimals.
-
Scientific Measurements: Many scientific measurements are expressed as decimals, making conversions necessary for data analysis and calculations.
-
Engineering and Design: Decimals are essential for precise measurements and calculations in engineering and design projects.
-
Everyday Life: Dividing food, sharing resources, or calculating proportions frequently involves working with fractions and their decimal equivalents.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Incorrect placement of the decimal point: Carefully align the decimal point during long division to avoid errors.
-
Forgetting to add zeros: If the numerator is smaller than the denominator, remember to add zeros after the decimal point to continue the division.
-
Not simplifying the fraction: Simplifying the fraction first can simplify the long division process and minimize the chance of errors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
A: No. Some fractions, when converted to decimals, result in repeating decimals (e.g., 1/3 = 0.333...). 14/20, however, converts to a terminating decimal (0.7).
Q: What is the difference between a terminating and a repeating decimal?
A: A terminating decimal has a finite number of digits after the decimal point. A repeating decimal has a digit or a sequence of digits that repeat infinitely.
Q: Are there other methods to convert fractions to decimals?
A: While long division is the most common method, other techniques involve using calculators or software programs that can perform the conversion automatically.
Conclusion
Converting the fraction 14/20 to its decimal equivalent, 0.7, is a straightforward process achievable using long division, simplifying the fraction first, or utilizing knowledge of common decimal equivalents. Understanding the different methods, along with the underlying concepts of fractions and decimals, empowers you to tackle similar conversions with confidence. Remember to practice regularly and address any misconceptions you encounter to solidify your understanding and enhance your mathematical skills. The ability to confidently convert fractions to decimals is a valuable asset in various academic and real-world applications. This skill forms a foundation for further mathematical exploration and problem-solving across numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 14 20 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.