16/3 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
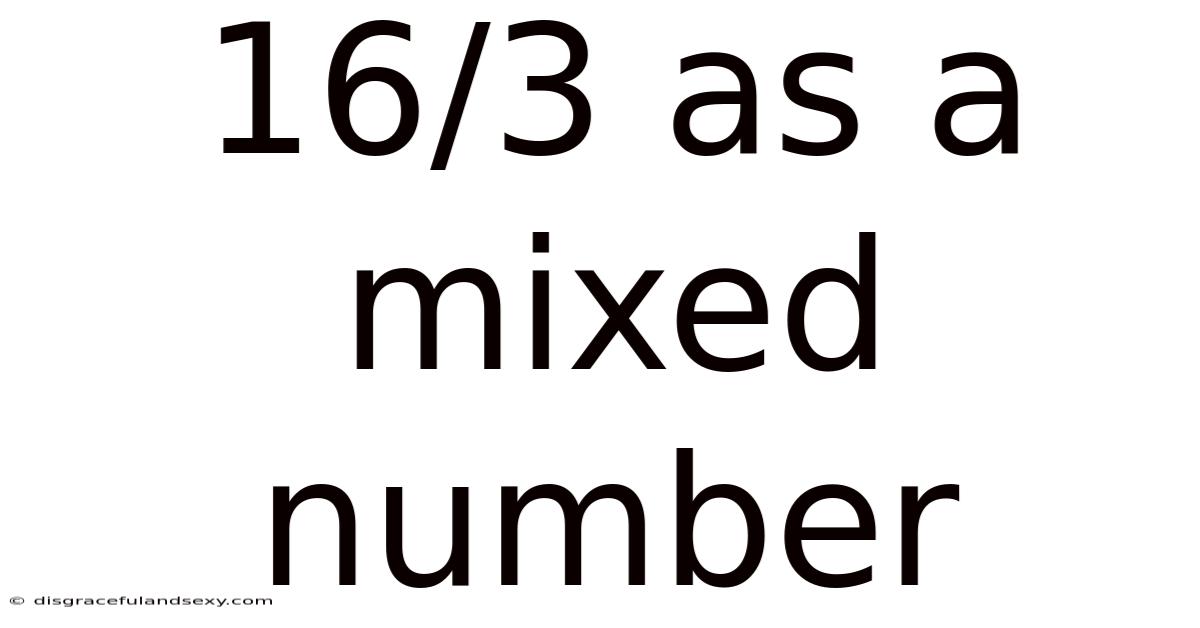
Table of Contents
Understanding 16/3 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple fraction 16/3 might appear straightforward at first glance. However, understanding how to convert it into a mixed number opens a door to a deeper understanding of fractions, their representation, and their practical applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of converting 16/3 into a mixed number, explore the underlying mathematical principles, and equip you with the knowledge to tackle similar fraction conversions with confidence.
Introduction: What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ½, 3 ¼, and 7 ⅔ are all mixed numbers. They offer a more intuitive way to represent fractions larger than one. Understanding mixed numbers is crucial in various areas, from cooking and construction to advanced mathematical calculations.
Converting 16/3 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Approach
The process of converting an improper fraction (like 16/3, where the numerator is larger than the denominator) to a mixed number involves a simple division. Here's how it's done:
-
Divide the Numerator by the Denominator: We begin by dividing the numerator (16) by the denominator (3). 16 ÷ 3 = 5 with a remainder of 1.
-
Identify the Whole Number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of our mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 5.
-
Determine the Fractional Part: The remainder (1) becomes the numerator of the fractional part, while the denominator remains the same (3). This gives us the fraction 1/3.
-
Combine the Whole Number and Fraction: Finally, we combine the whole number and the fraction to form the mixed number. Therefore, 16/3 is equal to 5 ⅓.
Visualizing the Conversion: A Practical Example
Imagine you have 16 equally sized pizza slices. If each pizza has 3 slices, how many whole pizzas do you have and how many slices are leftover?
You can divide the 16 slices into groups of 3. You'll have 5 groups of 3 slices (5 whole pizzas) and 1 slice leftover. This leftover slice represents the fraction 1/3 of a pizza. Thus, you have 5 ⅓ pizzas. This visual representation reinforces the mathematical process described above.
The Mathematical Principles Behind the Conversion
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number relies on the fundamental principle of fraction representation. The improper fraction 16/3 represents 16 divided by 3. Performing the division and expressing the result as a whole number and a remaining fraction essentially decomposes the original fraction into its constituent parts. It doesn't change the overall value; it merely presents it in a different, more readily understandable format.
Applications of Mixed Numbers in Real-World Scenarios
Mixed numbers are frequently encountered in everyday life and various professional fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often call for mixed number measurements, like 2 ½ cups of flour or 1 ¾ teaspoons of baking powder.
-
Construction and Engineering: Measurements in building and engineering projects frequently utilize mixed numbers for precision and clarity. For example, a beam might measure 5 ⅔ feet long.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: When presenting data, mixed numbers can offer a more concise and understandable representation than improper fractions.
-
Time Measurement: The expression of time, such as 1 hour and 30 minutes (1 ½ hours), uses a mixed number format.
Understanding Equivalent Fractions: A Deeper Dive
It's important to understand that the improper fraction 16/3 and the mixed number 5 ⅓ are equivalent. They represent the same quantity. This equivalence stems from the ability to convert between the two forms without altering the value. You can always convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction, and vice-versa.
Converting a Mixed Number Back to an Improper Fraction
To convert 5 ⅓ back to an improper fraction, follow these steps:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 5 x 3 = 15
-
Add the numerator: 15 + 1 = 16
-
Keep the denominator the same: The denominator remains 3.
Therefore, the improper fraction is 16/3, confirming the equivalence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why is it important to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers? Mixed numbers offer a more intuitive and easily understood representation of quantities larger than one. They are more practical in many real-world applications.
-
Can all improper fractions be converted to mixed numbers? Yes, any improper fraction can be converted to a mixed number using the division method explained above.
-
What if the remainder is zero after division? If the remainder is zero, then the improper fraction is already a whole number. For example, 12/3 = 4.
-
Are there other ways to represent 16/3? Yes, besides 5 ⅓, you could represent it as a decimal (5.333...), but the mixed number offers a precise and easily understandable fractional form.
-
How do I compare mixed numbers? When comparing mixed numbers, first compare the whole number parts. If they are different, the larger whole number represents the larger mixed number. If the whole numbers are the same, then compare the fractional parts.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Conversions
Converting fractions, particularly improper fractions like 16/3, into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process, while seemingly simple, underpins a deeper understanding of fractional representation and its practical applications. By mastering this conversion, you gain a valuable tool for tackling various mathematical problems and interpreting data in a clearer, more intuitive way. The ability to effortlessly switch between improper fractions and mixed numbers enhances your mathematical fluency and opens doors to more advanced concepts. This comprehensive guide has provided not only the "how" but also the "why" behind this important mathematical skill, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to confidently approach and solve similar fraction-related problems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 16/3 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.