17/3 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
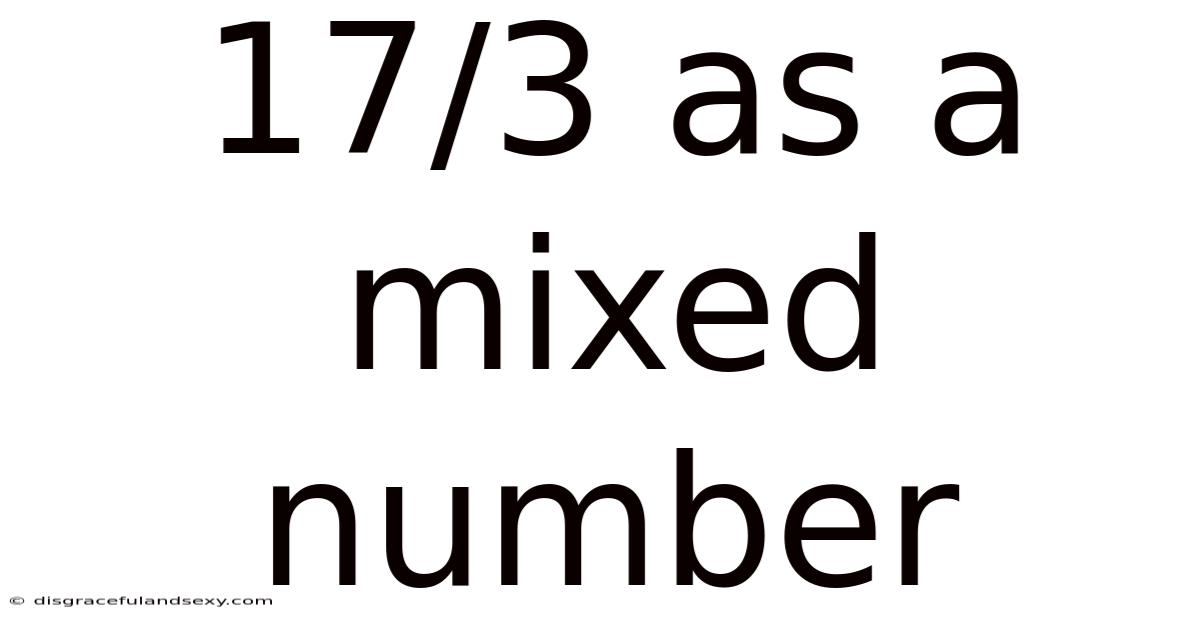
Table of Contents
Understanding 17/3 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 17/3, also known as seventeen-thirds, represents seventeen parts of a whole divided into three equal parts. While this improper fraction is perfectly valid, it's often more intuitive and easier to visualize as a mixed number. This article will delve deep into converting 17/3 into a mixed number, exploring the underlying mathematical concepts, providing step-by-step instructions, and addressing common questions surrounding this type of fraction conversion. We'll also examine the practical applications of understanding mixed numbers and their role in various mathematical operations.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before we dive into converting 17/3, let's clarify what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ¾, 2 ⅓, and 5 ⅛ are all mixed numbers. They represent a quantity that's greater than one whole unit.
Conversely, an improper fraction, like our 17/3, has a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator. While improper fractions are perfectly acceptable mathematically, mixed numbers are often preferred for their ease of understanding and practical application in real-world scenarios.
Converting 17/3 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting an improper fraction like 17/3 to a mixed number involves a simple division process. Here's a breakdown of the steps:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: We divide 17 (the numerator) by 3 (the denominator). 17 ÷ 3 = 5 with a remainder of 2.
-
Identify the whole number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of our mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 5.
-
Identify the fractional part: The remainder (the number left over after the division) becomes the numerator of the fractional part of our mixed number. The denominator remains the same as the original fraction. Thus, the remainder 2 becomes the numerator, and the denominator stays as 3. This gives us the fraction ⅔.
-
Combine the whole number and the fraction: Combine the whole number (5) and the fraction (⅔) to form the mixed number. Therefore, 17/3 as a mixed number is 5 ⅔.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 17 slices of pizza, and you want to divide them equally among 3 people. You can give each person 5 whole slices (5 x 3 = 15 slices). You'll have 2 slices left over (17 - 15 = 2). Those 2 slices represent ⅔ of a whole pizza. So, each person gets 5 whole slices and ⅔ of a slice, which is represented by the mixed number 5 ⅔.
The Mathematical Rationale
The process of converting an improper fraction to a mixed number is essentially based on the principle of dividing a larger quantity into smaller, equal parts. The division process determines how many whole units are contained within the improper fraction, and the remainder represents the leftover portion expressed as a fraction.
Formally, we can represent the conversion as follows:
17/3 = (3 x 5 + 2) / 3 = (3 x 5)/3 + 2/3 = 5 + 2/3 = 5 ⅔
This shows that 17/3 can be expressed as the sum of five whole units (5 x 3/3) and a remaining fraction of 2/3.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's important to understand the reverse process as well. To convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction, follow these steps:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: In our example (5 ⅔), multiply 5 (the whole number) by 3 (the denominator). 5 x 3 = 15.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result from step 1 to the numerator of the fraction. 15 + 2 = 17.
-
Keep the denominator: The denominator remains the same.
-
Combine: The result becomes the numerator of the improper fraction, and the denominator stays the same. Therefore, 5 ⅔ becomes 17/3.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently used in everyday life and various fields, including:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often use mixed numbers to specify ingredient quantities (e.g., 2 ½ cups of flour).
-
Measurements: Measuring lengths, weights, or volumes often involves mixed numbers (e.g., 3 ⅛ inches).
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in these fields, and mixed numbers allow for accurate representation of quantities.
-
Time: Time is frequently expressed using mixed numbers (e.g., 1 hour and 15 minutes can be represented as 1 ¼ hours).
-
Finance: Calculations involving money might utilize mixed numbers (e.g., a price of $2.75 could be seen as 2 ¾ dollars).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can all improper fractions be converted to mixed numbers?
A: Yes, all improper fractions can be converted to mixed numbers, as long as the denominator is not zero (division by zero is undefined).
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 12/3 = 4 (the remainder is 0), so it's not expressed as a mixed number but simply as the whole number 4.
Q: Is there a difference between 5 ⅔ and 17/3 in terms of their mathematical value?
A: No, 5 ⅔ and 17/3 represent exactly the same quantity. They are simply different ways of expressing the same value; one as a mixed number and the other as an improper fraction. The choice often depends on context and convenience.
Q: Why are mixed numbers preferred in some situations over improper fractions?
A: Mixed numbers are often preferred because they are more intuitive and easier to visualize, especially in real-world applications where dealing with whole units is common. They offer a clearer understanding of the magnitude of the quantity being represented.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 17/3 to its mixed number equivalent (5 ⅔) is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process, based on simple division, allows for a more user-friendly representation of quantities greater than one whole unit. Understanding this conversion and its underlying principles is crucial for numerous applications across various disciplines, making it a valuable concept to master. The ability to easily switch between improper fractions and mixed numbers enhances mathematical proficiency and aids in solving problems more efficiently. Whether you're baking a cake, measuring a distance, or working on a complex engineering project, the ability to confidently use and convert between these forms of fractions is an essential skill.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 17/3 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.