17/4 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
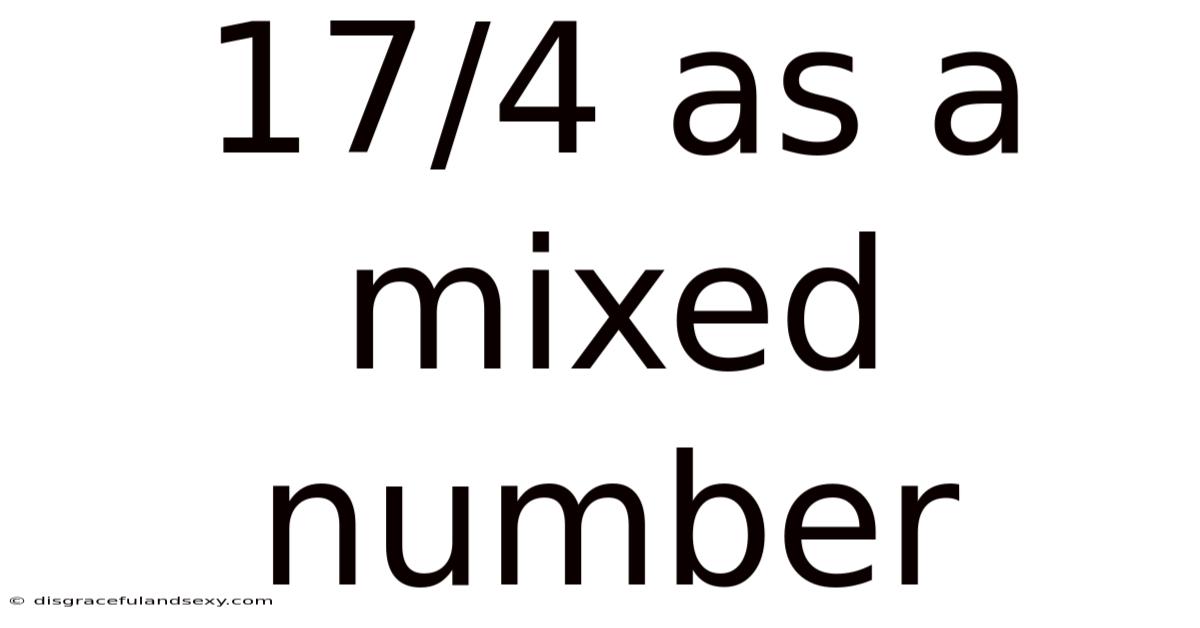
Table of Contents
Understanding 17/4 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 17/4, also known as seventeen-fourths, represents a value greater than one. Understanding how to express this as a mixed number – a whole number and a proper fraction – is a fundamental skill in arithmetic. This article will delve deep into the concept, exploring not just the mechanics of conversion but also the underlying mathematical principles and practical applications. We'll also cover frequently asked questions and provide examples to solidify your understanding.
Introduction: Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before diving into the specifics of 17/4, let's briefly review the definitions of fractions and mixed numbers. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two integers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). For instance, in the fraction 17/4, 17 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator.
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4). Mixed numbers are a convenient way to represent values larger than one in a more easily understandable format than an improper fraction (like 17/4).
Converting 17/4 to a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step Guide
Converting an improper fraction like 17/4 to a mixed number involves a simple division process:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: Divide 17 by 4. This gives you a quotient (the whole number part of the mixed number) and a remainder (the numerator of the fractional part).
17 ÷ 4 = 4 with a remainder of 1
-
Write the quotient as the whole number: The quotient, 4, becomes the whole number part of your mixed number.
-
Write the remainder as the numerator of the fraction: The remainder, 1, becomes the numerator of the fraction.
-
Keep the original denominator: The denominator of the fraction remains the same as the original denominator, which is 4.
-
Combine the whole number and the fraction: This gives you the mixed number 4 1/4.
Therefore, 17/4 expressed as a mixed number is 4 1/4.
Visual Representation: Understanding the Concept
Imagine you have 17 quarters. A quarter is 1/4 of a dollar. To understand 17/4 visually, consider grouping these quarters:
- You can make four groups of four quarters each (4 x 4 = 16 quarters). Each group represents a whole dollar.
- You have one quarter left over.
This visually represents 4 whole dollars (the whole number) and 1/4 of a dollar (the fraction), confirming that 17/4 equals 4 1/4.
The Mathematical Principle Behind the Conversion
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is based on the concept of equivalent fractions and the distributive property of multiplication. We can express 17/4 as:
17/4 = (16 + 1)/4
Using the distributive property, we can rewrite this as:
17/4 = 16/4 + 1/4
Since 16/4 simplifies to 4, we get:
17/4 = 4 + 1/4 = 4 1/4
This mathematically demonstrates the validity of the conversion process.
Converting Back to an Improper Fraction: The Reverse Process
It's equally important to understand how to convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction. Let's reverse the process using 4 1/4 as an example:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: Multiply 4 (the whole number) by 4 (the denominator). This gives 16.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result (16) to the numerator of the fraction (1). This gives 17.
-
Keep the original denominator: The denominator remains 4.
Therefore, 4 1/4 is equivalent to 17/4.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently used in various real-world scenarios:
-
Measurement: Measuring lengths, weights, or volumes often results in values expressed as mixed numbers. For example, a board might measure 4 1/4 feet long.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes frequently use mixed numbers to specify ingredient quantities, like 2 1/2 cups of flour.
-
Time: Time is often represented using mixed numbers, such as 1 hour and 15 minutes (1 1/4 hours).
Beyond 17/4: Working with Other Improper Fractions
The same principles apply to converting any improper fraction to a mixed number. For example:
- 23/5: 23 ÷ 5 = 4 with a remainder of 3, resulting in the mixed number 4 3/5.
- 31/6: 31 ÷ 6 = 5 with a remainder of 1, resulting in the mixed number 5 1/6.
The key is always to divide the numerator by the denominator and express the result as a whole number and a proper fraction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why do we use mixed numbers?
- A: Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive and easily understandable representation of values greater than one compared to improper fractions. They are particularly useful in everyday contexts where fractional parts need to be clearly visualized.
-
Q: Can all improper fractions be converted to mixed numbers?
- A: Yes, any improper fraction can be converted to a mixed number.
-
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
- A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 12/4 = 3. There's no fractional part.
-
Q: How do I compare mixed numbers?
- A: To compare mixed numbers, first compare the whole number parts. If the whole numbers are different, the larger whole number represents the larger mixed number. If the whole numbers are the same, then compare the fractional parts.
-
Q: Are there any limitations to using mixed numbers?
- A: While mixed numbers are useful for everyday calculations, in advanced mathematical operations, it’s often easier to work with improper fractions. For example, multiplying or dividing fractions is often simpler when working with improper fractions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion
Converting an improper fraction like 17/4 to its equivalent mixed number, 4 1/4, is a crucial skill in mathematics. This article has explored the process step-by-step, explained the underlying mathematical principles, and highlighted the practical applications of mixed numbers. By understanding the conversion process and its rationale, you'll be better equipped to tackle more complex mathematical problems and confidently navigate real-world situations involving fractions. Remember to practice converting both ways – from improper fractions to mixed numbers and vice versa – to solidify your understanding. This fundamental skill will serve you well throughout your mathematical journey.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 17/4 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.