2 3 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
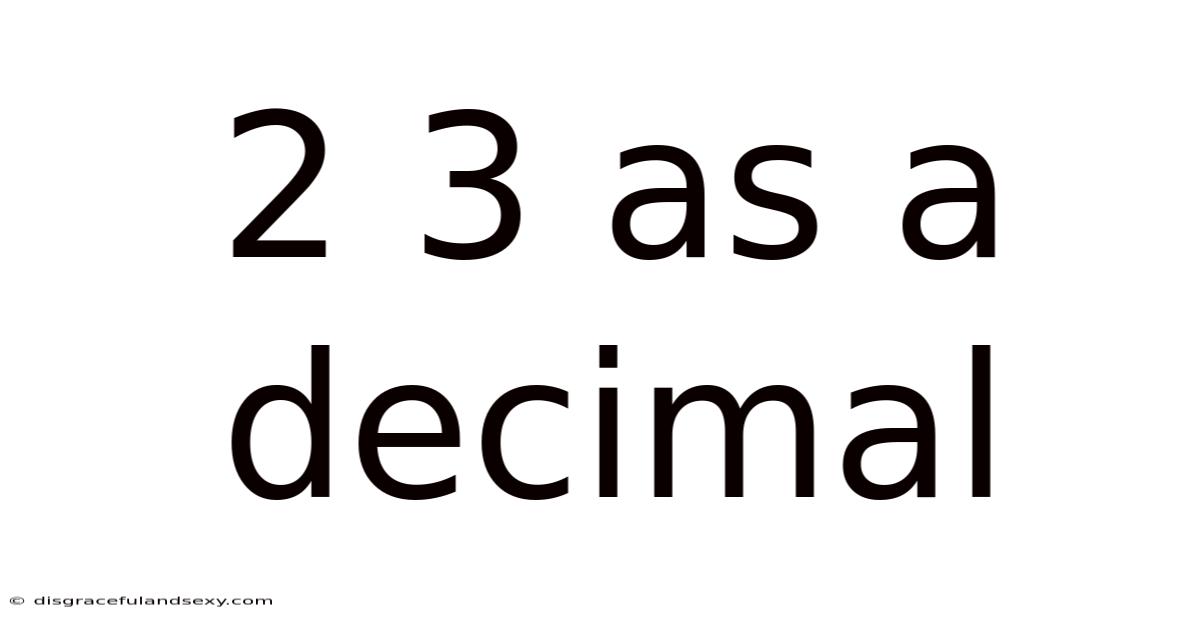
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: 2/3 as a Decimal
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is a fundamental skill in mathematics. While seemingly simple, the conversion of fractions to decimals can sometimes present challenges. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the conversion of the fraction 2/3 to its decimal representation, exploring various methods, underlying principles, and practical applications. We'll also tackle common misconceptions and frequently asked questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of this essential concept. By the end of this article, you'll not only know the decimal equivalent of 2/3 but also possess a robust understanding of fraction-to-decimal conversion.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we dive into the conversion of 2/3, let's briefly revisit the concepts of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). For example, in the fraction 2/3, 2 is the numerator and 3 is the denominator. This means we have 2 parts out of a total of 3 parts.
A decimal, on the other hand, is a number expressed in base-10, using a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. Each digit to the right of the decimal point represents a power of 10 (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on). For example, 0.5 represents five-tenths (5/10), and 0.25 represents twenty-five hundredths (25/100).
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting a fraction to a decimal is through long division. To convert 2/3 to a decimal, we divide the numerator (2) by the denominator (3):
0.6666...
3 | 2.0000
-1 8
0 20
-1 8
0 20
-1 8
0 20
-1 8
0 2
As you can see, the division process continues indefinitely, resulting in a repeating decimal: 0.6666... This repeating pattern is often represented using a bar over the repeating digit(s): 0.<u>6</u>.
Method 2: Understanding the Concept of Recurring Decimals
The result of converting 2/3 to a decimal reveals an important concept: recurring decimals. A recurring decimal is a decimal number with a digit or group of digits that repeat infinitely. In the case of 2/3, the digit "6" repeats endlessly. This is because the fraction 2/3 represents a rational number – a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Not all rational numbers result in terminating decimals (decimals that end); some result in recurring decimals.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
While long division provides a deeper understanding, a calculator offers a quick and easy way to obtain the decimal equivalent. Simply enter 2 ÷ 3 into your calculator, and you'll get the result: 0.666666... or a similar representation depending on your calculator's display capabilities. Many calculators will round the result to a certain number of decimal places, but the true value remains a recurring decimal.
The Significance of Recurring Decimals
The recurring nature of the decimal representation of 2/3 highlights the limitations of representing certain rational numbers using a finite number of decimal places. While we often round the decimal to a specific number of places for practical purposes (e.g., 0.67), it's crucial to remember that this is an approximation; the true value remains 0.<u>6</u>. This precision is important in fields requiring high accuracy, such as engineering, finance, and scientific calculations.
Practical Applications of 2/3 as a Decimal
The decimal equivalent of 2/3 finds applications in various situations. Consider the following:
-
Percentage Calculations: To express 2/3 as a percentage, we multiply the decimal equivalent by 100: 0.666... × 100 ≈ 66.67%. This is frequently used in calculating discounts, profits, or proportions.
-
Measurement and Scaling: Imagine scaling a blueprint where a length is represented by 2/3 of a unit. Converting 2/3 to its decimal equivalent (0.666...) allows for easy calculations using decimal units.
-
Data Analysis: In statistical analysis, you might encounter data represented as fractions. Converting these to decimals allows for easier calculations and representation in charts and graphs.
-
Everyday Calculations: Many everyday tasks involving proportions or sharing can be simplified by converting fractions to decimals.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that rounding 0.666... to 0.67 makes it equivalent to 2/3. While 0.67 is a close approximation, it's not precisely equal to 2/3. The difference, though small, becomes significant when dealing with large quantities or precise calculations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is 0.666... a rational number?
A1: Yes, 0.666... is a rational number because it can be expressed as the fraction 2/3.
Q2: How many decimal places are there in 2/3?
A2: There are infinitely many decimal places because it is a recurring decimal.
Q3: Can I use 0.67 instead of 0.666... in all calculations?
A3: Using 0.67 is an acceptable approximation in many situations, but for precise calculations, it's best to retain the recurring decimal or use the fraction 2/3.
Q4: Why does 2/3 result in a recurring decimal?
A4: It results in a recurring decimal because the denominator (3) contains a prime factor (3) that is not a factor of 10 (2 x 5), the denominator's base in the decimal system.
Conclusion
Converting 2/3 to its decimal equivalent – 0.<u>6</u> – highlights the essential relationship between fractions and decimals. Understanding the concept of recurring decimals is crucial for accurate mathematical calculations and interpreting numerical data correctly. While calculators provide a quick solution, mastering the long division method offers a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. This comprehensive guide has not only provided the answer but also equipped you with the knowledge to confidently tackle similar fraction-to-decimal conversions in the future. Remember that while approximations are useful in everyday life, precision is key in scientific and technical applications. This understanding will serve you well in various academic and practical contexts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 3 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.