2.5 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 19, 2025 · 6 min read
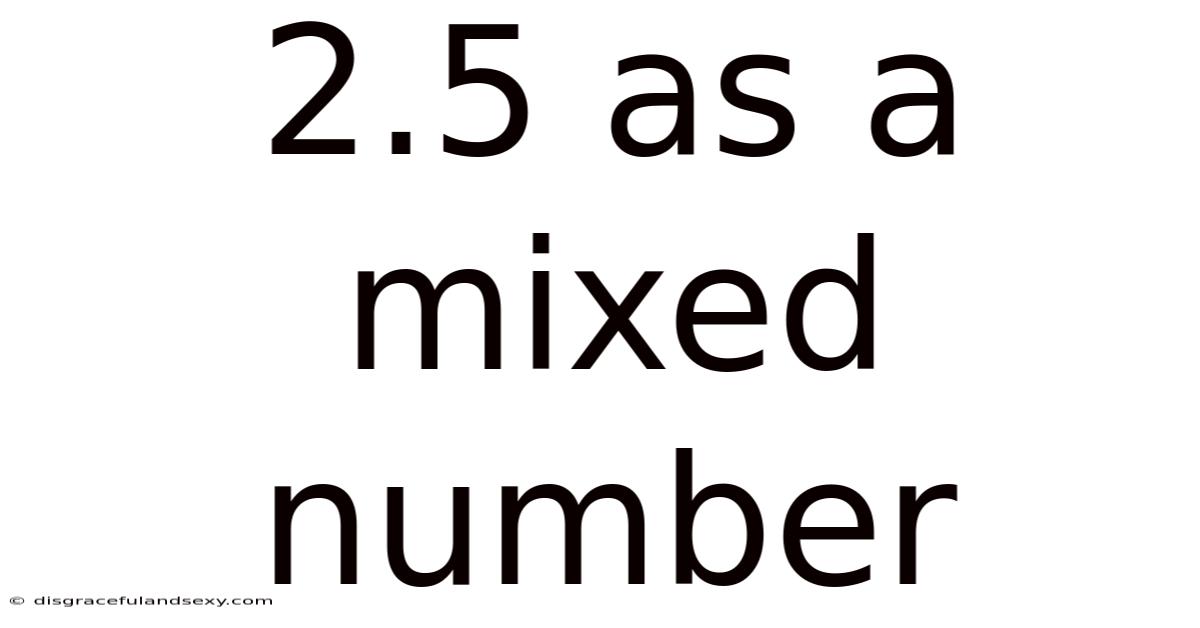
Table of Contents
Understanding 2.5 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The decimal number 2.5 might seem simple at first glance, but understanding its representation as a mixed number opens doors to a deeper understanding of fractions and decimals. This comprehensive guide will explore 2.5, explaining its conversion into a mixed number, providing a step-by-step process, delving into the underlying mathematical principles, and answering frequently asked questions. This will equip you with the knowledge to confidently handle similar conversions and solidify your grasp of fractional arithmetic.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before diving into the conversion of 2.5, let's clarify what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (the top number) smaller than its denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ¾, 3 ⅔, and 10 ¹/₅ are all mixed numbers. They represent quantities larger than one whole unit but not a whole number.
Converting 2.5 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
Converting 2.5 to a mixed number involves understanding the place value of the decimal. The number 2.5 can be broken down into two parts: the whole number part (2) and the decimal part (0.5). Here's the step-by-step process:
-
Identify the Whole Number: The whole number part of 2.5 is simply 2. This will form the whole number part of our mixed number.
-
Convert the Decimal Part to a Fraction: The decimal part is 0.5. To convert this to a fraction, we write it as a fraction with a denominator of 10 (because 0.5 represents five-tenths): 5/10.
-
Simplify the Fraction: The fraction 5/10 can be simplified by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator (5) and the denominator (10). The GCD of 5 and 10 is 5. Divide both the numerator and the denominator by 5: (5 ÷ 5) / (10 ÷ 5) = 1/2.
-
Combine the Whole Number and the Simplified Fraction: Now, combine the whole number from step 1 and the simplified fraction from step 3. This gives us the mixed number: 2 ½.
Therefore, 2.5 as a mixed number is 2 ½.
Understanding the Underlying Mathematical Principles
The conversion process relies on the fundamental relationship between decimals and fractions. Decimals represent parts of a whole using powers of 10 (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, etc.). Fractions represent parts of a whole using a numerator and a denominator. The conversion process essentially translates between these two representations.
-
Place Value in Decimals: The digit to the right of the decimal point represents tenths. So, 0.5 represents 5/10. If we had 0.25, it would represent 25/100. The number of digits after the decimal point determines the denominator's power of 10.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms. This doesn't change the value of the fraction, only its representation. Simplifying fractions makes them easier to work with and understand. For instance, 5/10 represents the same quantity as 1/2; both represent half of a whole.
-
Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions: It's important to note the relationship between mixed numbers and improper fractions. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. 2.5 can also be represented as the improper fraction 5/2. The conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is another crucial concept in fractional arithmetic. To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. Keep the same denominator. In the case of 2 ½, this would be (2 * 2) + 1 = 5, resulting in 5/2. Conversely, to convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, you divide the numerator by the denominator; the quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction, keeping the same denominator.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently used in various real-world scenarios, especially those involving measurements, quantities, and divisions:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often call for amounts like 2 ½ cups of flour or 1 ¼ teaspoons of baking powder.
-
Construction and Engineering: Measurements in blueprints and building plans often utilize mixed numbers to represent precise dimensions.
-
Data Analysis: When dealing with averages or proportions, mixed numbers can provide a more intuitive representation of the data than decimal values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all decimal numbers be converted into mixed numbers?
A1: No, only decimal numbers that represent quantities greater than or equal to one can be converted into mixed numbers. Decimal numbers less than one (like 0.75) can only be represented as proper fractions.
Q2: What if the decimal part doesn't simplify easily?
A2: If the decimal part doesn't simplify easily, you can still represent it as a fraction. For instance, if you have 3.375, the fraction would be 375/1000. You would then simplify this fraction to its lowest terms, which in this case is 3/8, resulting in the mixed number 3 3/8.
Q3: How do I convert a mixed number back to a decimal?
A3: To convert a mixed number back to a decimal, divide the numerator of the fraction by the denominator and add the whole number. For example, 2 ½: 1 ÷ 2 = 0.5, then add 2 to get 2.5.
Q4: Are there other ways to represent 2.5 besides as a mixed number and a decimal?
A4: Yes, 2.5 can also be represented as an improper fraction (5/2) or as a percentage (250%). All three represent the same quantity, just using different notations.
Q5: Why is it important to understand mixed numbers?
A5: Understanding mixed numbers is crucial for proficiency in arithmetic and algebra. They provide a more intuitive way to represent quantities that are not whole numbers, especially in real-world applications involving measurements and proportions. It enhances your mathematical versatility and problem-solving skills.
Conclusion
Converting 2.5 to a mixed number, resulting in 2 ½, is a simple yet fundamental operation showcasing the connection between decimals and fractions. This guide has not only demonstrated the conversion process but also delved into the underlying mathematical principles, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic. By mastering these concepts, you’ll strengthen your foundation in mathematics and be better equipped to handle various mathematical challenges involving fractions and decimals in diverse real-world scenarios. The ability to seamlessly convert between decimal and fractional forms, and specifically to understand and utilize mixed numbers, significantly enhances problem-solving abilities and builds a strong base for more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember, practice makes perfect! Continue practicing conversions to build your confidence and fluency in working with mixed numbers.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2.5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.