2 Divided By X Squared
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 5 min read
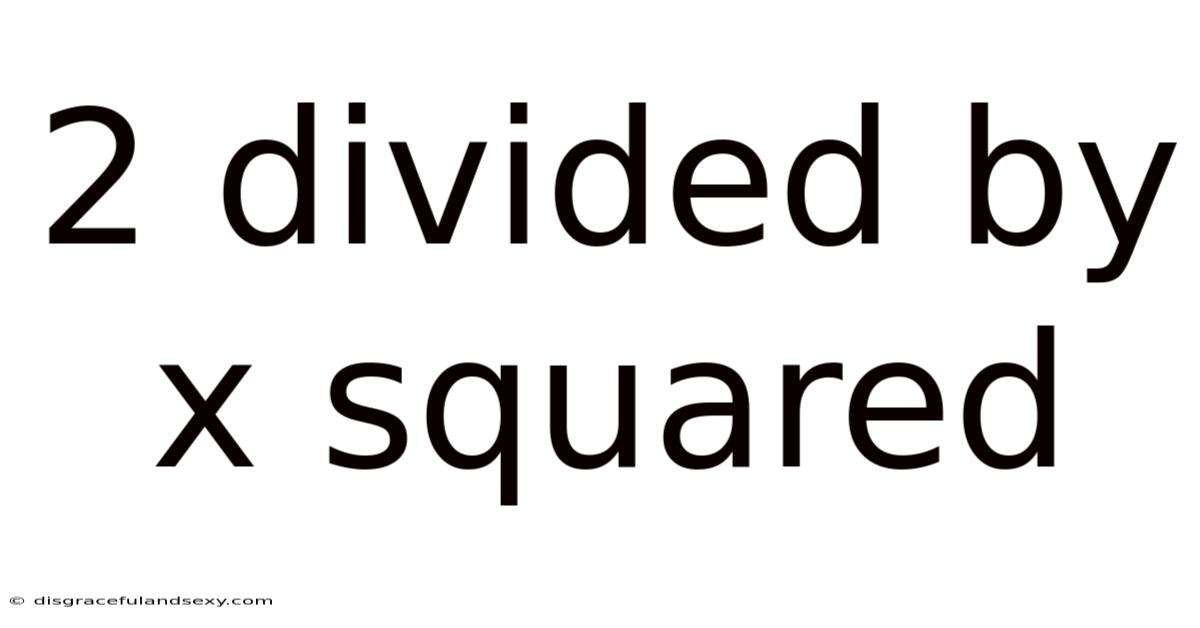
Table of Contents
2 Divided by x Squared: A Deep Dive into the Mathematical Landscape
Understanding the expression "2 divided by x squared," or mathematically represented as 2/x², is fundamental to grasping many concepts in algebra, calculus, and beyond. This seemingly simple expression opens doors to a wealth of mathematical explorations, revealing intricacies that extend far beyond basic arithmetic. This article will provide a comprehensive guide, covering everything from its basic interpretation and graphical representation to its applications in more advanced mathematical fields. We will delve into its properties, explore its behavior as 'x' changes, and answer frequently asked questions. This in-depth analysis will equip you with a solid understanding of this crucial mathematical expression.
Understanding the Basics: 2/x²
At its core, 2/x² represents a rational function. A rational function is simply a ratio of two polynomials, in this case, the constant polynomial 2 and the polynomial x². This means we are essentially dividing the number 2 by the square of the variable 'x'. The value of this expression depends entirely on the value of 'x'.
Key Features:
- Variable Dependence: The expression's value is entirely dependent on the value assigned to 'x'. Different values of 'x' will yield different results.
- Reciprocal Relationship: The expression is inversely proportional to the square of 'x'. This means that as 'x' increases, the value of 2/x² decreases, and vice versa. This inverse square relationship is crucial in understanding its behavior.
- Undefined Points: The expression is undefined when the denominator, x², equals zero. This occurs only when x = 0. At x = 0, the expression is undefined because division by zero is an undefined operation in mathematics.
Visualizing the Function: The Graph of 2/x²
The best way to understand the behavior of 2/x² is to visualize it graphically. Plotting the expression on a Cartesian coordinate system reveals a clear picture of its characteristics.
The graph of y = 2/x² exhibits the following key features:
- Asymptotic Behavior: The graph approaches the x-axis (y = 0) as x approaches positive or negative infinity. The x-axis acts as a horizontal asymptote. This means the function gets arbitrarily close to zero but never actually reaches it.
- Vertical Asymptote: A vertical asymptote exists at x = 0. The graph approaches infinity as x approaches 0 from either the positive or negative side. This visually represents the undefined nature of the expression at x = 0.
- Symmetry: The graph is symmetric with respect to the y-axis. This is because squaring 'x' eliminates any distinction between positive and negative values. Therefore, f(x) = f(-x).
- Always Positive: The value of 2/x² is always positive, regardless of the value of x (except at x=0). This is due to the fact that both the numerator (2) and the denominator (x²) are always positive (excluding x=0).
Exploring Different Values of 'x'
Let's explore how the expression behaves for different values of x:
- x = 1: 2/1² = 2
- x = 2: 2/2² = 2/4 = 0.5
- x = 3: 2/3² = 2/9 ≈ 0.22
- x = 10: 2/10² = 2/100 = 0.02
- x = -1: 2/(-1)² = 2
- x = -2: 2/(-2)² = 2/4 = 0.5
As you can see, as the absolute value of x increases, the value of 2/x² decreases. This demonstrates the inverse square relationship.
Applications in Advanced Mathematics
The expression 2/x² finds applications in various advanced mathematical fields:
-
Calculus: This function is frequently used in examples and exercises related to limits, derivatives, and integrals. Understanding its behavior is essential for mastering these concepts. Calculating the derivative and integral of 2/x² provides further insights into its mathematical properties. For example, the integral is -2/x + C (where C is the constant of integration).
-
Physics: Inverse square laws are prevalent in physics. For example, gravitational force and electrostatic force follow an inverse square relationship. The expression 2/x² serves as a simplified model to understand such relationships.
-
Probability and Statistics: In probability distributions, functions with similar inverse square relationships might be encountered.
Mathematical Operations and Manipulations
Several mathematical operations can be performed on 2/x². These manipulations can help simplify expressions or solve equations.
-
Multiplication: Multiplying 2/x² by another expression follows standard rules of fraction multiplication. For example, (2/x²) * (3x) = 6x/x² = 6/x (assuming x ≠ 0).
-
Division: Dividing 2/x² by another expression involves inverting the second expression and multiplying. For example, (2/x²) / (1/x) = (2/x²) * (x/1) = 2/x (assuming x ≠ 0).
-
Addition and Subtraction: Adding or subtracting 2/x² to/from another rational expression requires finding a common denominator.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the domain of the function 2/x²?
A1: The domain of the function is all real numbers except x = 0. This is because the function is undefined at x = 0 due to division by zero.
Q2: What is the range of the function 2/x²?
A2: The range of the function is all positive real numbers. The function is always positive and approaches zero as x approaches infinity.
Q3: Does the function 2/x² have any roots?
A3: No, the function 2/x² does not have any roots (zeros). The numerator is always 2, so the function can never equal zero.
Q4: How can I solve an equation involving 2/x²?
A4: Solving equations involving 2/x² often requires algebraic manipulation. You might need to multiply both sides of the equation by x², isolate x, and then solve for x. Remember to check your solution to ensure it's within the domain of the function.
Q5: What is the difference between 2/x² and 2x⁻²?
A5: There is no difference. 2x⁻² is simply an alternative way of writing 2/x² using negative exponents. This notation is often used in calculus and other advanced mathematical contexts.
Conclusion: Mastering 2/x² and Beyond
The seemingly simple expression 2/x² reveals a surprisingly rich mathematical landscape. Understanding its behavior, properties, and applications is crucial for success in various mathematical and scientific fields. From its graphical representation to its use in calculus and physics, this expression provides a valuable foundation for more advanced studies. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with a strong understanding of this fundamental concept, enabling you to confidently tackle more complex mathematical challenges. Remember that consistently practicing problem-solving is key to mastering these concepts and expanding your mathematical capabilities. Don't hesitate to explore further and delve into related topics to solidify your understanding and appreciation for the beauty and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 Divided By X Squared . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.