2 N 3 13 2n
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
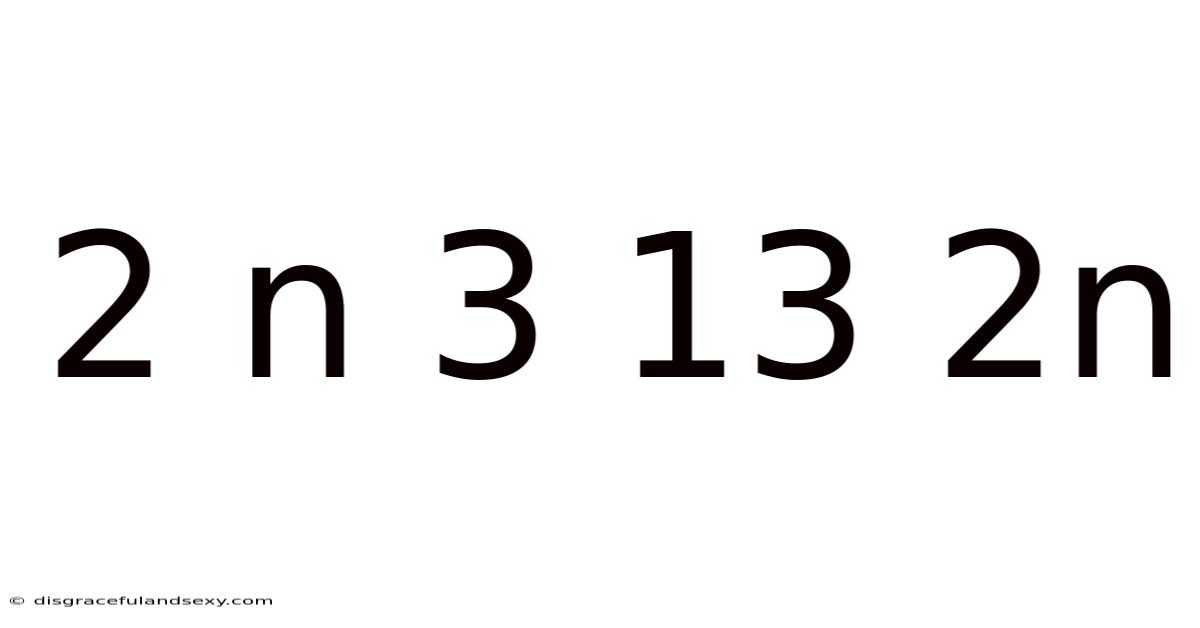
Table of Contents
Decoding the Sequence: Exploring the Mathematical Puzzle of 2, n, 3, 13, 2n
This article delves into the fascinating mathematical sequence: 2, n, 3, 13, 2n. We'll explore various approaches to understand the pattern, including potential underlying rules and the implications of the unknown variable 'n'. This seemingly simple sequence offers a compelling opportunity to explore logical reasoning, pattern recognition, and the beauty of mathematical problem-solving. We'll unpack the puzzle, offering multiple perspectives and considering the potential for multiple solutions, highlighting the creative aspects of mathematical thinking.
Understanding the Challenge: The Role of 'n'
The presence of 'n' immediately introduces an element of uncertainty. It signifies that this isn't a strictly defined sequence; instead, it's a template, a pattern with a missing piece. This 'n' acts as a wildcard, altering the sequence's behavior depending on its assigned value. Our task is to determine the rules governing the sequence, which will dictate the acceptable values for 'n' and the resulting progression of numbers.
Potential Approaches: Deconstructing the Sequence
Several approaches can be used to tackle this mathematical puzzle. Let's consider some common strategies employed in sequence analysis:
-
Looking for Arithmetic Differences: This involves calculating the differences between consecutive terms to identify a potential arithmetic progression. However, with the variable 'n', a consistent arithmetic difference isn't immediately apparent.
-
Analyzing Geometric Ratios: Here, we'd look for a constant ratio between consecutive terms. Again, the presence of 'n' complicates the analysis, preventing a straightforward identification of a geometric progression.
-
Exploring Polynomial Relationships: More complex sequences may follow polynomial rules. We could attempt to fit the known terms (2, 3, 13) into a polynomial equation, considering 'n' as a variable. However, without further constraints, this approach might yield multiple valid solutions.
-
Considering Recursive Relationships: This is a powerful technique for describing sequences where each term is defined based on previous terms. We could hypothesize a relationship where the next term depends on the current term and 'n' in some way. This method might lead us to a recursive definition for the sequence.
Hypothetical Rules and Solutions
Let's explore some possible rules that could govern the sequence 2, n, 3, 13, 2n, keeping in mind that multiple valid rules might exist:
Hypothesis 1: Alternating Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions
We could hypothesize that the sequence alternates between an arithmetic and a geometric progression. For instance:
- The odd-numbered terms (2, 3, 2n) form an arithmetic progression with a common difference. Let’s say the difference is ‘x’. Then 3 - 2 = x, and 2n - 3 = x. This implies 2n - 3 = 1, which means 2n = 4, so n = 2.
- The even-numbered terms (n, 13) form a geometric progression. If n = 2, then the ratio is 13/2 = 6.5. This approach provides a possible solution, but it’s not uniquely determined.
Hypothesis 2: A Piecewise Function
We might model the sequence using a piecewise function, where different rules apply to different positions within the sequence. For example:
- a<sub>1</sub> = 2
- a<sub>2</sub> = n
- a<sub>3</sub> = 3
- a<sub>4</sub> = 13
- a<sub>5</sub> = 2n
This provides flexibility, but without further information, the specific rules for each position remain arbitrary.
Hypothesis 3: A Recursive Relationship involving 'n'
Let's consider a recursive definition. A simple example could be:
- a<sub>1</sub> = 2
- a<sub>2</sub> = n
- a<sub>3</sub> = a<sub>1</sub> + 1 = 3
- a<sub>4</sub> = 2 * a<sub>3</sub> + 7 = 13
- a<sub>5</sub> = 2 * n
This recursive rule ties the third term to the first and the fourth term to the third, while the others explicitly define 'n'. Again, different recursive relations could be devised.
The Importance of Context and Constraints
The ambiguity inherent in the sequence 2, n, 3, 13, 2n underscores the critical role of context in mathematical problem-solving. Without additional information or constraints, the number of possible solutions is vast. For example:
- Specific domain for 'n': If 'n' is restricted to integers, the solution space shrinks considerably.
- Further terms in the sequence: Knowing additional terms would provide crucial data to refine our hypotheses and test the validity of our rules.
- Underlying mathematical context: Knowing the origin or purpose of the sequence could suggest specific mathematical structures or relationships that govern it.
Extending the Analysis: Deeper Mathematical Explorations
To go beyond the basic pattern recognition, we can explore more advanced mathematical tools and concepts:
- Generating functions: These powerful tools can represent sequences in a compact algebraic form, aiding analysis and prediction.
- Difference equations: These equations relate consecutive terms of a sequence, often providing a more systematic approach to finding underlying patterns.
- Number theory: Depending on the context, number theory concepts (like prime factorization or modular arithmetic) might prove relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there only one solution to this sequence?
A: No, without additional constraints or context, there are multiple potential solutions. The sequence is underdetermined, allowing for a variety of valid rules.
Q: How can I determine the "correct" solution?
A: The "correct" solution depends entirely on the context in which the sequence arose. More information is needed to uniquely determine the underlying rule.
Q: What if 'n' is a complex number?
A: Allowing 'n' to be a complex number significantly broadens the possibilities. The solutions would be much more complex and require advanced mathematical techniques to fully explore.
Q: Can this sequence be related to known mathematical sequences?
A: Without more information, it's difficult to definitively link this sequence to any established mathematical sequence. However, by analyzing the relationships between terms under different hypotheses, we might discover similarities to known patterns.
Conclusion: The Power of Mathematical Inquiry
The seemingly simple sequence 2, n, 3, 13, 2n serves as an excellent example of how mathematical problems can stimulate critical thinking and creative problem-solving. The presence of the unknown variable 'n' introduces an element of uncertainty, emphasizing the importance of context and constraints in formulating a definitive solution. While we’ve explored several potential approaches and hypotheses, the true value lies in the process of exploration and the development of problem-solving skills. This puzzle highlights the multifaceted nature of mathematics, demonstrating the power of diverse strategies and the need for careful consideration of underlying assumptions. The journey of uncovering the rules governing this sequence is more important than arriving at a single, definitive answer. It encourages a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of mathematical inquiry.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 N 3 13 2n . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.