2 X 1 3x 1
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
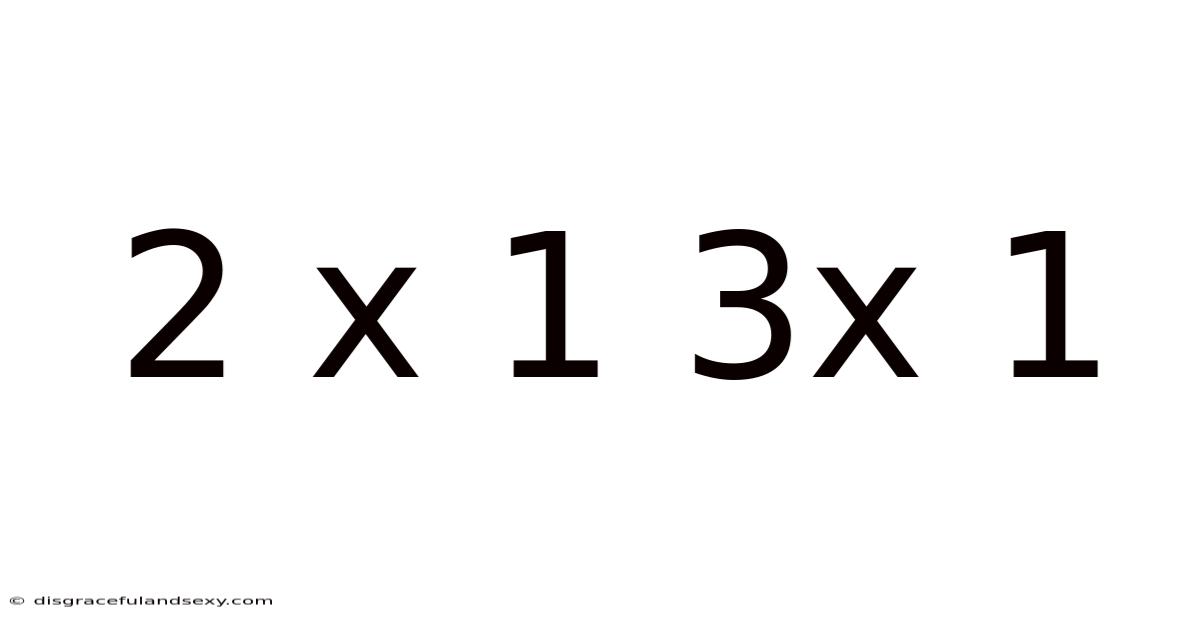
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Exploring the Mathematical Significance of "2 x 1" and "3 x 1"
This article delves into the seemingly simple yet fundamentally important mathematical concepts represented by "2 x 1" and "3 x 1." While these expressions might appear trivial at first glance, they form the bedrock of multiplication, a crucial operation in arithmetic and beyond. We will explore their meaning, applications, and how they relate to more complex mathematical ideas. Understanding these basic expressions is key to grasping more advanced concepts in algebra, calculus, and beyond.
Introduction: Understanding Multiplication's Building Blocks
Multiplication, at its core, is repeated addition. "2 x 1" can be interpreted as adding one to itself twice: 1 + 1 = 2. Similarly, "3 x 1" represents adding one to itself three times: 1 + 1 + 1 = 3. These simple equations reveal the multiplicative identity property of 1: any number multiplied by 1 equals itself. This property is essential in various mathematical operations and problem-solving scenarios.
The Multiplicative Identity Property: 1 as a Unique Number
The number 1 holds a unique position in mathematics. It's neither prime nor composite, and it's the multiplicative identity. This means that when any number is multiplied by 1, the result is the original number. This seemingly simple concept has far-reaching consequences. For example, in algebra, we use the multiplicative identity property to simplify expressions and solve equations. Consider the equation 5x = 5. To solve for x, we multiply both sides by 1/5 (the multiplicative inverse of 5), resulting in x = 1. This simple manipulation hinges on the understanding of the multiplicative identity.
Expanding on "2 x 1" and "3 x 1": Real-World Applications
While "2 x 1" and "3 x 1" appear basic, their applications are widespread. Consider these scenarios:
-
Counting Objects: Imagine you have two bags, and each bag contains one apple. To find the total number of apples, you perform the calculation 2 x 1 = 2. This simple multiplication reflects a real-world counting problem. Similarly, if you have three boxes, each with one toy car, the calculation 3 x 1 = 3 gives you the total number of toy cars.
-
Unit Conversions: Imagine converting 2 meters to centimeters. Since there are 100 centimeters in a meter, you would multiply 2 by 100. However, before you reach that point, the underlying understanding of "2 x 1" is crucial: you have 2 units (meters) and each unit contains 1 unit of itself. This forms the first step in a more complex calculation.
-
Scaling and Proportions: If a recipe calls for 1 cup of sugar for one batch of cookies, and you want to make 3 batches, the multiplication "3 x 1" helps you determine the required amount of sugar (3 cups). This extends to any scaling problem where a single unit is replicated multiple times.
Beyond the Basics: Connecting to Advanced Concepts
The seemingly simple equations "2 x 1" and "3 x 1" are not just foundational; they serve as building blocks for much more complex mathematical operations:
-
Vectors and Matrices: In linear algebra, vectors and matrices are used to represent data and perform transformations. The concept of multiplying a vector by a scalar (a single number) is directly related to "2 x 1" and "3 x 1." For example, multiplying a vector [1, 1] by the scalar 2 results in [2, 2]—akin to doubling each component of the vector. This is a fundamental operation in computer graphics, physics simulations, and many other fields.
-
Calculus and Derivatives: In calculus, the concept of the derivative involves finding the instantaneous rate of change of a function. This process often involves limiting operations where small changes (represented by numbers approaching 1) play a crucial role. The understanding of the behavior of multiplication with 1 is essential for fully grasping the intricacies of calculus.
-
Probability and Statistics: Probability theory involves calculating the likelihood of events. Simple probabilities often involve multiplying probabilities of independent events. The base understanding of multiplying by one is crucial to building on these concepts.
Exploring the Commutative Property and its Implications
Multiplication is commutative, meaning the order of the numbers doesn't affect the result. That is, 2 x 1 = 1 x 2 = 2, and 3 x 1 = 1 x 3 = 3. This commutative property, while seemingly obvious in these simple examples, extends to more complex multiplications and becomes significant in abstract algebra and other advanced fields. It allows us flexibility in how we approach problems and simplifies calculations.
Visual Representations: Making Multiplication Concrete
Visual aids are powerful tools for understanding mathematical concepts. For "2 x 1," imagine two rows of one object each. This concrete representation helps solidify the concept of repeated addition. Similarly, for "3 x 1," picture three rows of one object each. These simple visuals provide a tangible understanding of the mathematical operations, making them relatable and easier to grasp, especially for young learners.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
A common misconception, especially among beginners, is the belief that multiplication always results in a larger number. While this is often true when multiplying numbers greater than 1, it's crucial to understand that multiplying by 1 preserves the original number. This subtlety is important in understanding the behavior of multiplication in various mathematical contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What happens if we multiply a number by 0 instead of 1?
- A: Multiplying any number by 0 always results in 0. This is the multiplicative property of zero. It is distinct from the multiplicative identity property of 1.
-
Q: Is there a similar property for addition?
- A: Yes, the additive identity property states that adding 0 to any number does not change the number. This is analogous to the multiplicative identity property of 1.
-
Q: Why is the multiplicative identity property important?
- A: The multiplicative identity property is fundamental to algebra, simplifying equations and allowing us to manipulate expressions. It's a cornerstone of many mathematical operations.
-
Q: Are "2 x 1" and "3 x 1" only useful for simple calculations?
- A: No, they are foundational concepts that underpin more complex mathematical operations in areas like linear algebra, calculus, and probability. Their simplicity belies their profound importance.
Conclusion: The Unsung Power of Simplicity
"2 x 1" and "3 x 1" might appear insignificant, but they represent foundational concepts in mathematics. Understanding these simple expressions is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation. They are not merely trivial calculations but building blocks upon which more complex mathematical operations and concepts rest. From simple counting problems to advanced mathematical theories, the understanding of these basic multiplications is paramount. Mastering these fundamentals empowers individuals to tackle more challenging mathematical problems and appreciate the elegance and power of mathematics as a whole. Their simplicity belies their profound impact on our understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 X 1 3x 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.