2 X 1 3x 5
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
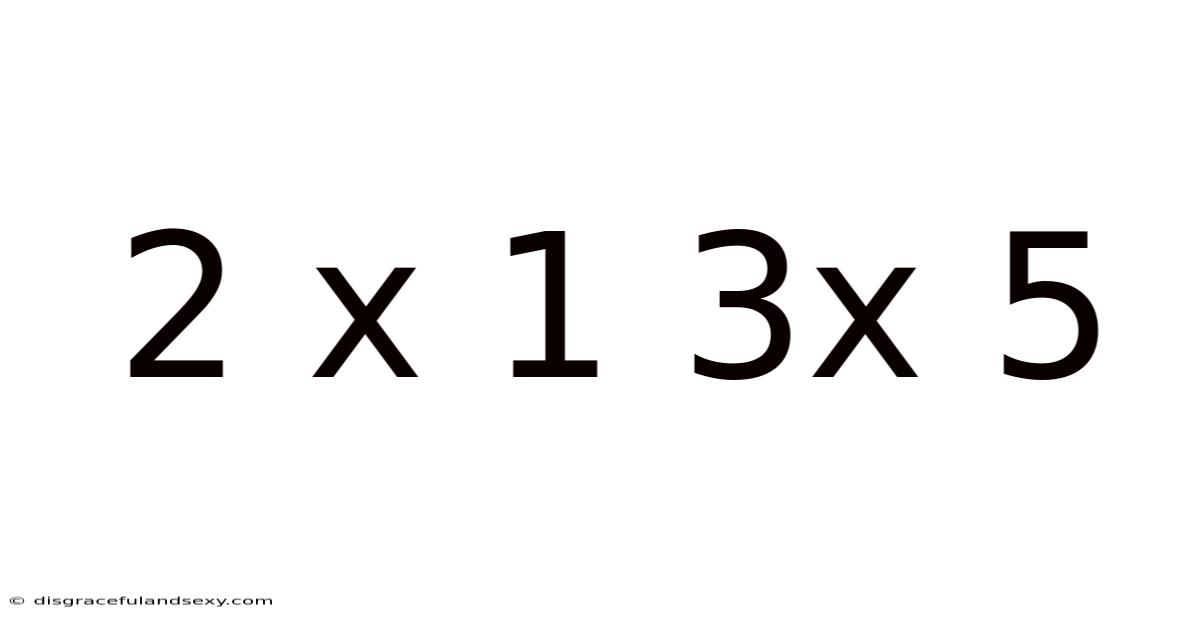
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Exploring the Mathematical Relationships within "2 x 1, 3 x 5"
This article delves into the seemingly simple mathematical expressions "2 x 1" and "3 x 5," unpacking their individual meanings and exploring the broader mathematical concepts they represent. While these expressions may appear elementary at first glance, they serve as excellent entry points to understand fundamental principles of multiplication, number theory, and even the foundations of algebra. We'll unpack these concepts, examining various perspectives and applications, making this exploration accessible to learners of all levels.
Introduction: Multiplication's Building Blocks
At their core, "2 x 1" and "3 x 5" are simple multiplication problems. Multiplication, in its simplest form, represents repeated addition. 2 x 1 means adding the number 2 one time (2), and 3 x 5 means adding the number 3 five times (3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15). These basic operations form the bedrock of more complex mathematical concepts. Understanding these fundamental operations is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation. This exploration will move beyond simple calculation and examine the underlying structures and relationships inherent in these expressions.
Dissecting 2 x 1: The Identity Element
The expression "2 x 1" highlights a critical concept in mathematics: the multiplicative identity. The number 1, when multiplied by any number, leaves that number unchanged. This property makes 1 the multiplicative identity element. In this case, 2 multiplied by 1 remains 2. This seemingly simple equation underscores a fundamental principle in algebra and other branches of mathematics. The identity element is essential in various algebraic manipulations, allowing for simplification and solving equations.
Understanding the Significance: The significance of the multiplicative identity extends beyond basic arithmetic. It's fundamental in abstract algebra, where more complex number systems are explored. The existence of an identity element is a key property that defines many algebraic structures, such as groups and rings.
Real-World Application: While seemingly abstract, the multiplicative identity has practical applications. Consider calculating the cost of a single item. If one item costs $2, then the total cost of buying one item is 2 x 1 = $2. The identity element simplifies the calculation, making it intuitive and easily understood.
Deconstructing 3 x 5: Exploring Factors and Products
The expression "3 x 5" introduces the concepts of factors and products. In this case, 3 and 5 are the factors, and 15 is the product. Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number without leaving a remainder. The product is the result of multiplying the factors together. Understanding factors and products is crucial for working with fractions, simplifying expressions, and solving equations.
Prime Factorization: The expression "3 x 5" is also relevant to prime factorization. Both 3 and 5 are prime numbers—numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. The prime factorization of 15 is 3 x 5. Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory and has applications in cryptography and other advanced mathematical fields.
Finding Factors: To understand factors more deeply, consider finding all the factors of 15. They are 1, 3, 5, and 15. This exercise helps in grasping the relationship between numbers and their divisors, laying the groundwork for more complex number theory concepts.
Real-World Applications: The concept of factors and products has many practical applications. Imagine dividing 15 cookies equally among friends. The factors of 15 (1, 3, 5, and 15) represent the possible number of friends you can share the cookies with, while maintaining equal distribution.
Connecting the Expressions: A Comparative Analysis
While seemingly disparate, "2 x 1" and "3 x 5" offer valuable insights when compared. They represent different aspects of multiplication, illustrating the properties of the multiplicative identity and the concept of factors and products. Comparing these expressions highlights the versatility and power of multiplication as a fundamental arithmetic operation.
Scale and Magnitude: The difference in magnitude between the products (2 and 15) highlights the impact of different factors. The larger the factors, the larger the product. This observation is crucial for understanding the growth of quantities in various contexts, from population growth to compound interest calculations.
Number Properties: Comparing these expressions illuminates different properties of numbers. "2 x 1" emphasizes the identity property, while "3 x 5" highlights prime factorization and the relationship between factors and products.
Beyond Basic Arithmetic: Expanding the Scope
The expressions "2 x 1" and "3 x 5" serve as stepping stones to more advanced mathematical concepts. Let's explore some of these connections:
-
Algebra: These expressions can be generalized using variables. For instance, "a x 1 = a" represents the multiplicative identity for any variable 'a', and "a x b = c" represents the general form of multiplication, where 'a' and 'b' are factors and 'c' is the product.
-
Geometry: Multiplication finds its application in calculating areas and volumes. Consider a rectangle with sides of length 3 and 5 units. The area is calculated as 3 x 5 = 15 square units. This connection links arithmetic operations to geometric concepts.
-
Number Theory: As mentioned earlier, prime factorization, exemplified by "3 x 5," is a cornerstone of number theory. This field explores the properties and relationships between numbers, offering a deeper understanding of numerical structures.
-
Data Analysis: Understanding multiplication is critical in analyzing and interpreting data. Calculations involving percentages, ratios, and proportions rely on multiplication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between a factor and a multiple?
A: A factor is a number that divides evenly into another number, while a multiple is a number obtained by multiplying a given number by an integer. For example, 3 is a factor of 15, but 15 is a multiple of 3.
Q: Are there any other multiplicative identities?
A: In the realm of real numbers, 1 is the unique multiplicative identity. However, in more abstract algebraic structures, other elements might serve as multiplicative identities depending on the rules defining the structure.
Q: Why is prime factorization important?
A: Prime factorization is crucial because every integer greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers. This unique representation has significant applications in cryptography and other areas of mathematics.
Q: How can I improve my understanding of multiplication?
A: Practice is key! Start with basic problems, gradually increasing the difficulty. Use visual aids like arrays and diagrams to understand the concept of repeated addition. Explore different methods of multiplication and apply your knowledge to real-world problems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Simplicity
The seemingly simple expressions "2 x 1" and "3 x 5" offer a powerful gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts. From the multiplicative identity to prime factorization, these expressions serve as building blocks for more advanced mathematical exploration. By examining these equations from various perspectives, we've highlighted their significance in arithmetic, algebra, geometry, number theory, and data analysis. Understanding these fundamental principles lays the groundwork for mastering more complex mathematical concepts and applying them to solve a wide range of problems in various fields. The journey from simple arithmetic to advanced mathematical understanding starts with a firm grasp of these basic yet powerful principles. Remember, even the most complex concepts are built upon a foundation of seemingly simple ideas, and a deeper understanding of the fundamentals is crucial for unlocking the wonders of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 X 1 3x 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.