20/7 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
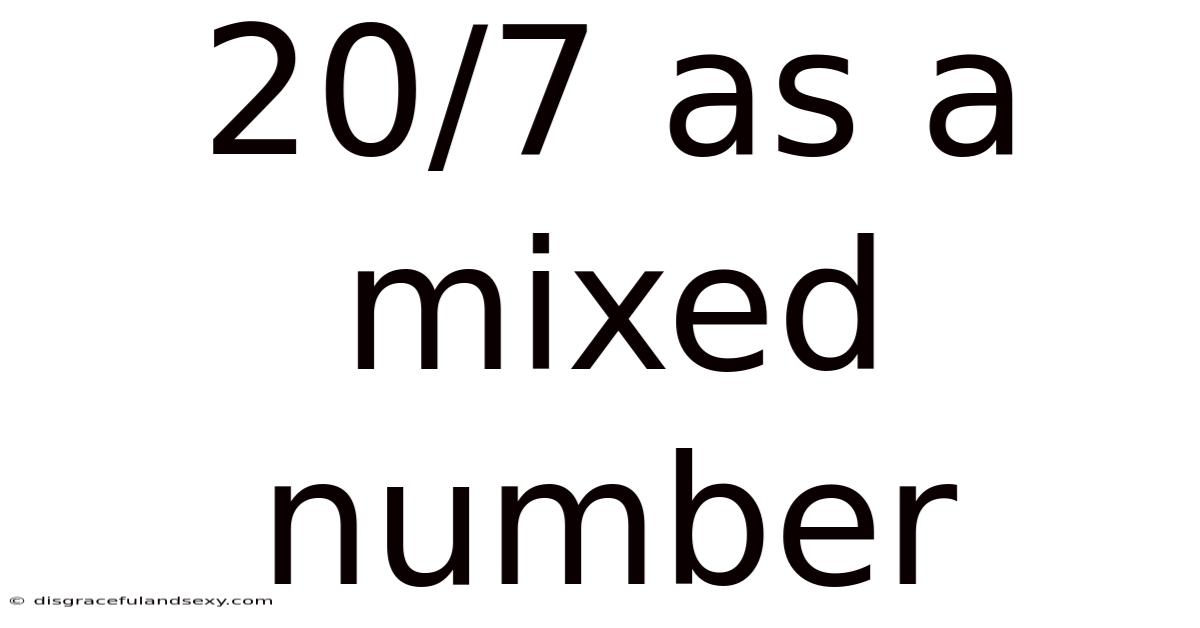
Table of Contents
Understanding 20/7 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 20/7, while seemingly simple, offers a valuable opportunity to delve into the concept of mixed numbers – a fundamental concept in arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will not only explain how to convert 20/7 into a mixed number but also explore the underlying principles, provide practical examples, and address frequently asked questions. Understanding mixed numbers is crucial for various mathematical operations and real-world applications. This article aims to provide a clear and concise explanation, making this seemingly complex topic accessible to all.
Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before diving into the conversion of 20/7, let's establish a solid foundation. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of two parts: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered.
A mixed number, on the other hand, combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4). Mixed numbers are useful for representing quantities that are greater than one but not whole numbers. For example, 2 1/2 represents two whole units and half of another unit.
Converting 20/7 into a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let's convert the improper fraction 20/7 into a mixed number. An improper fraction is one where the numerator is larger than or equal to the denominator. This indicates that the fraction represents a quantity greater than or equal to one. Here's the process:
Step 1: Perform Long Division
Divide the numerator (20) by the denominator (7).
2
7 | 20
14
6
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and Remainder
The quotient (the result of the division) is 2, which represents the whole number part of our mixed number. The remainder is 6.
Step 3: Form the Mixed Number
The remainder (6) becomes the numerator of the fractional part, and the original denominator (7) remains the same. Therefore, 20/7 as a mixed number is 2 6/7.
Visual Representation and Real-World Application
Let's visualize this. Imagine you have 20 identical cookies, and you want to divide them equally among 7 friends. Using long division, you find that each friend gets 2 whole cookies (the quotient). There are 6 cookies remaining (the remainder), which you can't divide equally among your friends without cutting them. Therefore, you have 2 whole cookies per friend and a remaining 6/7 of a cookie. This perfectly represents the mixed number 2 6/7.
This concept has numerous real-world applications. Imagine measuring ingredients for a recipe: if a recipe calls for 20/7 cups of flour, you would measure 2 and 6/7 cups. The same principle applies to various measurements, including length, weight, and time.
Mathematical Operations with Mixed Numbers
Understanding mixed numbers is crucial for various mathematical operations. Let's briefly explore addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with mixed numbers:
Addition and Subtraction: It is generally easier to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions before adding or subtracting. For example, to add 2 6/7 and 1 1/7, convert them to 20/7 and 8/7, respectively. Then add the fractions: 20/7 + 8/7 = 28/7 = 4.
Multiplication and Division: You can either convert mixed numbers to improper fractions or use the distributive property. However, converting to improper fractions often simplifies the process. For example, to multiply 2 6/7 by 3, convert 2 6/7 to 20/7, and then multiply: (20/7) * 3 = 60/7. This can then be converted back into a mixed number: 8 4/7.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers: A More General Approach
The method demonstrated with 20/7 applies to all improper fractions. To convert any improper fraction to a mixed number, follow these steps:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator.
- The quotient is the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder is the numerator of the fractional part.
- The denominator remains the same.
For instance, consider the improper fraction 17/5:
- 17 ÷ 5 = 3 with a remainder of 2.
- The whole number is 3.
- The remainder is 2.
- The denominator is 5.
Therefore, 17/5 as a mixed number is 3 2/5.
Understanding the Relationship Between Fractions and Decimals
It's important to understand the relationship between fractions and decimals. Any fraction can be expressed as a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator. For 20/7, this results in a recurring decimal: approximately 2.85714285714... While decimals provide a different representation of the same value, mixed numbers are often preferred when dealing with quantities that involve whole units and parts of units.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
Yes, every improper fraction can be converted into a mixed number. This is because an improper fraction represents a value greater than or equal to one, which can always be expressed as a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
Q2: Why is it sometimes easier to work with improper fractions than mixed numbers?
When performing multiplication and division, it is often simpler to work with improper fractions because it avoids the need to apply the distributive property. However, when adding and subtracting, working with improper fractions can be cumbersome for some.
Q3: What if the remainder is zero after performing the division?
If the remainder is zero, the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 21/7 = 3, with a remainder of 0.
Q4: How do I convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction?
To convert a mixed number (a whole number and a fraction) back to an improper fraction, you multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and keep the same denominator. For example, to convert 2 6/7 back to an improper fraction: (2 * 7) + 6 = 20. Therefore, 2 6/7 is equal to 20/7.
Conclusion: Mastering Mixed Numbers
Mastering the conversion between improper fractions and mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide has explored the concept of mixed numbers, provided a detailed step-by-step process for converting 20/7 into a mixed number (2 6/7), offered practical examples, and addressed frequently asked questions. Understanding this concept is not just about performing calculations; it's about understanding the representation of quantities and applying this knowledge to various real-world scenarios. This skill forms the bedrock for more advanced mathematical concepts and applications, making it essential for any student or individual seeking a deeper understanding of arithmetic. Through practice and a solid understanding of the underlying principles, you can confidently navigate the world of fractions and mixed numbers.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 20/7 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.