22/5 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
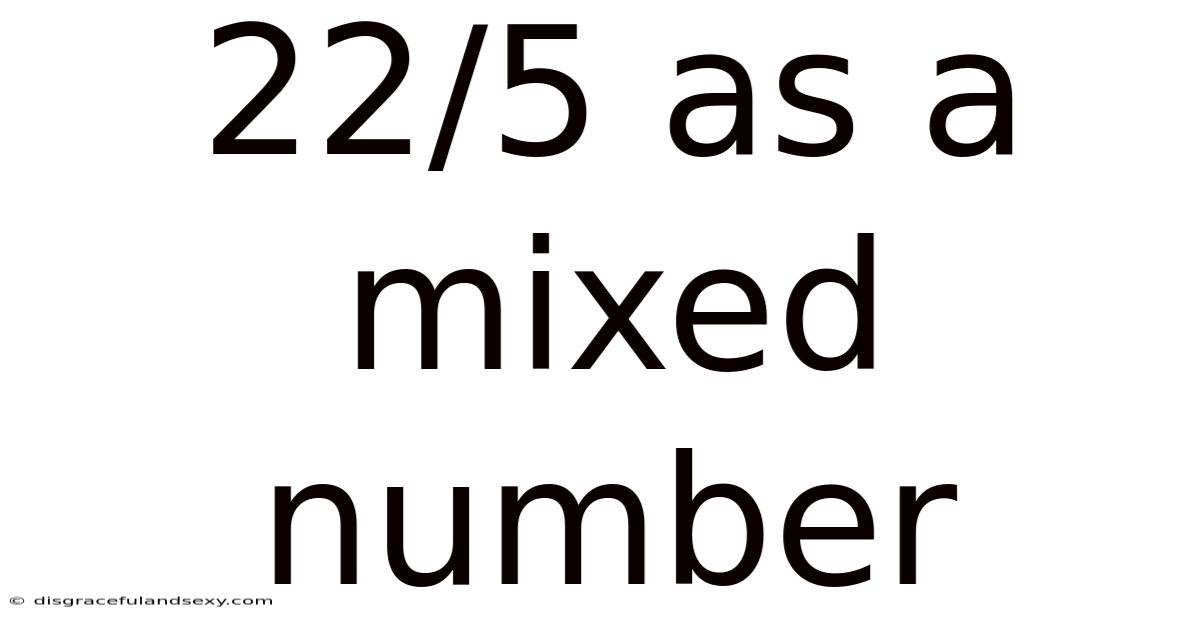
Table of Contents
Understanding 22/5 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 22/5, representing twenty-two fifths, is an improper fraction because the numerator (22) is larger than the denominator (5). Understanding how to convert improper fractions like 22/5 into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic arithmetic to more advanced concepts. This comprehensive guide will explore the conversion process, delve into the underlying mathematical principles, and offer practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is one where the numerator is smaller than the denominator. For example, 1 ¾, 2 ⅓, and 5 ⅛ are all mixed numbers. They represent a quantity greater than one but not expressed solely as a whole number. Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers helps to visualize and understand the magnitude of the fraction more intuitively.
Converting 22/5 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Approach
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part, retaining the original denominator.
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Divide 22 (the numerator) by 5 (the denominator):
22 ÷ 5 = 4 with a remainder of 2
Step 2: Determine the Whole Number
The quotient (the result of the division) is 4. This becomes the whole number part of our mixed number.
Step 3: Determine the Fractional Part
The remainder is 2. This becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains the same (5).
Step 4: Write the Mixed Number
Combine the whole number and the fraction to form the mixed number:
4 2/5
Therefore, 22/5 as a mixed number is 4 2/5. This means that 22/5 represents four whole units and two-fifths of another unit.
Visual Representation and Real-World Application
Imagine you have 22 cookies, and you want to divide them equally among 5 friends. Using the fraction 22/5, you can calculate how many cookies each friend receives. Dividing 22 cookies by 5 friends, each friend gets 4 whole cookies (the whole number part of the mixed number). There are 2 cookies remaining (the remainder), which can be divided equally among the 5 friends, giving each friend an additional 2/5 of a cookie.
This real-world example illustrates how mixed numbers provide a practical and easily understandable way to represent quantities that are not whole numbers.
The Mathematical Explanation Behind the Conversion
The process of converting an improper fraction to a mixed number relies on the fundamental principle of division and the concept of equivalent fractions. We can express the improper fraction as a sum of whole numbers and a proper fraction.
Consider 22/5. We can rewrite this as:
22/5 = (20/5) + (2/5)
Since 20/5 = 4, we can simplify the expression to:
22/5 = 4 + 2/5 = 4 2/5
This demonstrates that the conversion is essentially breaking down the improper fraction into its equivalent whole number and fractional components. It shows the inherent relationship between division and the representation of fractions.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand the reverse process – converting a mixed number back to an improper fraction. This is useful for performing calculations involving mixed numbers. The process is as follows:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 4 x 5 = 20
- Add the numerator: 20 + 2 = 22
- Keep the denominator the same: The denominator remains 5.
Therefore, 4 2/5 converts back to 22/5. This demonstrates the equivalence between the improper fraction and the mixed number representation.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Addition and Subtraction
Adding and subtracting mixed numbers requires careful attention to both the whole number and fractional parts. Here's a breakdown:
Addition:
Let's add 4 2/5 and 2 3/5:
- Add the whole numbers: 4 + 2 = 6
- Add the fractions: 2/5 + 3/5 = 5/5 = 1
- Combine the results: 6 + 1 = 7
Therefore, 4 2/5 + 2 3/5 = 7
Subtraction:
Let's subtract 1 1/5 from 4 2/5:
- Subtract the whole numbers: 4 - 1 = 3
- Subtract the fractions: 2/5 - 1/5 = 1/5
- Combine the results: 3 + 1/5 = 3 1/5
Therefore, 4 2/5 - 1 1/5 = 3 1/5
Sometimes, you may encounter situations where the fractional part of the second number is larger than the fractional part of the first number. In this case, you’ll need to borrow one from the whole number part.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division of mixed numbers are slightly more complex and often involve converting the mixed numbers to improper fractions before performing the operation.
Multiplication:
To multiply 4 2/5 by 2, first convert 4 2/5 to an improper fraction (22/5). Then multiply:
(22/5) x 2 = 44/5. This can then be converted back to a mixed number: 8 4/5
Division:
To divide 4 2/5 by 2, first convert 4 2/5 to an improper fraction (22/5). Then divide:
(22/5) ÷ 2 = 22/10 = 11/5. This can then be converted back to a mixed number: 2 1/5
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is it important to learn how to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers?
A: Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers is essential for simplifying calculations, visualizing quantities, and understanding the relationships between different fractional representations. It's a fundamental skill that builds a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Q: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
A: Yes, every improper fraction can be converted into an equivalent mixed number. The process of division will always produce a whole number quotient and a remainder, allowing for the creation of a mixed number.
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 20/5 = 4, which is a whole number and doesn't require a mixed number representation.
Q: Are there any shortcuts or tricks for converting improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: While the long division method is precise, some individuals may find mental arithmetic strategies helpful. Familiarity with multiplication tables can speed up the process.
Q: How can I check if my conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is correct?
A: You can always convert the mixed number back to an improper fraction using the method described earlier. If you obtain the original improper fraction, your conversion was accurate.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 22/5 to its mixed number equivalent, 4 2/5, is a crucial skill in mathematics. Understanding this conversion not only simplifies calculations but also provides a more intuitive way to represent and understand quantities. This detailed guide has covered the steps involved, explained the underlying mathematical principles, and provided practical examples and FAQs to ensure a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental mathematical concept. Mastering this skill will greatly enhance your mathematical abilities and problem-solving skills across various contexts. Remember to practice regularly to build fluency and confidence in converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 22/5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.