25/18 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
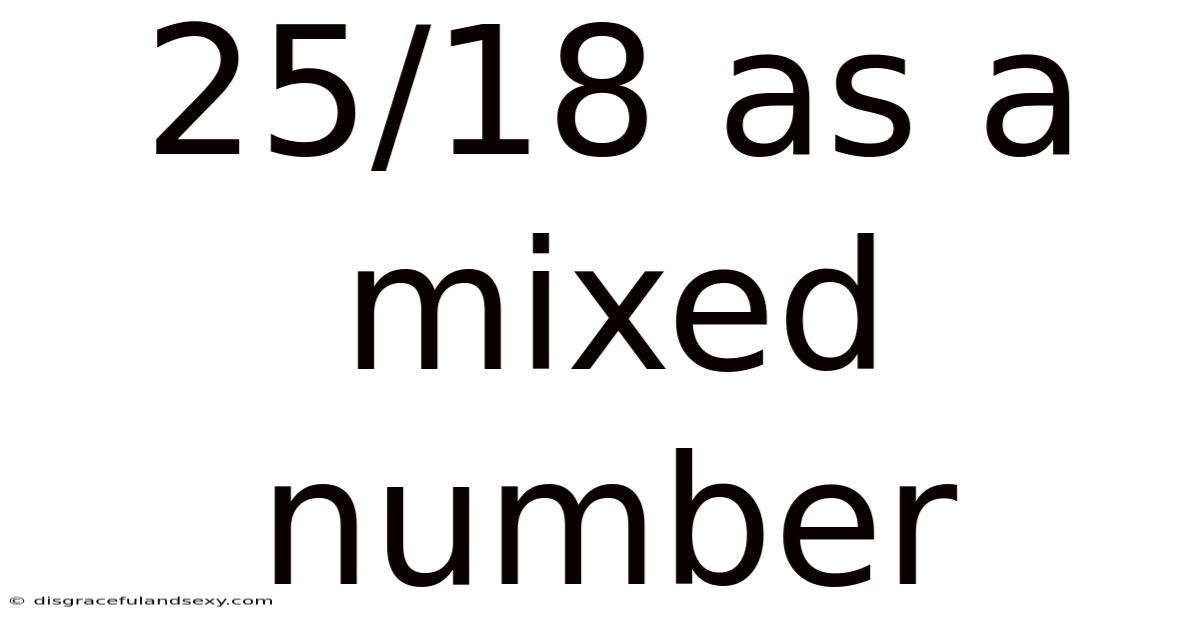
Table of Contents
Understanding 25/18 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of mixed numbers is fundamental in mathematics, bridging the gap between fractions and whole numbers. This article will delve into the process of converting the improper fraction 25/18 into a mixed number, exploring the underlying principles, providing step-by-step instructions, and addressing common questions. Understanding this conversion is crucial for various mathematical operations and real-world applications. We'll cover not just the mechanics but also the underlying reasoning, ensuring a thorough grasp of the topic.
Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before we tackle the conversion of 25/18, let's review the basic terminology. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). For example, in the fraction 25/18, 25 is the numerator and 18 is the denominator.
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 25/18, 7/4, 10/10). This indicates that the fraction represents a value greater than or equal to one whole.
A mixed number, on the other hand, combines a whole number and a proper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator, e.g., 1/2, 3/4). For example, 1 ¾ is a mixed number, representing one whole and three-quarters. Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to represent improper fractions, especially in practical applications.
Converting 25/18 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Approach
The conversion of an improper fraction to a mixed number involves division. Here's how to convert 25/18:
Step 1: Perform the Division
Divide the numerator (25) by the denominator (18).
25 ÷ 18 = 1 with a remainder of 7
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number
The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 1.
Step 3: Identify the Numerator of the Fraction
The remainder (the amount left over after the division) becomes the numerator of the fraction in the mixed number. Here, the remainder is 7.
Step 4: Retain the Denominator
The denominator of the fraction in the mixed number remains the same as the denominator of the original improper fraction. So, the denominator remains 18.
Step 5: Combine the Whole Number and the Fraction
Combine the whole number from Step 2 and the fraction from Steps 3 and 4 to form the mixed number.
Therefore, 25/18 as a mixed number is 1 7/18.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 25 slices of pizza, and each pizza has 18 slices. You can make one complete pizza (18 slices) and have 7 slices left over. This leftover represents the fraction 7/18. Thus, you have 1 whole pizza and 7/18 of another pizza, which is represented by the mixed number 1 7/18.
The Mathematical Explanation Behind the Conversion
The conversion process is based on the fundamental principle of representing a quantity in different forms while retaining its value. The improper fraction 25/18 represents the same quantity as the mixed number 1 7/18. This can be demonstrated by converting the mixed number back to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 1 * 18 = 18
- Add the numerator: 18 + 7 = 25
- Keep the denominator: The denominator remains 18.
This gives us the original improper fraction: 25/18. This demonstrates the equivalence between the improper fraction and the mixed number.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Addition, Subtraction, and More
Once you've converted an improper fraction to a mixed number, you can use it in various mathematical operations. However, it's often easier to work with improper fractions when performing multiplication and division. For addition and subtraction, converting to mixed numbers can sometimes simplify the process, depending on the specific numbers involved.
Let’s look at an example of addition:
Add 1 7/18 + 2 5/18
-
Convert both mixed numbers to improper fractions:
- 1 7/18 = (1 * 18 + 7)/18 = 25/18
- 2 5/18 = (2 * 18 + 5)/18 = 41/18
-
Add the improper fractions: 25/18 + 41/18 = 66/18
-
Simplify the resulting improper fraction: 66/18 = 11/3
-
Convert back to a mixed number if needed: 11/3 = 3 2/3
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is it important to learn how to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A1: Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers is essential for several reasons: It improves understanding of fractional values, simplifies calculations, especially in addition and subtraction, and provides a more intuitive representation of quantities greater than one whole, which is helpful in various practical applications.
Q2: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
A2: Yes, all improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers. The only exception is when the numerator is exactly divisible by the denominator, resulting in a whole number. For example, 18/18 =1, which is already a whole number.
Q3: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A3: If the remainder is zero, it means the numerator is exactly divisible by the denominator. In this case, the result is a whole number, and there's no fractional part in the mixed number. The fraction would simply be the whole number.
Q4: How do I convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction?
A4: To convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction, follow these steps: 1. Multiply the whole number by the denominator. 2. Add the numerator to the result from step 1. 3. Keep the same denominator.
Q5: Are there any shortcuts for converting improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A5: While the long division method is the most reliable, with practice, you might be able to quickly estimate the whole number and the remainder, speeding up the conversion process. However, it's crucial to double-check your mental calculations to avoid errors.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 25/18 to a mixed number (1 7/18) is a straightforward process involving division and understanding the relationship between fractions and whole numbers. This conversion is a fundamental skill in mathematics, enabling us to represent quantities in a clearer and more manageable way, facilitating various mathematical operations and real-world applications. Mastering this concept is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematics and its applications. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and develop fluency in converting between these two important representations of numbers.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 25/18 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.