28 32 In Simplest Form
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
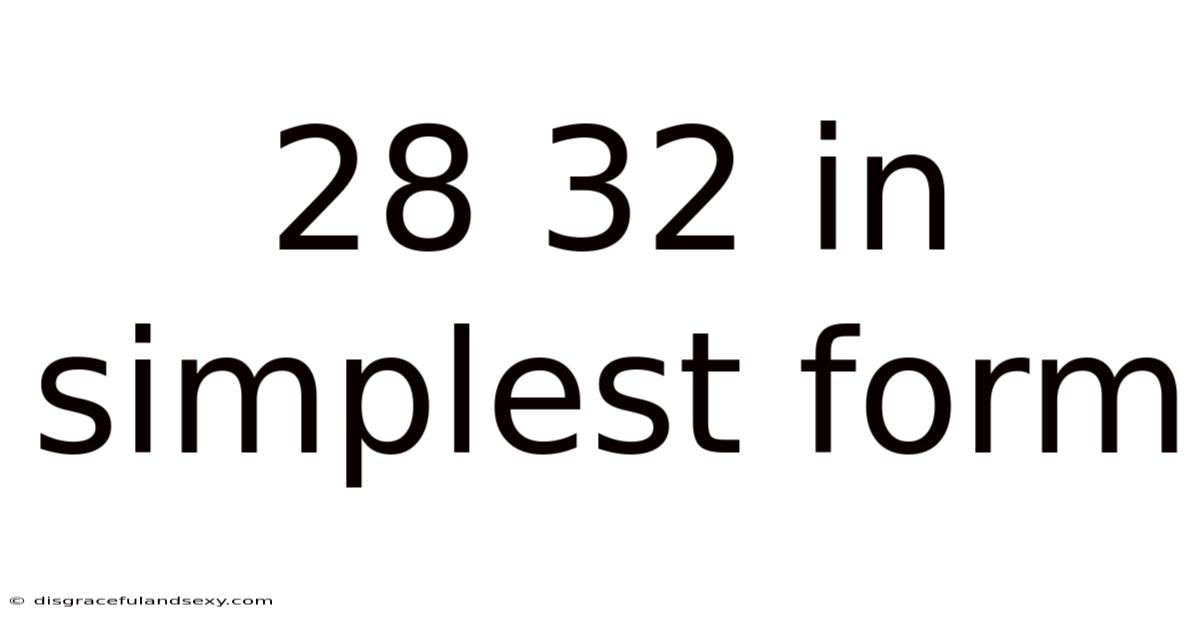
Table of Contents
Simplifying Fractions: Understanding 28/32 in its Simplest Form
Finding the simplest form of a fraction is a fundamental concept in mathematics. It's about expressing a fraction in its most concise and efficient way, eliminating any unnecessary complexity. This article will guide you through the process of simplifying the fraction 28/32, explaining the underlying principles and providing a deeper understanding of fraction simplification. We'll cover multiple methods, address common questions, and explore the practical applications of this skill.
Introduction to Fraction Simplification
A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to an equivalent fraction with a smaller numerator and denominator, while maintaining its value. This is achieved by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) or highest common factor (HCF) of both the numerator and denominator and dividing both by it.
The fraction 28/32, for instance, represents 28 parts out of a total of 32 parts. Our goal is to find an equivalent fraction that expresses the same proportion but uses smaller numbers. This is not only aesthetically pleasing but also crucial for simplifying calculations and understanding the relationship between the parts and the whole.
Method 1: Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The most efficient way to simplify a fraction is by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. There are several ways to find the GCD:
-
Listing Factors: List all the factors of both 28 and 32. The largest number that appears in both lists is the GCD.
Factors of 28: 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28 Factors of 32: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
The largest common factor is 4.
-
Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down both numbers into their prime factors. The GCD is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
28 = 2 x 2 x 7 = 2² x 7 32 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁵
The common prime factor is 2, and the lowest power is 2². Therefore, the GCD is 2² = 4.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This is a more sophisticated method, particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
32 ÷ 28 = 1 with a remainder of 4 28 ÷ 4 = 7 with a remainder of 0
The last non-zero remainder is 4, so the GCD is 4.
Once we've established that the GCD of 28 and 32 is 4, we can simplify the fraction:
28/32 = (28 ÷ 4) / (32 ÷ 4) = 7/8
Therefore, the simplest form of 28/32 is 7/8.
Method 2: Successive Division by Common Factors
This method is simpler for smaller numbers and involves repeatedly dividing the numerator and denominator by common factors until no more common factors exist.
-
We know that both 28 and 32 are even numbers, so we can start by dividing both by 2:
28/32 = 14/16
-
Both 14 and 16 are also even, so we divide by 2 again:
14/16 = 7/8
Now, 7 and 8 have no common factors other than 1. Therefore, 7/8 is the simplest form. This method achieves the same result as using the GCD, but it might require multiple steps.
Visual Representation: Understanding the Simplification
Imagine you have a pizza cut into 32 slices. You have 28 slices. The fraction 28/32 represents your portion. Simplifying the fraction means finding an equivalent representation with fewer slices. Dividing both the numerator and denominator by 4 means grouping the slices into sets of 4. You now have 7 groups of 4 slices out of a total of 8 groups of 4 slices. This visually demonstrates that 28/32 and 7/8 represent the same portion of the pizza.
Further Applications and Extensions
Understanding fraction simplification is crucial for various mathematical operations:
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions: Before adding or subtracting fractions, you need to find a common denominator. Simplifying fractions beforehand can significantly simplify this process.
- Multiplying and Dividing Fractions: Simplifying fractions before performing these operations can lead to smaller numbers and easier calculations.
- Solving Equations: Fractions often appear in algebraic equations. Simplifying fractions within the equation can make it easier to solve.
- Real-world Applications: Fraction simplification is used in numerous real-world applications, from cooking and construction to finance and engineering. Understanding proportions and ratios is essential in many fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is there a way to check if a fraction is in its simplest form?
A1: Yes, check if the numerator and denominator have any common factors other than 1. If they do not, the fraction is in its simplest form.
Q2: What if the numerator is 0?
A2: If the numerator is 0, the fraction is equal to 0, regardless of the denominator. It's already in its simplest form.
Q3: What if the denominator is 0?
A3: A fraction with a denominator of 0 is undefined. Division by zero is not allowed in mathematics.
Q4: Can I simplify a fraction by dividing only the numerator or only the denominator?
A4: No. To simplify a fraction, you must divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same number (their greatest common divisor). Dividing only one part changes the value of the fraction.
Q5: Are there any shortcuts for simplifying larger fractions?
A5: While the Euclidean algorithm is efficient for larger numbers, understanding divisibility rules (e.g., divisibility by 2, 3, 5) can help identify common factors more quickly. Practice and familiarity with prime numbers will also enhance your ability to simplify fractions efficiently.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Simplification
Simplifying fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. It allows for efficient calculations, clearer representation of quantities, and a deeper understanding of numerical relationships. By mastering the methods outlined in this article – finding the greatest common divisor, successive division, and even visual representations – you'll develop a strong foundation in working with fractions, enabling you to confidently tackle more complex mathematical problems in various contexts. Remember, practice is key to developing fluency and efficiency in simplifying fractions. The more you practice, the quicker and more intuitive the process will become. So, grab a pencil and paper and start practicing!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 28 32 In Simplest Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.