2x 2 3x X 2
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
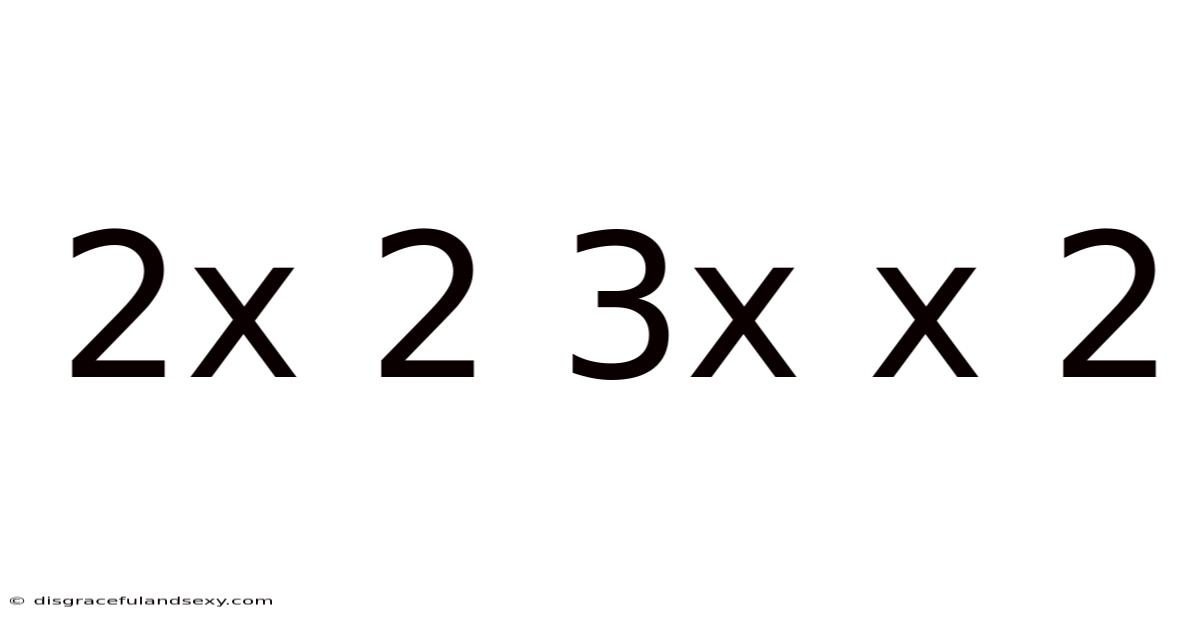
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mathematical Puzzle: 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2
This article delves into the intricacies of solving the equation 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2, providing a step-by-step guide suitable for students and anyone curious about algebraic manipulation. We'll explore the different methods of solving quadratic equations, analyze the solutions obtained, and discuss the practical applications of such problems. Understanding this type of equation is crucial for developing a strong foundation in algebra and its various applications in science, engineering, and everyday life.
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Equations
The equation 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2 is a quadratic equation. A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, 'x') is 2. These equations are characterized by their U-shaped graphs (parabolas) and often have two solutions, although sometimes they may have only one or even no real solutions. Solving quadratic equations involves finding the values of 'x' that satisfy the equation—the values that make the left-hand side equal to the right-hand side.
Step-by-Step Solution: Simplifying and Solving
Our first step in tackling 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2 is to simplify the equation by bringing all terms to one side, making it equal to zero. This standard form makes solving significantly easier.
-
Rearrange the Equation: Subtract 2x + 2 from both sides of the equation:
0 = x² + x - 4
-
Identify Coefficients: Now we have a standard quadratic equation in the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where:
- a = 1
- b = 1
- c = -4
-
Solving Using the Quadratic Formula: The quadratic formula is a powerful tool for solving any quadratic equation. It states:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting our values (a=1, b=1, c=-4), we get:
x = [-1 ± √(1² - 4 * 1 * -4)] / (2 * 1) x = [-1 ± √(1 + 16)] / 2 x = [-1 ± √17] / 2
-
Finding the Two Solutions: This gives us two distinct solutions:
- x₁ = (-1 + √17) / 2 ≈ 1.56
- x₂ = (-1 - √17) / 2 ≈ -2.56
Therefore, the solutions to the equation 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2 are approximately x ≈ 1.56 and x ≈ -2.56.
Alternative Solution Methods
While the quadratic formula is a universal approach, other methods can be used to solve quadratic equations, depending on the specific equation's characteristics. Let's explore a couple:
-
Factoring: Factoring involves expressing the quadratic equation as a product of two linear expressions. This method is only applicable when the quadratic equation can be easily factored. Unfortunately, our equation, x² + x - 4 = 0, doesn't factor neatly using integers.
-
Completing the Square: This technique involves manipulating the equation to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily solved by taking the square root. While effective, it can be more complex than the quadratic formula for equations with non-integer coefficients.
For our equation, the quadratic formula remains the most straightforward and efficient method.
Graphical Representation and Interpretation
The solutions we found, x ≈ 1.56 and x ≈ -2.56, represent the x-intercepts (points where the graph crosses the x-axis) of the parabola represented by the equation y = x² + x - 4. Graphing this equation visually confirms these solutions. The parabola intersects the x-axis at approximately x = 1.56 and x = -2.56, demonstrating that these values indeed satisfy the original equation. The graph also visually illustrates that a quadratic equation can have two real solutions.
Explanation of the Mathematical Concepts
Let's delve deeper into the underlying mathematical principles:
-
Quadratic Functions: The equation y = x² + x - 4 represents a quadratic function. This function maps each input value of 'x' to a corresponding output value of 'y'. The graph of a quadratic function is always a parabola.
-
Roots or Zeros: The solutions of a quadratic equation are also called the roots or zeros of the corresponding quadratic function. They represent the values of 'x' where the function's output (y) is equal to zero. These are the points where the parabola intersects the x-axis.
-
The Discriminant (b² - 4ac): The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant. It determines the nature of the solutions:
- If the discriminant is positive (as in our case), the equation has two distinct real solutions.
- If the discriminant is zero, the equation has one real solution (a repeated root).
- If the discriminant is negative, the equation has no real solutions (the solutions are complex numbers).
-
Parabola's Vertex: The vertex of the parabola is the lowest (or highest) point on the graph. Its x-coordinate can be found using the formula -b/2a. In our case, the x-coordinate of the vertex is -1/2, and the y-coordinate is (-1/2)² + (-1/2) - 4 = -4.25. This means the vertex of the parabola is at (-0.5, -4.25).
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have a vast array of real-world applications across various fields:
-
Physics: Projectile motion, where objects are thrown or launched, is often described using quadratic equations to model the trajectory.
-
Engineering: Design of bridges, buildings, and other structures often relies on quadratic equations to calculate forces, stresses, and stability.
-
Economics: Quadratic functions can model cost, revenue, and profit functions in business and economic analysis.
-
Computer Graphics: Parabolas are used extensively in computer graphics to create curved shapes and smooth transitions.
-
Data Analysis: Quadratic regression is a statistical method used to fit a quadratic model to data sets, allowing for the prediction of future values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if I get a negative number inside the square root in the quadratic formula?
A: If the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is negative, the quadratic equation has no real solutions. The solutions will be complex numbers involving the imaginary unit 'i' (where i² = -1).
Q: Is there a way to solve quadratic equations without using the quadratic formula?
A: Yes, factoring and completing the square are alternative methods, but the quadratic formula is a more general and reliable approach, especially for equations that are difficult to factor.
Q: Can a quadratic equation have only one solution?
A: Yes, if the discriminant (b² - 4ac) is equal to zero, the quadratic equation has one real solution (a repeated root). This occurs when the parabola touches the x-axis at only one point.
Q: How do I check if my solutions are correct?
A: Substitute each solution back into the original equation. If both sides are equal, the solution is correct.
Q: Why is understanding quadratic equations important?
A: Quadratic equations are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and science. Mastering them builds a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering Quadratic Equations
Solving the equation 2x + 2 = 3x + x² - 2, as demonstrated above, involves understanding the principles of quadratic equations, employing appropriate solving techniques (like the quadratic formula), and interpreting the results. Whether you're a student aiming for academic success or simply curious about the beauty of mathematics, grasping the concepts discussed here opens doors to a deeper understanding of algebra and its widespread applications in the real world. The ability to solve quadratic equations is a valuable skill that will serve you well in various academic and professional pursuits. Remember to practice regularly to hone your skills and develop confidence in tackling more complex algebraic problems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2x 2 3x X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.