2x 7 X 1 0
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
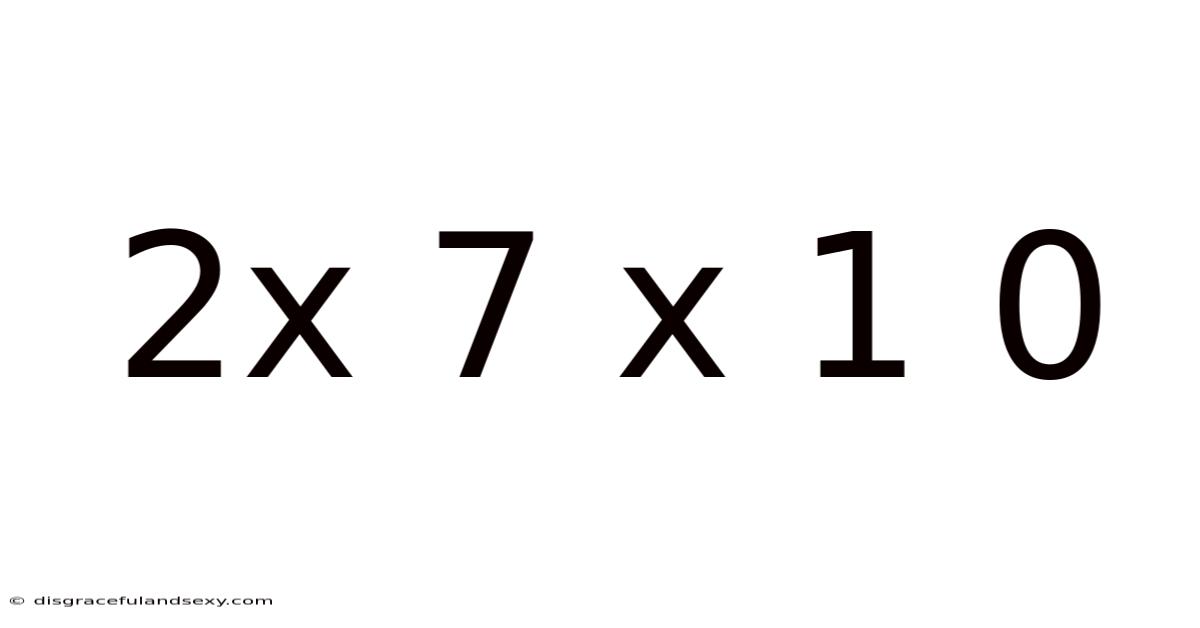
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Mysteries of 2 x 7 x 10: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and Beyond
This seemingly simple mathematical expression, 2 x 7 x 10, offers a gateway to explore fundamental concepts in arithmetic, number theory, and even the broader applications of mathematics in the real world. While the answer itself is easily calculated (140), the journey to understanding its components and implications is far more enriching. This article will delve into the intricacies of this expression, examining its constituent parts, exploring different methods of calculation, and considering its relevance within a wider mathematical context.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication and its Properties
At the heart of 2 x 7 x 10 lies the operation of multiplication. Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. For instance, 2 x 7 can be visualized as adding two sevens together: 7 + 7 = 14. This understanding forms the bedrock of grasping more complex multiplications.
Multiplication possesses several key properties that are crucial for efficient calculation and problem-solving:
-
Commutative Property: The order of the numbers being multiplied doesn't affect the result. This means 2 x 7 x 10 is the same as 7 x 2 x 10, 10 x 7 x 2, and so on. This property significantly simplifies calculations, allowing us to rearrange the numbers for easier computation.
-
Associative Property: We can group the numbers in different ways without altering the outcome. (2 x 7) x 10 is identical to 2 x (7 x 10). This allows for strategic grouping to simplify complex calculations.
-
Distributive Property: This property links multiplication with addition (and subtraction). It states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. While not directly applied in the simple expression 2 x 7 x 10, it becomes crucial when dealing with more complex expressions involving sums and products.
-
Identity Property: Multiplying any number by 1 results in the original number. In our expression, the presence of 10 highlights the significance of this property in understanding the multiplicative process.
Multiple Methods of Calculation: From Basic to Advanced
The simplicity of 2 x 7 x 10 allows us to explore several calculation methods, demonstrating the flexibility and interconnectedness of mathematical operations:
1. Direct Multiplication: This is the most straightforward approach. We start by multiplying 2 and 7 to get 14, and then multiply the result by 10 to obtain 140. This method relies on basic multiplication tables and demonstrates a linear progression through the calculation.
2. Utilizing the Commutative and Associative Properties: We can rearrange and regroup the numbers for easier computation. For example:
-
(2 x 10) x 7 = 20 x 7 = 140 This method leverages the commutative property to bring the 2 and 10 together, resulting in a simpler multiplication step.
-
2 x (7 x 10) = 2 x 70 = 140 This demonstrates the associative property, simplifying the calculation by first multiplying 7 and 10.
3. Mental Math Techniques: For those proficient in mental arithmetic, this expression can be solved quickly through mental calculation strategies. The multiplication by 10 simply involves adding a zero to the end of the number (14 becomes 140), making the calculation exceptionally efficient.
4. Visual Representations: While less practical for this specific problem, visual representations such as arrays or area models can be helpful in understanding the concept of multiplication, particularly for younger learners. An array representing 2 x 7 would consist of two rows of seven objects each, which can then be extended to visualize the multiplication by 10.
Expanding the Scope: Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Although 2 x 7 x 10 appears as a simple mathematical exercise, its underlying principles find extensive applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Everyday Calculations: Calculating the total cost of items, determining the number of units in a shipment, or even figuring out the number of days in two weeks (2 weeks x 7 days/week x 10 (if considering 10 similar orders)) all involve similar multiplicative processes.
-
Engineering and Physics: Many engineering and physics problems require calculations involving multiple factors, similar to the structure of 2 x 7 x 10. Calculations involving volume, area, speed, and other physical quantities frequently involve multiplication of multiple variables.
-
Financial Mathematics: Interest calculations, compound interest, and other financial computations rely heavily on multiplicative processes, often involving the multiplication of several factors.
-
Computer Science: Programming and algorithms frequently utilize multiplication for operations such as array manipulation, image processing, and data structure management.
Delving Deeper: Number Theory and Prime Factorization
Analyzing the numbers 2, 7, and 10 through the lens of number theory reveals further insights.
-
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- 2 is a prime number.
- 7 is a prime number.
- 10 can be factorized as 2 x 5.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 140 (2 x 7 x 10) is 2 x 2 x 5 x 7. This demonstrates the fundamental building blocks of the number 140 and illustrates the concept of prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory.
- Divisibility Rules: Understanding divisibility rules allows for quicker assessment of whether a number is divisible by certain integers. 140 is clearly divisible by 2, 5, 7, 10, 14, and 20, among other factors. These divisibility rules provide efficient shortcuts for calculations and problem-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the answer to 2 x 7 x 10?
A: The answer is 140.
Q: Why is the order of multiplication not important in this expression?
A: This is due to the commutative property of multiplication, which states that changing the order of the numbers does not change the product.
Q: Can I use a calculator to solve this?
A: Yes, a calculator can easily compute 2 x 7 x 10. However, understanding the underlying principles is more important than simply obtaining the answer.
Q: What are some real-world applications of this type of calculation?
A: Numerous applications exist, including calculating costs, determining quantities, and solving problems in engineering, physics, and finance.
Q: How does prime factorization relate to this expression?
A: Prime factorization helps break down the number 140 into its fundamental prime factors (2 x 2 x 5 x 7), providing a deeper understanding of its numerical structure.
Conclusion: Beyond the Calculation
The seemingly simple expression 2 x 7 x 10 provides a rich foundation for exploring various mathematical concepts. From the fundamental properties of multiplication to advanced concepts like prime factorization and real-world applications, this expression unveils the interconnectedness and practicality of mathematics. Understanding this simple equation allows us not only to calculate the answer but also to appreciate the beauty and power of mathematical reasoning. It emphasizes that even seemingly basic mathematical problems can lead to a deeper understanding of broader mathematical principles and their importance in our world. The journey of exploration, from the straightforward calculation to the intricate details of number theory, showcases the multifaceted nature of mathematics and its enduring relevance in various fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2x 7 X 1 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.