2x2 + 7x + 3
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 7 min read
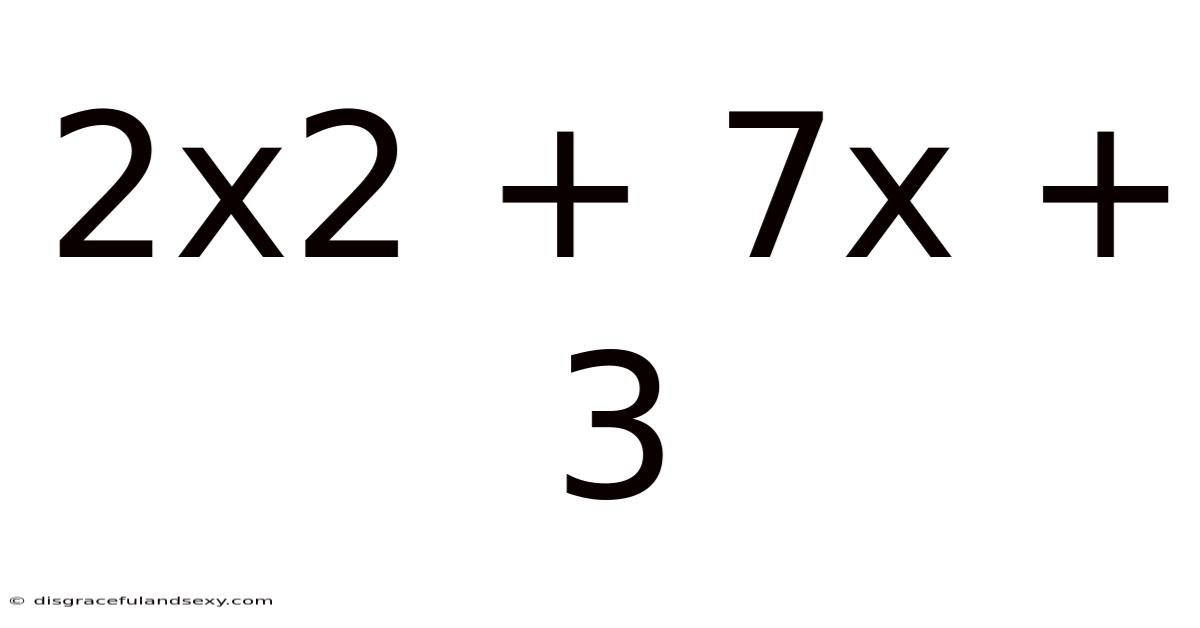
Table of Contents
Decoding the Quadratic Expression: 2x² + 7x + 3
Understanding quadratic expressions is fundamental to success in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the expression 2x² + 7x + 3, exploring its various aspects, from factoring and solving for x to its graphical representation and real-world applications. Whether you're a high school student grappling with algebra or a curious individual seeking to refresh your mathematical knowledge, this article will provide a clear and insightful exploration of this seemingly simple yet powerfully expressive equation.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into the specifics of 2x² + 7x + 3, let's establish a foundational understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic). In our case, a = 2, b = 7, and c = 3.
The term 'quadratic' originates from the Latin word 'quadratus', meaning 'square', referring to the x² term. Quadratic expressions are ubiquitous in mathematics and science, modelling various phenomena involving curved relationships, from the trajectory of a projectile to the area of a rectangle with variable sides.
Factoring the Quadratic Expression: 2x² + 7x + 3
Factoring is the process of breaking down a polynomial into simpler expressions that, when multiplied together, result in the original polynomial. Factoring 2x² + 7x + 3 allows us to solve the quadratic equation 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0 and gain a deeper understanding of its roots (solutions).
Several methods exist for factoring quadratic expressions. For 2x² + 7x + 3, we can use the following approach:
-
Find factors of 'ac' that add up to 'b': In our expression, a = 2, b = 7, and c = 3. Therefore, ac = 2 * 3 = 6. We need to find two factors of 6 that add up to 7. These factors are 6 and 1.
-
Rewrite the middle term: Rewrite the middle term (7x) using the factors we found: 6x + 1x. Our expression now becomes 2x² + 6x + 1x + 3.
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the common factor from each pair:
2x² + 6x + 1x + 3 = 2x(x + 3) + 1(x + 3)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that (x + 3) is a common factor in both terms. Factor it out:
2x(x + 3) + 1(x + 3) = (2x + 1)(x + 3)
Therefore, the factored form of 2x² + 7x + 3 is (2x + 1)(x + 3).
Solving the Quadratic Equation: 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0
Now that we've factored the expression, we can solve the corresponding quadratic equation, 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0. The solutions (also called roots or zeros) are the values of 'x' that make the equation true. Since we have the factored form (2x + 1)(x + 3) = 0, we can use the zero product property, which states that if the product of two factors is zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero. This gives us two equations:
- 2x + 1 = 0
- x + 3 = 0
Solving each equation for x:
- 2x + 1 = 0 => 2x = -1 => x = -1/2
- x + 3 = 0 => x = -3
Therefore, the solutions to the quadratic equation 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0 are x = -1/2 and x = -3. These are the roots of the quadratic equation.
Graphical Representation of 2x² + 7x + 3
Quadratic expressions are graphically represented as parabolas. A parabola is a U-shaped curve. The graph of y = 2x² + 7x + 3 will be a parabola that opens upwards (since the coefficient of x², which is 2, is positive).
The x-intercepts of the parabola are the points where the graph intersects the x-axis (where y = 0). These x-intercepts correspond to the roots of the quadratic equation we solved earlier: x = -1/2 and x = -3. The y-intercept is the point where the graph intersects the y-axis (where x = 0). To find the y-intercept, substitute x = 0 into the equation: y = 2(0)² + 7(0) + 3 = 3. So, the y-intercept is (0, 3).
The vertex of the parabola is the lowest point (in this case, since the parabola opens upwards). The x-coordinate of the vertex can be found using the formula x = -b / 2a, where a = 2 and b = 7. Therefore, x = -7 / (2 * 2) = -7/4. Substitute this x-value back into the equation to find the y-coordinate of the vertex.
The Discriminant and Nature of Roots
The discriminant of a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 is given by the expression b² - 4ac. The discriminant provides information about the nature of the roots:
- b² - 4ac > 0: The equation has two distinct real roots.
- b² - 4ac = 0: The equation has one real root (a repeated root).
- b² - 4ac < 0: The equation has no real roots (the roots are complex numbers).
For our equation, 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0, the discriminant is:
7² - 4 * 2 * 3 = 49 - 24 = 25
Since the discriminant is positive (25), the equation has two distinct real roots, which we already found to be x = -1/2 and x = -3.
Completing the Square
Another method to solve quadratic equations is completing the square. This technique involves manipulating the equation to form a perfect square trinomial, which can then be easily factored. Let's apply it to 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0:
-
Divide by 'a': Divide the entire equation by 2 (the coefficient of x²):
x² + (7/2)x + (3/2) = 0
-
Move the constant term: Move the constant term (3/2) to the right side of the equation:
x² + (7/2)x = -3/2
-
Complete the square: To complete the square, take half of the coefficient of x ((7/2)/2 = 7/4), square it ((7/4)² = 49/16), and add it to both sides of the equation:
x² + (7/2)x + 49/16 = -3/2 + 49/16
-
Factor the perfect square trinomial: The left side is now a perfect square trinomial:
(x + 7/4)² = 25/16
-
Solve for x: Take the square root of both sides:
x + 7/4 = ±5/4
x = -7/4 ± 5/4
This gives us the two solutions: x = -1/2 and x = -3, the same as before.
The Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a general formula used to solve any quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
Applying this formula to our equation 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0 (where a = 2, b = 7, and c = 3):
x = (-7 ± √(7² - 4 * 2 * 3)) / (2 * 2) x = (-7 ± √25) / 4 x = (-7 ± 5) / 4
This gives us the same solutions: x = (-7 + 5) / 4 = -1/2 and x = (-7 - 5) / 4 = -3.
Real-World Applications
Quadratic equations and expressions have numerous applications in various fields:
- Physics: Calculating the trajectory of projectiles, analyzing the motion of objects under constant acceleration.
- Engineering: Designing structures, optimizing processes, modeling electrical circuits.
- Economics: Modeling supply and demand curves, analyzing cost functions.
- Computer Graphics: Creating curves and shapes for images and animations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between a quadratic expression and a quadratic equation?
A: A quadratic expression is a mathematical phrase containing a variable raised to the power of 2, such as 2x² + 7x + 3. A quadratic equation is a statement that sets a quadratic expression equal to zero, like 2x² + 7x + 3 = 0.
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored easily?
A: No. Some quadratic expressions have roots that are irrational or complex numbers, making them difficult or impossible to factor using simple integer methods. In these cases, the quadratic formula or completing the square are useful alternatives.
Q: What does the vertex of a parabola represent?
A: The vertex of a parabola represents the minimum (or maximum, if the parabola opens downwards) value of the quadratic function. It's a key point in understanding the behavior of the quadratic expression.
Q: What is the significance of the roots of a quadratic equation?
A: The roots of a quadratic equation represent the x-intercepts of the corresponding parabola. They indicate the values of x where the quadratic expression equals zero.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple quadratic expression 2x² + 7x + 3 offers a rich landscape for exploring fundamental algebraic concepts. From factoring and solving equations to graphical representation and real-world applications, understanding this expression provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems. This article has provided a comprehensive overview, employing various methods to solve the equation and emphasizing the interconnectedness of different mathematical concepts. Mastering quadratic expressions is a significant step toward fluency in algebra and a deeper appreciation of the power of mathematics in the real world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2x2 + 7x + 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.