3 4 X 2 9
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
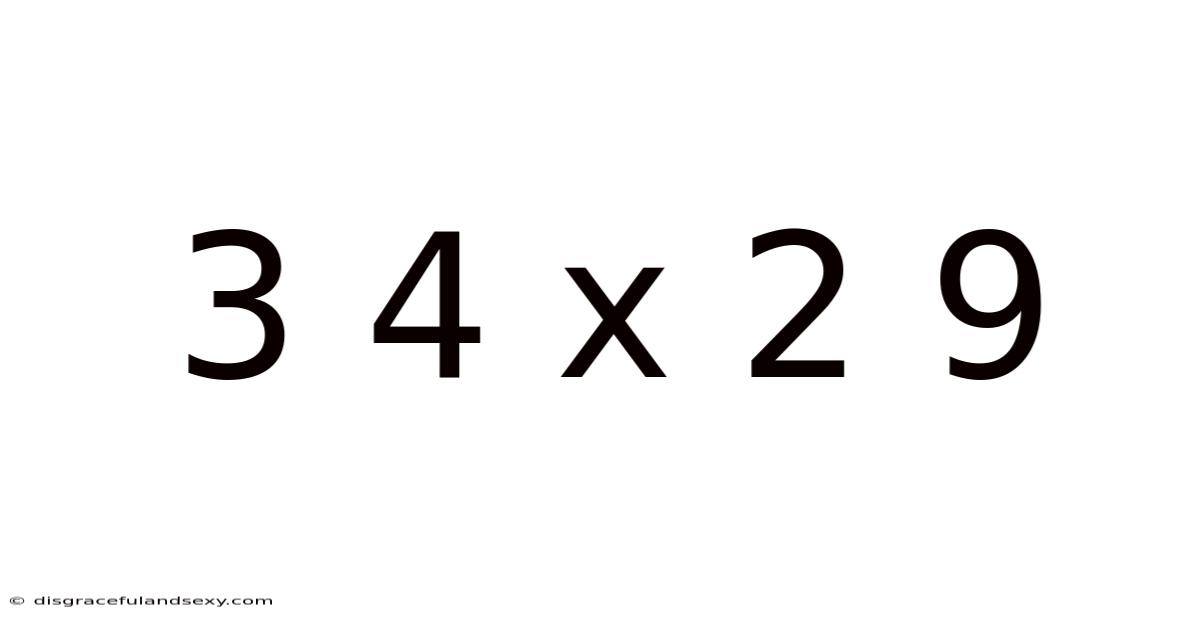
Table of Contents
Decoding 34 x 29: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and Beyond
This article explores the seemingly simple multiplication problem, 34 x 29, as a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts, diverse calculation methods, and the practical applications of multiplication in everyday life. We'll move beyond a simple answer and delve into the 'why' behind the process, exploring different approaches, historical context, and real-world examples. This will be beneficial for anyone looking to solidify their understanding of multiplication, or for educators seeking enriching teaching materials.
I. Understanding the Basics: What is 34 x 29?
At its core, 34 x 29 represents repeated addition. It asks: what is the total if you add 34 to itself 29 times? While this approach is conceptually clear, it's impractical for larger numbers. The standard method, however, relies on place value and the distributive property of multiplication. This property states that multiplying a sum by a number is the same as multiplying each addend by the number and then adding the products. In simpler terms, a(b+c) = ab + ac.
We break down 34 and 29 into tens and units:
- 34 = 30 + 4
- 29 = 20 + 9
Applying the distributive property, we get:
(30 + 4) x (20 + 9) = (30 x 20) + (30 x 9) + (4 x 20) + (4 x 9)
This leads to the following calculation:
- 30 x 20 = 600
- 30 x 9 = 270
- 4 x 20 = 80
- 4 x 9 = 36
Adding these partial products together: 600 + 270 + 80 + 36 = 986
Therefore, 34 x 29 = 986.
II. Alternative Methods of Multiplication: Exploring Different Approaches
While the standard method is efficient, several alternative techniques can be used to solve 34 x 29, each offering unique insights into the underlying mathematical principles.
A. The Lattice Method: This visual method is particularly helpful for learners who struggle with carrying over digits. It involves drawing a grid, partitioning the numbers, and performing single-digit multiplications within each cell. The results are then added diagonally. While less common today, its visual clarity can aid understanding.
B. The Box Method: Similar to the lattice method, the box method organizes the multiplication process visually, breaking down the numbers into their place values and multiplying accordingly. It’s a structured approach that helps in keeping track of partial products.
C. The Russian Peasant Method: A fascinating historical method, the Russian Peasant algorithm involves repeatedly halving one number and doubling the other, discarding any even results in the halved number column. The remaining numbers in the doubled column are then added to arrive at the final product. While seemingly unconventional, it provides a unique perspective on multiplication.
D. Using Vedic Mathematics: Vedic mathematics, an ancient Indian system, offers several techniques to perform multiplication quickly and mentally. These methods often involve unique patterns and shortcuts, allowing for faster calculations.
III. The Significance of Place Value and the Distributive Property
The solution to 34 x 29 hinges on a deep understanding of place value and the distributive property. Place value dictates that the position of a digit in a number determines its value (e.g., in 34, the '3' represents 30). The distributive property, as demonstrated earlier, allows us to break down the problem into smaller, more manageable calculations, making complex multiplication less daunting.
IV. Real-World Applications of Multiplication: Beyond the Classroom
Multiplication isn't confined to the realm of mathematics textbooks. It forms the basis of countless real-world applications:
- Calculating Costs: Determining the total cost of multiple items, such as 29 packs of pencils at $34 each.
- Area Measurement: Calculating the area of a rectangular space, like a room or a field (length x width).
- Scaling Recipes: Adjusting the ingredients in a recipe to feed a larger number of people.
- Financial Calculations: Calculating interest, determining total earnings, or managing budgets.
- Data Analysis: In statistics and data science, multiplication is used extensively in various calculations and analyses.
- Engineering and Physics: Multiplication plays a pivotal role in various calculations in engineering and physics, such as determining forces, velocities, and other quantities.
V. Expanding on the Concept: Exploring Factors and Multiples
Understanding 34 x 29 allows us to explore broader mathematical concepts like factors and multiples. Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number, while multiples are numbers obtained by multiplying a given number by an integer.
The factors of 34 are 1, 2, 17, and 34. The factors of 29 are 1 and 29 (29 is a prime number). Understanding factors can be helpful in simplifying calculations or solving problems involving divisibility.
Multiples of 34 include 34, 68, 102, 136, and so on. Multiples of 29 include 29, 58, 87, 116, and so on.
VI. Historical Context: The Evolution of Multiplication Techniques
Multiplication techniques have evolved over centuries. Ancient civilizations used different methods, from tallying to employing various forms of abaci (counting frames) and algorithms. The development of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system and the adoption of place value significantly streamlined multiplication processes. Understanding the history of mathematical concepts adds another layer to appreciating their significance.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the easiest way to multiply 34 x 29?
A: The "easiest" method depends on individual preference and mathematical aptitude. The standard algorithm is generally efficient, while visual methods like the lattice or box method might be more intuitive for some.
Q: Are there any shortcuts for multiplying larger numbers?
A: Yes, several mental math techniques and algorithms exist, including Vedic mathematics and other specialized approaches, allowing for faster calculations of larger numbers. However, mastery of these requires practice and understanding of underlying principles.
Q: Why is understanding multiplication important?
A: Multiplication is a fundamental operation used extensively in various fields, from everyday calculations to complex scientific and engineering applications. A solid grasp of multiplication is essential for further mathematical learning and problem-solving in numerous contexts.
Q: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A: Consistent practice is key. Start with smaller numbers, gradually increasing difficulty. Use various methods and techniques to find what works best for you. Engage with interactive learning resources and consider seeking help from a tutor or teacher if needed.
VIII. Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of 34 x 29
The seemingly simple problem, 34 x 29, serves as a powerful illustration of core mathematical principles. Exploring different solution methods reveals the beauty and versatility of mathematics. Understanding these principles extends beyond rote calculation, equipping individuals with essential tools for navigating the quantitative aspects of daily life and unlocking the door to more advanced mathematical concepts. The journey from a simple multiplication problem to a deeper comprehension of underlying concepts highlights the richness and relevance of mathematical exploration. The answer, 986, is only the beginning of a much more profound mathematical journey.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 4 X 2 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.