3.6 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
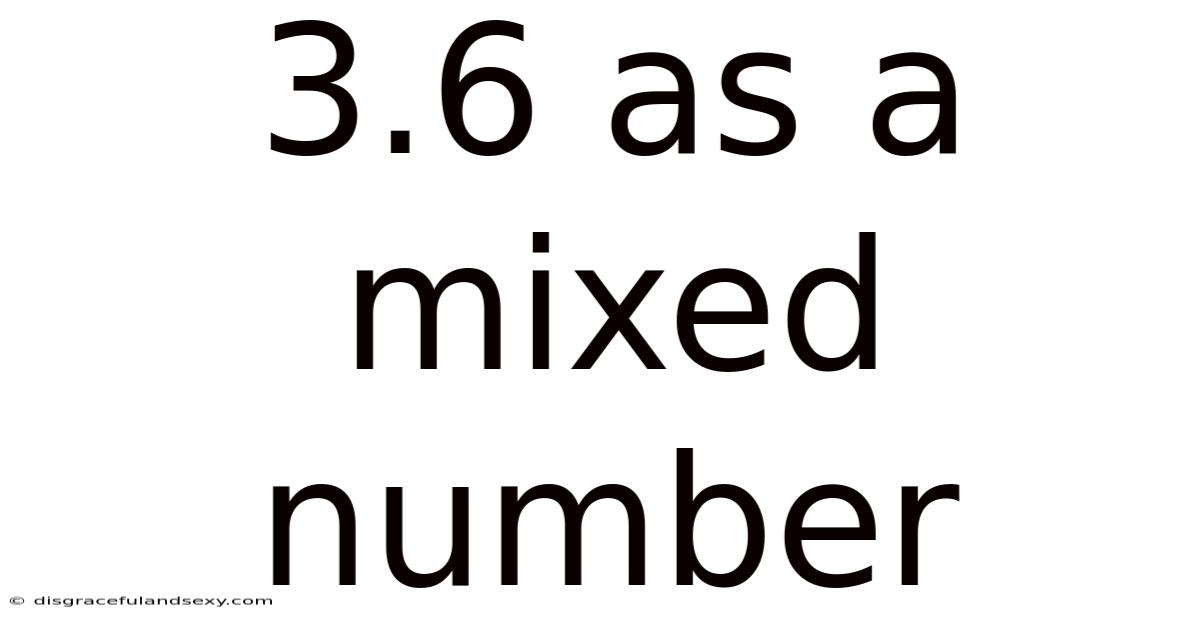
Table of Contents
Understanding 3.6 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The decimal number 3.6 might seem straightforward, but understanding its representation as a mixed number opens up a deeper understanding of fractional concepts. This comprehensive guide will explore the conversion process, delve into the underlying mathematical principles, and address common questions surrounding this seemingly simple topic. We'll break down the process step-by-step, making it accessible for learners of all levels. This article will cover converting decimals to fractions, simplifying fractions, and understanding the relationship between decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers.
Understanding Decimals, Fractions, and Mixed Numbers
Before we jump into converting 3.6, let's establish a firm foundation. A decimal number uses a base-ten system, with digits to the right of the decimal point representing tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. A fraction, on the other hand, expresses a part of a whole, represented by a numerator (top number) and a denominator (bottom number). A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator). Understanding these core concepts is crucial for seamless conversion.
Converting 3.6 to a Fraction
The first step in converting 3.6 to a mixed number is to express it as an improper fraction. This means we need to represent the entire value of 3.6 as a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. We start by focusing on the decimal part, 0.6.
-
Identifying the Place Value: The digit 6 is in the tenths place. This means 0.6 represents six-tenths, which can be written as the fraction 6/10.
-
Expressing the Whole Number: The whole number part, 3, remains unchanged. We can represent it as a fraction with a denominator of 1: 3/1.
-
Combining the Fractions: Now we have two fractions: 3/1 and 6/10. To combine them, we need a common denominator. The least common multiple of 1 and 10 is 10. Therefore, we convert 3/1 to an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 10: (3/1) * (10/10) = 30/10.
-
Adding the Fractions: We now add the two fractions with the common denominator: 30/10 + 6/10 = 36/10. This is our improper fraction representation of 3.6.
Simplifying the Fraction
The fraction 36/10 is not in its simplest form. To simplify a fraction, we find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and the denominator and divide both by it. The GCD of 36 and 10 is 2.
- Dividing by the GCD: Dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2, we get: 36/2 = 18 and 10/2 = 5. This simplifies the fraction to 18/5.
Converting the Improper Fraction to a Mixed Number
Now we have the improper fraction 18/5. To convert this to a mixed number, we perform division:
-
Performing the Division: Divide the numerator (18) by the denominator (5). 18 divided by 5 is 3 with a remainder of 3.
-
Writing the Mixed Number: The quotient (3) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. The remainder (3) becomes the numerator of the fraction, and the denominator remains the same (5). Therefore, the mixed number representation of 18/5 is 3 3/5.
Therefore, 3.6 as a mixed number is 3 3/5.
The Mathematical Principles Behind the Conversion
The conversion from a decimal to a mixed number relies on the fundamental principle of representing numbers in different forms while preserving their value. The process involves:
-
Place Value Understanding: Accurately identifying the place value of each digit in the decimal is paramount. This allows us to correctly represent the decimal as a fraction.
-
Finding Common Denominators: Adding or subtracting fractions requires a common denominator. This process ensures that we are adding or subtracting like quantities.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Simplifying fractions is essential for representing numbers in their most concise form. It improves readability and allows for easier manipulation in further calculations.
-
Division and Remainders: Converting an improper fraction to a mixed number involves division. The quotient represents the whole number part, while the remainder forms the numerator of the fractional part.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all decimals be converted to mixed numbers?
A1: Yes, all terminating decimals (decimals that end) can be converted to fractions, and subsequently to mixed numbers if the fraction is improper. Recurring decimals (decimals that repeat infinitely) require a slightly different approach, involving the use of algebraic equations.
Q2: What if the decimal only has a whole number component?
A2: If the decimal only has a whole number component (e.g., 3.0), the mixed number representation is simply the whole number itself (3). The fractional part would be 0/1, which simplifies to 0.
Q3: Is there more than one way to represent 3.6 as a mixed number?
A3: No, there is only one simplified mixed number representation of 3.6, which is 3 3/5. While you might arrive at an equivalent fraction (e.g., 6/20, 9/15) during the simplification process, the final simplified mixed number will always be the same.
Q4: Why is it important to learn this conversion?
A4: Understanding the relationship between decimals and fractions is crucial in various mathematical contexts, including algebra, geometry, and everyday problem-solving. This conversion skill enhances number sense and facilitates a deeper understanding of numerical representation.
Conclusion
Converting 3.6 to the mixed number 3 3/5 isn't just about following a set of steps; it's about grasping the fundamental principles that govern numerical representation. This process reinforces the interconnectedness of decimals and fractions, highlighting the flexibility of representing the same quantity in different forms. This understanding provides a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills. By mastering this conversion, you build a stronger numerical foundation that will serve you well in your mathematical journey. The seemingly simple act of converting 3.6 to a mixed number unlocks a deeper appreciation for the elegance and interconnectedness of mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3.6 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.