30 X 5 X 4
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
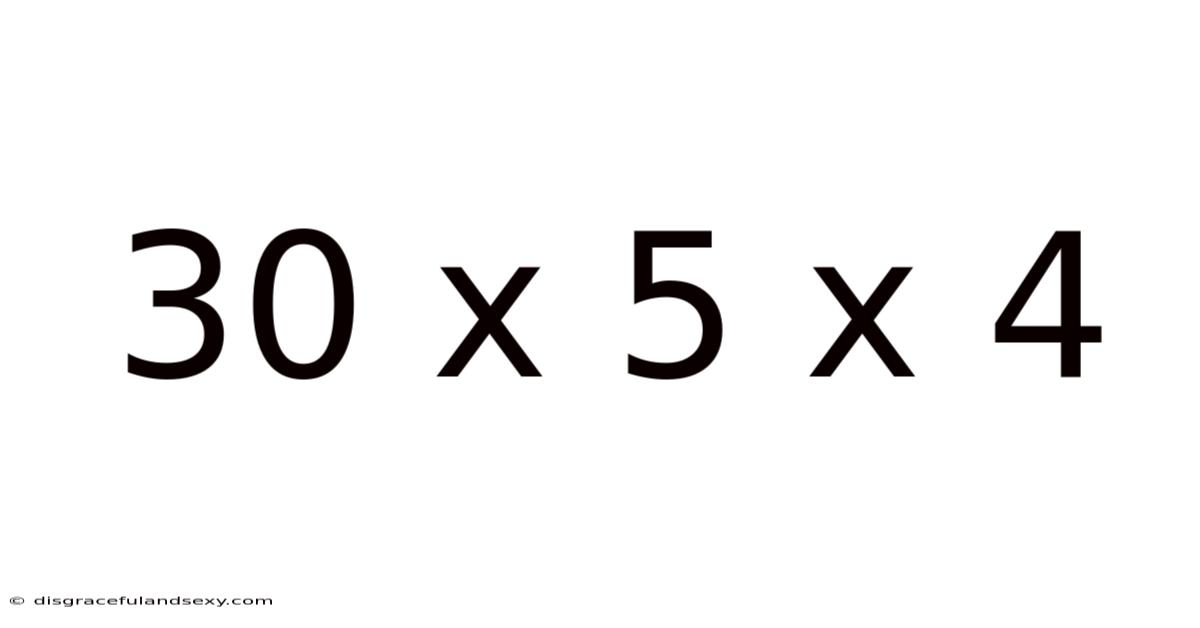
Table of Contents
Decoding 30 x 5 x 4: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation 30 x 5 x 4, delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying mathematical principles and demonstrate its practical applications across various fields. We will examine different approaches to solving this problem, highlighting the power of multiplication and its relevance in everyday life, from simple budgeting to complex engineering calculations. This exploration will be suitable for learners of all levels, offering a comprehensive understanding of multiplication and its real-world significance.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication as Repeated Addition
At its core, multiplication is a simplified form of repeated addition. When we say 30 x 5, we're essentially adding 30 to itself five times: 30 + 30 + 30 + 30 + 30 = 150. This fundamental concept helps us grasp the essence of multiplication, regardless of the numbers involved. Similarly, 30 x 5 x 4 can be interpreted as repeatedly adding the result of 30 x 5 (which is 150) four times: 150 + 150 + 150 + 150 = 600.
Solving 30 x 5 x 4: Different Approaches
There are several ways to approach this calculation, each showcasing different mathematical properties:
1. Sequential Multiplication: This is the most straightforward method. We begin by multiplying the first two numbers, then multiply the result by the third number.
- 30 x 5 = 150
- 150 x 4 = 600
2. Commutative Property: Multiplication possesses the commutative property, meaning the order of the numbers doesn't affect the final result. We can rearrange the numbers to simplify the calculation. For example:
- 5 x 4 = 20
- 30 x 20 = 600
This approach is often advantageous when dealing with easier multiplications, like 5 x 4, before tackling larger numbers.
3. Distributive Property: The distributive property allows us to break down larger numbers into smaller, more manageable parts. While less efficient for this specific problem, it's a valuable concept for understanding more complex multiplications. For instance, we could rewrite 30 as 3 x 10:
- (3 x 10) x 5 x 4
- (3 x 5 x 4) x 10
- 60 x 10 = 600
This demonstrates how breaking down numbers can sometimes simplify the calculation.
Beyond the Calculation: Exploring the Significance of 600
The answer to 30 x 5 x 4 is 600. While this number might seem insignificant on its own, its context defines its meaning. Let’s explore several practical examples:
1. Real-world Scenarios:
- Inventory Management: Imagine a warehouse storing boxes of products. If each box contains 30 items, there are 5 boxes per pallet, and 4 pallets in the warehouse, then the total number of items is 600 (30 x 5 x 4).
- Project Planning: Consider a construction project where 30 workers each work 5 hours a day for 4 days. The total number of worker-hours is 600 (30 x 5 x 4).
- Financial Calculations: If you invest $30 per month for 5 years (60 months), and earn 4% interest annually, the total invested amount would be a portion of the total calculation involved (600). Though the total final figure would be higher due to compounding interest, understanding the simple multiplication is a foundation for more complex financial equations.
- Event Planning: If you’re planning an event with 30 tables, 5 guests per table, and 4 courses per meal, you’ll need to prepare food for 600 people (30 x 5 x 4).
2. Geometric Applications:
- Volume Calculation: Imagine a rectangular prism (box) with dimensions 30 units long, 5 units wide, and 4 units high. The volume of this box is 600 cubic units (30 x 5 x 4). This demonstrates how multiplication is crucial in determining the three-dimensional space occupied by an object.
3. Data Analysis:
- Statistical Calculations: Many statistical calculations involve multiplication. For example, calculating the total score of 30 students who each answered 5 questions worth 4 points each would involve 30 x 5 x 4 = 600.
Expanding the Understanding: Factors and Multiples
Understanding factors and multiples is essential to working with numbers efficiently. The number 600, the result of our calculation, has many factors. A factor is a number that divides evenly into another number without leaving a remainder. Some factors of 600 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 75, 100, 120, 150, 200, 300, and 600. Understanding factors helps in simplifying calculations and solving problems in algebra and other advanced mathematical fields.
A multiple is a number obtained by multiplying a given number by an integer. 600 is a multiple of 30, 5, 4, 150, 20, 120, and many other numbers. The concept of multiples helps in finding common denominators when dealing with fractions.
Advanced Applications: Algebra and Beyond
The seemingly simple equation 30 x 5 x 4 lays the groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts. In algebra, this could be represented as:
- x = 30 * y * z, where y = 5 and z = 4
This shows how multiplication is a fundamental building block for algebraic expressions and equations. It's also fundamental to calculus, where rates of change and areas under curves often involve multiplication and its inverse, division.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the easiest way to calculate 30 x 5 x 4?
- A: The easiest way depends on your preference and familiarity with multiplication tables. Sequential multiplication (30 x 5 = 150, then 150 x 4 = 600) is straightforward. Rearranging using the commutative property (5 x 4 = 20, then 30 x 20 = 600) can also be easier for some.
-
Q: Are there any shortcuts for multiplying larger numbers?
- A: Yes, various techniques exist. For example, understanding place value (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.) and using mental math strategies can simplify calculations. Learning multiplication tables and understanding the distributive property are also essential.
-
Q: Why is it important to learn multiplication?
- A: Multiplication is fundamental to many aspects of life, from everyday calculations to advanced mathematical concepts. It's essential for problem-solving, critical thinking, and understanding various fields like engineering, finance, and computer science.
-
Q: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
- A: Practice is key! Regularly working through multiplication problems, using flashcards, and engaging in interactive math games can significantly improve your skills.
Conclusion: The Power of Multiplication
The seemingly simple equation 30 x 5 x 4 provides a springboard for exploring the power and versatility of multiplication. From its foundation as repeated addition to its applications in various fields, understanding multiplication is crucial for navigating the quantitative aspects of our world. The answer, 600, represents more than just a numerical result; it signifies a deep understanding of fundamental mathematical principles and their practical implications in everyday life and complex problem-solving. The more we explore and understand these principles, the better equipped we are to tackle challenges and uncover opportunities in the world around us. Therefore, embracing the power of multiplication is not merely about solving equations; it's about unlocking a fundamental key to understanding and interacting with the world in a more meaningful way.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30 X 5 X 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.