32 40 In Simplest Form
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
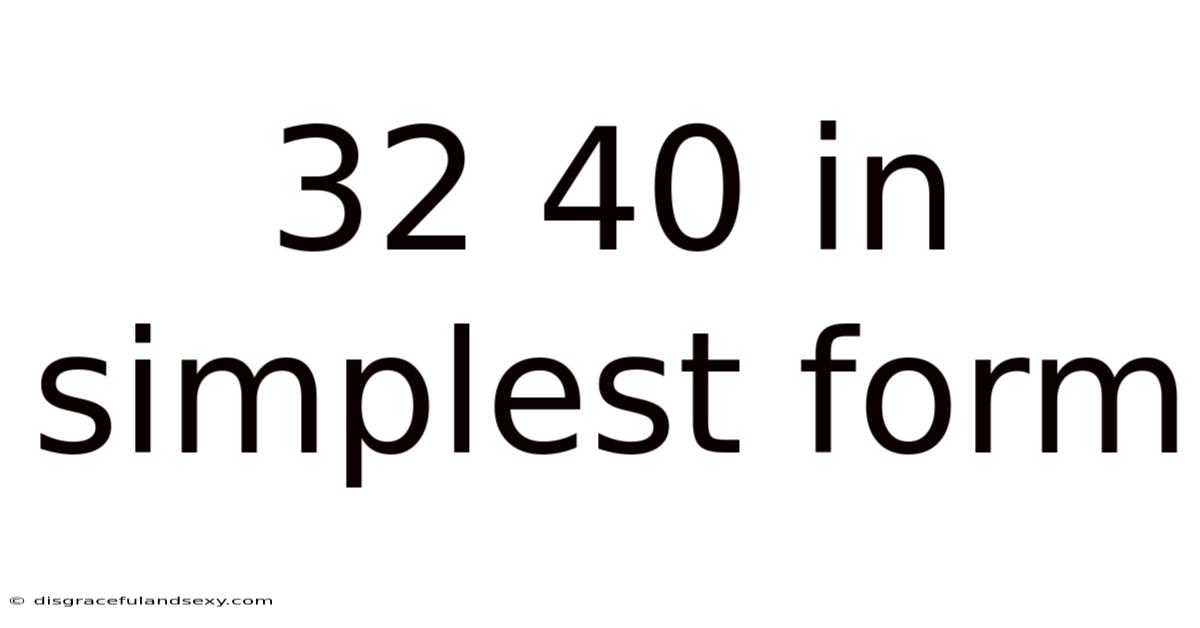
Table of Contents
Simplifying Fractions: A Deep Dive into 32/40
Understanding fractions is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for everything from baking a cake to understanding complex scientific principles. This article will explore the simplification of the fraction 32/40, providing a comprehensive explanation suitable for learners of all levels. We'll delve into the methods, the underlying mathematical principles, and offer practical applications to solidify your understanding. By the end, you'll not only know the simplest form of 32/40 but also have a solid grasp of fraction simplification in general.
Introduction to Fraction Simplification
A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms, where the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1. This makes the fraction easier to understand and work with. The process involves finding the greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), of the numerator and denominator.
The fraction 32/40 is not in its simplest form because both 32 and 40 share common factors. Our goal is to find the simplest equivalent fraction, a fraction that represents the same value but with smaller numbers.
Finding the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of 32 and 40
The GCD is the largest number that divides both 32 and 40 without leaving a remainder. There are several methods to find the GCD:
1. Listing Factors:
- Factors of 32: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
- Factors of 40: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 40
By comparing the lists, we can see that the largest common factor is 8.
2. Prime Factorization:
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- Prime factorization of 32: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2<sup>5</sup>
- Prime factorization of 40: 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 = 2<sup>3</sup> x 5
The GCD is found by taking the lowest power of each common prime factor. In this case, both numbers share three factors of 2 (2<sup>3</sup> = 8). Therefore, the GCD is 8.
3. Euclidean Algorithm:
This is a more efficient method for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly dividing the larger number by the smaller number and replacing the larger number with the remainder until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
- Divide 40 by 32: 40 ÷ 32 = 1 with a remainder of 8.
- Divide 32 by 8: 32 ÷ 8 = 4 with a remainder of 0.
The last non-zero remainder is 8, so the GCD is 8.
Simplifying 32/40
Now that we know the GCD of 32 and 40 is 8, we can simplify the fraction:
Divide both the numerator and the denominator by the GCD (8):
32 ÷ 8 = 4 40 ÷ 8 = 5
Therefore, the simplest form of 32/40 is 4/5.
Visual Representation of Fraction Simplification
Imagine you have a pizza cut into 40 equal slices. If you have 32 slices, you have 32/40 of the pizza. Simplifying the fraction to 4/5 means grouping the slices. You can group the 40 slices into 8 groups of 5 slices each. Out of these 8 groups, you possess 4 groups (32 slices / 8 slices per group = 4 groups). This visually demonstrates that 32/40 is equivalent to 4/5.
Practical Applications of Fraction Simplification
Simplifying fractions is essential in various real-world applications:
- Baking: Recipes often use fractions. Simplifying fractions helps in accurate measurement and scaling recipes.
- Construction: Measurements and proportions in construction rely heavily on fractions. Simplified fractions make calculations easier and more precise.
- Finance: Working with percentages and proportions in finance often involves fractions. Simplifying fractions aids in quick calculations and clearer understanding.
- Science: Many scientific concepts involve ratios and proportions expressed as fractions. Simplified fractions enhance understanding and data analysis.
Understanding Equivalent Fractions
It's important to understand that simplifying a fraction does not change its value. The fraction 32/40 and 4/5 are equivalent fractions. They represent the same portion of a whole. You can obtain equivalent fractions by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number.
For example:
- Multiplying both numerator and denominator of 4/5 by 2 gives 8/10, which is also equivalent to 32/40.
- Multiplying both numerator and denominator of 4/5 by 8 gives 32/40.
Further Exploration: Working with More Complex Fractions
The principles discussed here can be applied to simplify any fraction. The key is to find the GCD of the numerator and denominator. For larger numbers, the Euclidean algorithm is particularly efficient. If the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1, the fraction is already in its simplest form (it's said to be in lowest terms).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if I divide by a number that isn't the GCD?
A: You'll still get a simplified fraction, but it won't be in its simplest form. You'll have to repeat the process until you've divided by the GCD.
Q: Can I simplify a fraction with a negative number?
A: Yes, the process remains the same. Determine the GCD of the absolute values of the numerator and denominator, and then apply the simplification. The sign of the fraction (positive or negative) remains unchanged.
Q: How do I simplify fractions with decimals?
A: Convert the decimals to fractions first. For example, 0.25 is equivalent to 1/4, which can then be simplified if necessary.
Q: Why is simplifying fractions important?
A: Simplifying fractions makes them easier to understand, compare, and use in calculations. It improves clarity and accuracy in various applications.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction Simplification
Simplifying fractions is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. By mastering the techniques, including finding the greatest common divisor and understanding equivalent fractions, you enhance your mathematical abilities and gain a deeper understanding of numerical relationships. The process of simplifying 32/40 to 4/5, as explored in this article, serves as a practical illustration of these core concepts. Remember, practice is key to building proficiency in this essential mathematical operation. Through consistent effort, you'll gain confidence and expertise in simplifying fractions, paving the way for success in more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 32 40 In Simplest Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.