32/6 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
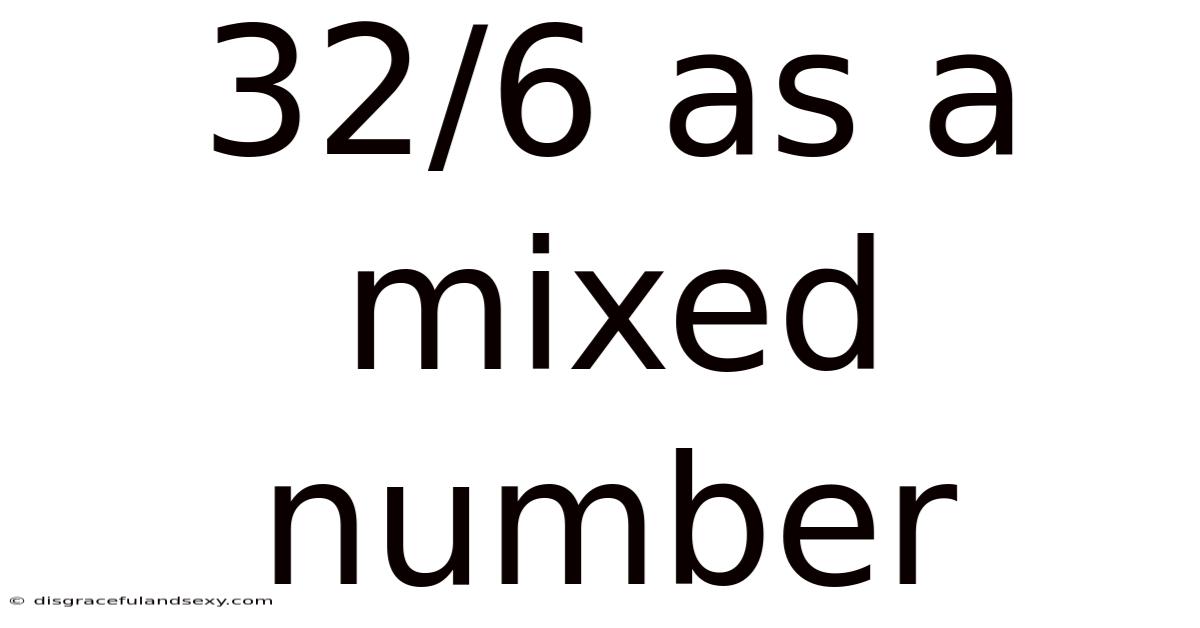
Table of Contents
Understanding 32/6 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Many mathematical operations involve fractions, and understanding how to convert improper fractions, like 32/6, into mixed numbers is a crucial skill. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of converting 32/6 into a mixed number, explaining the underlying concepts and providing practical examples. We'll explore the meaning of mixed numbers, the steps involved in the conversion, and delve into the reasoning behind this mathematical transformation. This guide aims to build a solid understanding, not just for solving this specific problem, but for mastering the broader concept of fraction manipulation.
What are Mixed Numbers?
Before diving into the conversion of 32/6, let's define what a mixed number is. A mixed number is a number that combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 2 ¾ is a mixed number; it represents two whole units and three-quarters of another unit. Mixed numbers are a convenient way to represent quantities that are greater than one but not a whole number. They offer a more intuitive representation than improper fractions, especially when dealing with real-world applications like measuring lengths or dividing quantities.
Converting an Improper Fraction to a Mixed Number
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. 32/6 is an example of an improper fraction. Converting an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains the same.
Let's apply this to 32/6:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: 32 ÷ 6 = 5 with a remainder of 2.
-
The quotient becomes the whole number: The quotient is 5, so the whole number part of our mixed number is 5.
-
The remainder becomes the new numerator: The remainder is 2, so this becomes the numerator of the fraction.
-
The denominator stays the same: The denominator remains 6.
Therefore, 32/6 as a mixed number is 5 ⅔.
Step-by-Step Guide: Converting 32/6 to a Mixed Number
To solidify your understanding, let's break down the conversion process into distinct steps:
Step 1: Identify the Numerator and Denominator
In the fraction 32/6, the numerator is 32 and the denominator is 6. This is crucial for performing the division.
Step 2: Perform the Division
Divide the numerator (32) by the denominator (6). You can use long division or a calculator. The result is 5 with a remainder of 2.
Step 3: Write the Whole Number
The quotient (the result of the division without the remainder) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the whole number is 5.
Step 4: Write the Fraction
The remainder (2) becomes the numerator of the fraction. The denominator remains the same (6). This gives us the fraction ⅔.
Step 5: Combine the Whole Number and the Fraction
Combine the whole number (5) and the fraction (⅔) to form the mixed number: 5 ⅔.
Visual Representation of 32/6
It can be helpful to visualize this conversion. Imagine you have 32 identical objects, and you want to group them into sets of 6. You'll be able to make 5 complete sets of 6, with 2 objects remaining. This visually represents the 5 whole units and the remaining ⅔.
Why is this Conversion Important?
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is important for several reasons:
-
Easier Understanding: Mixed numbers are generally easier to understand and visualize than improper fractions. It's easier to grasp the concept of "5 and two-thirds" than "thirty-two sixths."
-
Real-World Applications: Mixed numbers are frequently used in everyday life, particularly when dealing with measurements, quantities, and proportions. For example, measuring 5 ⅔ inches is more intuitive than measuring 32/6 inches.
-
Simplifying Calculations: In some calculations, using mixed numbers can simplify the process. Adding and subtracting mixed numbers can sometimes be more straightforward than working solely with improper fractions.
-
Foundation for Advanced Math: Understanding this conversion is crucial for tackling more complex mathematical concepts later on, including working with algebraic expressions and solving equations involving fractions.
Further Exploration: Simplifying Fractions
While 5 ⅔ is a perfectly valid mixed number representation of 32/6, it's important to note that the fractional part can sometimes be simplified. In this case, the fraction ⅔ is already in its simplest form because the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 2 and 6 is 2. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 2 gives us ⅔, which cannot be further simplified. However, if the fraction part were, for example, ⁴⁄₆, we could simplify it to ⅔ by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCD, which is 2. Always check if the fractional part of your mixed number can be simplified to its lowest terms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction?
A: Yes, absolutely. To convert a mixed number (like 5 ⅔) back into an improper fraction, you multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and keep the same denominator. In this example: (5 * 6) + 2 = 32, so the improper fraction would be 32/6.
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, if we had 30/6, the division would result in 5 with a remainder of 0. Therefore, 30/6 as a mixed number is simply 5.
Q: Are there other methods for converting improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: While the method described above (division) is the most common and straightforward, other methods may exist depending on the specific numbers involved. However, the division method provides a consistent and reliable approach for any improper fraction.
Q: Why is understanding improper and mixed numbers important in higher-level mathematics?
A: A firm grasp of this concept is crucial for advanced mathematical concepts like algebra, calculus, and other areas where manipulating fractions is fundamental. Being comfortable with conversions between improper fractions and mixed numbers significantly improves your ability to solve complex problems effectively.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 32/6 into its mixed number equivalent, 5 ⅔, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This guide provided a detailed, step-by-step approach, emphasizing the importance of understanding the underlying concepts. Mastering this conversion is not merely about solving a single problem; it’s about building a foundational understanding of fractions that will serve you well in more advanced mathematical studies and various real-world applications. Remember that the key is to understand the process of division and how the quotient and remainder translate into the whole number and fractional components of the mixed number. By practicing this conversion, you'll gain confidence and proficiency in working with fractions, making your mathematical journey smoother and more rewarding. Continue practicing with different improper fractions to further solidify your understanding and build fluency.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 32/6 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.