35/6 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
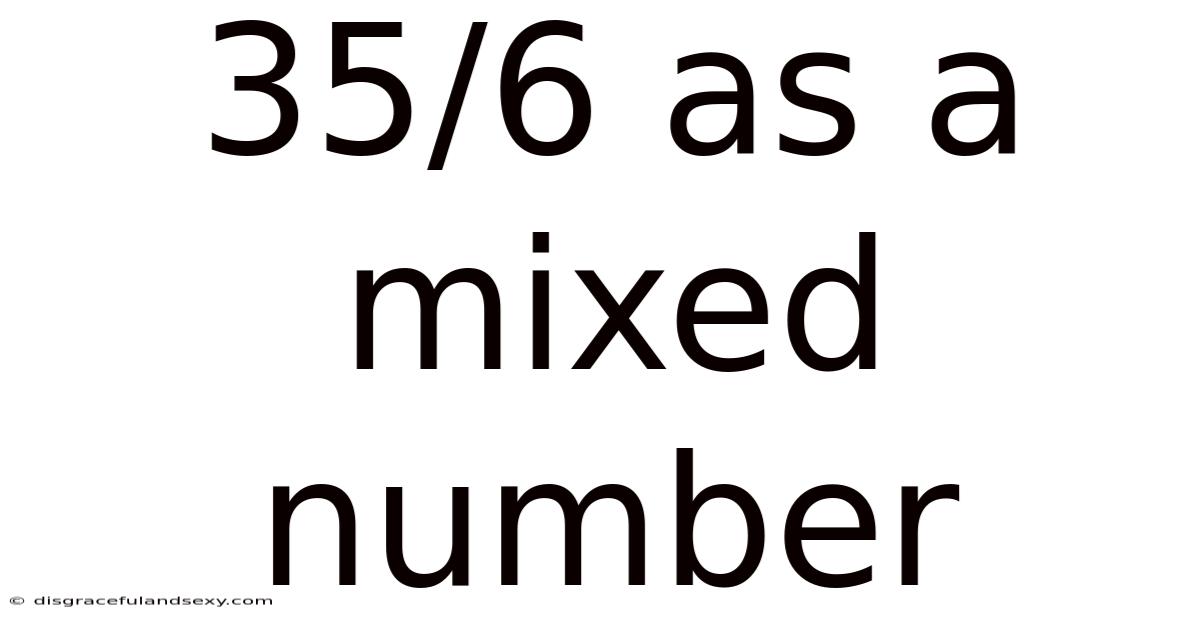
Table of Contents
Understanding 35/6 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Fractions can sometimes feel intimidating, but understanding them is crucial for navigating various aspects of math and everyday life. This article provides a comprehensive guide to converting the improper fraction 35/6 into a mixed number, explaining the process step-by-step, exploring the underlying mathematical principles, and addressing common questions. We'll delve into why this conversion is useful and how to apply this knowledge in practical scenarios.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (top number) is smaller than the denominator (bottom number), such as 1/2, 2/3, or 5/8. For example, 2 1/3 is a mixed number; it represents two whole units and one-third of another unit. Mixed numbers are a convenient way to represent quantities that are greater than one but not a whole number.
Converting 35/6 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Approach
The improper fraction 35/6 means that we have 35 parts, where each part represents 1/6 of a whole. To convert this to a mixed number, we need to determine how many whole units are contained within 35/6 and what fraction is left over. Here's the step-by-step process:
-
Divide the Numerator by the Denominator: We perform the division 35 ÷ 6.
-
Determine the Whole Number: The result of 35 ÷ 6 is 5 with a remainder of 5. The quotient (5) represents the whole number part of our mixed number.
-
Identify the Remainder: The remainder (5) becomes the numerator of the fractional part of our mixed number.
-
Retain the Original Denominator: The denominator of the fraction in the mixed number remains the same as the original fraction's denominator (6).
-
Combine the Whole Number and the Fraction: Putting it all together, we get the mixed number 5 5/6.
Therefore, 35/6 expressed as a mixed number is 5 5/6. This means that 35/6 represents five whole units and five-sixths of another unit.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 35 identical slices of pizza, where each slice represents 1/6 of a whole pizza. To visualize converting 35/6 to a mixed number, think of grouping these slices into whole pizzas. You can make 5 complete pizzas (5 x 6 = 30 slices), with 5 slices remaining. Those 5 remaining slices represent 5/6 of a pizza. This visual representation reinforces the concept of the mixed number 5 5/6.
The Importance of Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is valuable for several reasons:
-
Improved Understanding: Mixed numbers offer a more intuitive and readily understandable representation of quantities greater than one. They provide a clearer picture of the magnitude of the value.
-
Easier Calculations: In some mathematical operations, particularly addition and subtraction, mixed numbers can simplify calculations. For instance, adding 2 1/3 and 1 2/3 is easier than adding 7/3 and 5/3.
-
Real-World Applications: Mixed numbers are commonly used in everyday life, such as measuring ingredients in recipes (2 1/2 cups of flour), expressing lengths (3 3/4 inches), or representing time (1 1/2 hours).
Converting Mixed Numbers back to Improper Fractions
It's also important to understand the reverse process – converting a mixed number back into an improper fraction. This is often necessary when performing multiplication or division of fractions. The steps are as follows:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: In our example, 5 (whole number) x 6 (denominator) = 30.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result from step 1 to the numerator of the fraction: 30 + 5 (numerator) = 35.
-
Keep the same denominator: The denominator remains 6.
-
Form the improper fraction: The resulting improper fraction is 35/6.
This process demonstrates the equivalence between the mixed number 5 5/6 and the improper fraction 35/6.
Further Exploration: Working with Different Improper Fractions
The method described above applies universally to converting any improper fraction to a mixed number. Let's consider a few more examples:
-
17/4: Dividing 17 by 4 gives a quotient of 4 and a remainder of 1. Therefore, 17/4 = 4 1/4.
-
23/5: Dividing 23 by 5 gives a quotient of 4 and a remainder of 3. Therefore, 23/5 = 4 3/5.
-
31/7: Dividing 31 by 7 gives a quotient of 4 and a remainder of 3. Therefore, 31/7 = 4 3/7.
These examples highlight the consistent application of the division process to achieve the conversion.
Mathematical Principles Underlying the Conversion
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is fundamentally based on the concept of division and the relationship between whole numbers and fractions. The process essentially breaks down the larger quantity represented by the improper fraction into its whole number components and the remaining fractional part. The denominator remains consistent throughout the process because it represents the size of the fractional unit.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 12/3 = 4. There is no fractional part.
Q: Can I convert any fraction to a mixed number?
A: No, only improper fractions (where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator) can be converted to mixed numbers. Proper fractions (numerator smaller than the denominator) cannot be converted.
Q: Is there a shortcut method for this conversion?
A: While the long division method is most straightforward for understanding, with practice, you might develop a faster mental calculation approach. However, the core principle of division remains the same.
Q: Why is understanding this conversion important in advanced mathematics?
A: A firm grasp of fraction manipulation, including conversion between improper fractions and mixed numbers, is foundational for more advanced concepts like algebra, calculus, and other areas where working with rational numbers is prevalent.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 35/6 to a mixed number (5 5/6) is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding this process involves mastering division, recognizing the relationship between whole numbers and fractions, and appreciating the practical applications of mixed numbers in various contexts. By following the steps outlined, practicing with different examples, and understanding the underlying mathematical principles, you can confidently navigate fraction conversions and apply this knowledge to solve real-world problems. The ability to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers is a key building block for more advanced mathematical skills.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 35/6 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.