3x 2 10x 8 Factorise
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
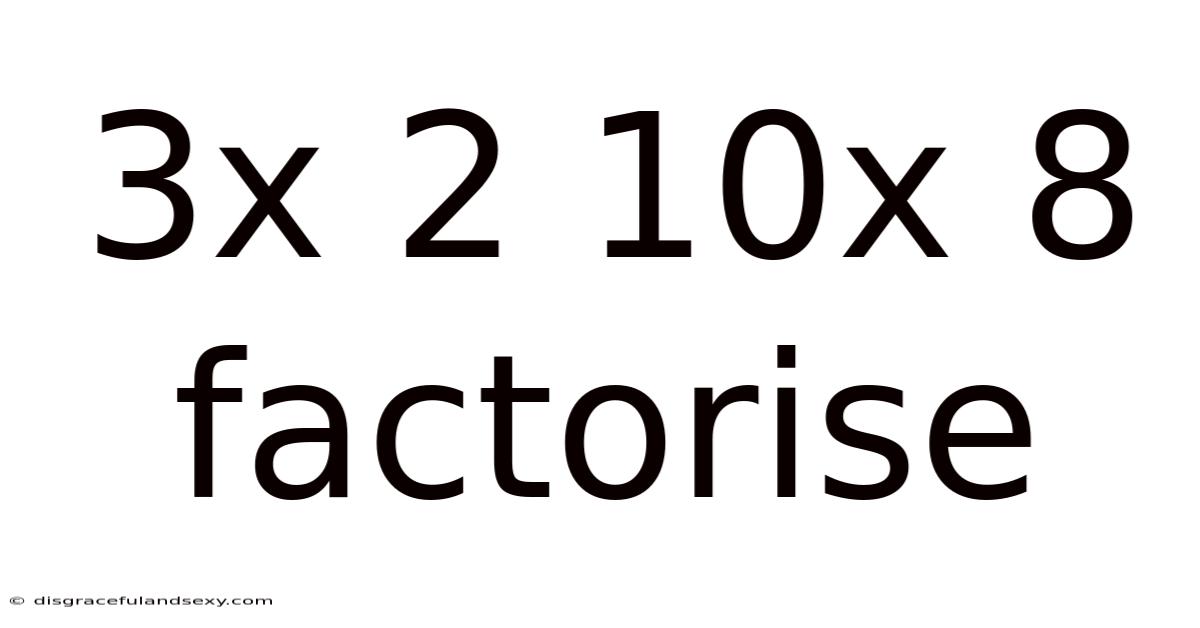
Table of Contents
Factoring Polynomials: A Deep Dive into 3x² + 10x + 8
Factoring polynomials is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to factoring the polynomial 3x² + 10x + 8, exploring various methods, explaining the underlying principles, and offering practice problems to solidify your understanding. We'll cover both the standard method and alternative approaches, making this a complete resource for learners of all levels.
Introduction: Understanding Polynomial Factoring
A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients, involving only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents. Factoring a polynomial means expressing it as a product of simpler polynomials. This process is the reverse of expanding brackets (or using the distributive property). For example, factoring (x + 2)(x + 3) gives the polynomial x² + 5x + 6. Our goal today is to reverse this process, starting with 3x² + 10x + 8 and finding its factored form.
This particular polynomial, 3x² + 10x + 8, is a quadratic trinomial – it has a degree of 2 (highest power of x is 2), and it contains three terms. Factoring quadratic trinomials often involves finding two binomials whose product results in the original trinomial.
Method 1: The AC Method (Standard Method)
This is the most common and widely applicable method for factoring quadratic trinomials of the form ax² + bx + c. Here's a step-by-step guide applied to 3x² + 10x + 8:
-
Identify a, b, and c: In our polynomial, a = 3, b = 10, and c = 8.
-
Find the product ac: ac = 3 * 8 = 24
-
Find two numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac: We need two numbers that add up to 10 (our 'b' value) and multiply to 24 (our 'ac' value). These numbers are 6 and 4 (6 + 4 = 10 and 6 * 4 = 24).
-
Rewrite the middle term: Rewrite the middle term (10x) using the two numbers we found: 3x² + 6x + 4x + 8
-
Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair:
3x(x + 2) + 4(x + 2)
-
Factor out the common binomial: Notice that both terms now share the common binomial (x + 2). Factor this out:
(x + 2)(3x + 4)
Therefore, the factored form of 3x² + 10x + 8 is (x + 2)(3x + 4).
Method 2: Trial and Error
This method is quicker if you're comfortable with mental multiplication and can quickly identify the correct binomial factors. It relies on understanding that the factored form will be of the type (px + q)(rx + s), where p, q, r, and s are integers.
-
Consider factors of the leading coefficient (a): The factors of 3 are 1 and 3. This means the first terms of our binomials will be 'x' and '3x' or '3x' and 'x'.
-
Consider factors of the constant term (c): The factors of 8 are 1 and 8, 2 and 4, 4 and 2, and 8 and 1.
-
Test combinations: We need to find a combination of factors that, when multiplied and added, give us the middle term (10x). Let's try some combinations:
- (x + 1)(3x + 8) expands to 3x² + 11x + 8 (Incorrect)
- (x + 2)(3x + 4) expands to 3x² + 10x + 8 (Correct!)
- (x + 4)(3x + 2) expands to 3x² + 14x + 8 (Incorrect)
By trial and error, we arrive at the same factored form: (x + 2)(3x + 4).
Method 3: Using the Quadratic Formula (Indirect Method)
While not a direct factoring method, the quadratic formula can help find the roots of the quadratic equation 3x² + 10x + 8 = 0. These roots can then be used to construct the factored form.
The quadratic formula is: x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Plugging in our values (a = 3, b = 10, c = 8):
x = [-10 ± √(10² - 4 * 3 * 8)] / (2 * 3) x = [-10 ± √(100 - 96)] / 6 x = [-10 ± √4] / 6 x = (-10 ± 2) / 6
This gives us two roots:
x₁ = (-10 + 2) / 6 = -8/6 = -4/3 x₂ = (-10 - 2) / 6 = -12/6 = -2
These roots can be used to construct the factored form:
a(x - x₁)(x - x₂) = 3(x + 4/3)(x + 2) = (3x + 4)(x + 2)
Again, we arrive at the same factored form: (x + 2)(3x + 4). This method is more useful when the factors are not easily discernible by inspection or by using the AC method.
A Deeper Look: The Significance of Factoring
Factoring polynomials is not merely a procedural exercise; it holds significant importance in various mathematical contexts:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring allows us to solve quadratic equations by setting each factor to zero and solving for x. For example, setting (x + 2)(3x + 4) = 0 leads to the solutions x = -2 and x = -4/3.
-
Simplifying Expressions: Factoring can significantly simplify complex algebraic expressions, making them easier to manipulate and analyze.
-
Finding Roots and x-intercepts: The roots (or zeros) of a polynomial are the values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero. These correspond to the x-intercepts of the graph of the polynomial. Factoring helps in easily identifying these roots.
-
Partial Fraction Decomposition: In calculus, factoring is essential for decomposing rational functions into simpler fractions, which simplifies integration processes.
-
Foundation for Advanced Topics: A strong understanding of factoring is a prerequisite for mastering more advanced algebraic concepts like polynomial division, solving higher-degree equations, and working with rational expressions.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you solidify your understanding of factoring quadratic trinomials:
- Factor 2x² + 7x + 3
- Factor 4x² - 4x - 3
- Factor 6x² - 13x + 6
- Factor x² + 5x - 6
- Factor 2x² - 5x - 12
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What if the polynomial cannot be factored easily?
- A: Some quadratic trinomials are prime meaning they cannot be factored using integer coefficients. In such cases, you might need to use the quadratic formula to find the roots or employ more advanced techniques.
-
Q: Is there only one way to factor a polynomial?
- A: The order of the factors might differ, but the factored form will essentially be the same. For example, (x + 2)(3x + 4) is equivalent to (3x + 4)(x + 2).
-
Q: What if the coefficient of x² is negative?
- A: It's often easier to factor out a -1 first, then proceed with the chosen method.
-
Q: How can I check if my factored form is correct?
- A: Simply expand the factored form using the distributive property. If you obtain the original polynomial, your factoring is correct.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Factoring
Factoring polynomials, specifically quadratic trinomials like 3x² + 10x + 8, is a vital skill in algebra. By understanding the various methods—the AC method, trial and error, and the indirect use of the quadratic formula—you equip yourself with the tools to tackle a wide range of problems. Remember that practice is key. The more you work through examples and practice problems, the more confident and efficient you'll become at factoring polynomials. The ability to factor is not just about solving equations; it’s about understanding the fundamental building blocks of algebra and laying a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. So keep practicing, and you’ll master this essential skill in no time!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3x 2 10x 8 Factorise . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.