3x 2 2x 3 0
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
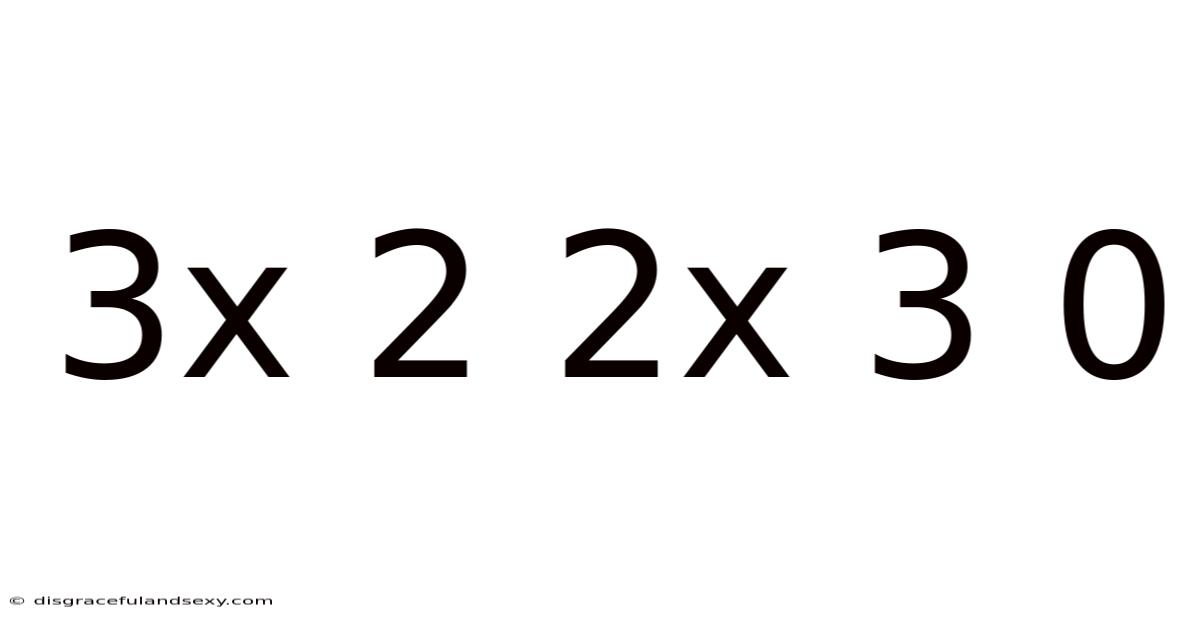
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: 3x2, 2x3, and the Significance of Zero
The seemingly simple equation, or rather, the series of expressions: 3 x 2, 2 x 3, and 0, might appear trivial at first glance. However, a deeper dive reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts, underlying principles, and even philosophical implications. This exploration will unpack the arithmetic, delve into the significance of zero, and consider the broader context of these seemingly simple numerical relationships. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for building a solid foundation in mathematics and appreciating its inherent beauty.
Introduction: The Basics of Multiplication
Before we delve into the intricacies of the provided expressions, let's establish a clear understanding of multiplication itself. Multiplication is fundamentally a repeated addition. For instance, 3 x 2 signifies adding the number 3 two times: 3 + 3 = 6. Similarly, 2 x 3 means adding the number 2 three times: 2 + 2 + 2 = 6. This seemingly simple concept forms the bedrock of numerous advanced mathematical operations and applications.
3 x 2 and 2 x 3: The Commutative Property
The expressions 3 x 2 and 2 x 3 both equal 6. This isn't a coincidence; it demonstrates a fundamental property of multiplication known as the commutative property. This property states that the order of the operands (the numbers being multiplied) does not affect the result. In simpler terms, you can switch the numbers around, and the answer remains the same: a x b = b x a. This seemingly simple principle is incredibly powerful and forms the basis for many algebraic manipulations and simplifications. Understanding the commutative property is crucial for solving more complex equations and working with abstract mathematical concepts.
The Significance of Zero: A Number Unlike Any Other
The inclusion of '0' in the given series introduces a unique element. Zero, unlike other numbers, represents the absence of quantity or magnitude. While seemingly straightforward, zero's significance extends far beyond simple counting. It plays a crucial role in defining many mathematical concepts:
-
Place Value: In our base-10 number system, zero acts as a placeholder, differentiating between numbers like 10, 100, and 1000. Without zero, we would lack a system for representing larger numbers effectively.
-
Additive Identity: Zero is the additive identity because adding zero to any number doesn't change the number's value (a + 0 = a). This property is crucial in various algebraic manipulations and solving equations.
-
Multiplicative Property: Zero also has a unique role in multiplication. Any number multiplied by zero results in zero (a x 0 = 0). This property, while simple, has significant implications in various mathematical fields.
-
Division by Zero: Division by zero is undefined. This is a crucial concept. It's not simply a matter of getting a very large or very small number; it's fundamentally impossible to divide by zero within the standard framework of arithmetic. This stems from the fact that division is the inverse operation of multiplication. If a/b = c, then a = b*c. If b were 0, then no matter what value c takes, a would always be 0, rendering the equation meaningless and impossible to solve. Attempting to divide by zero leads to inconsistencies and contradictions within the mathematical system.
Exploring the Implications: Beyond Basic Arithmetic
The simple expressions 3 x 2, 2 x 3, and 0 might seem like elementary school arithmetic, but they illuminate profound mathematical principles:
-
Abstraction: The numbers themselves are abstractions – they represent quantities but aren't the quantities themselves. This abstraction is fundamental to mathematics, allowing us to work with concepts beyond tangible objects.
-
Axiomatic Systems: Mathematics is built upon axioms – self-evident truths or assumptions. The commutative property and the properties of zero are examples of such axioms. These axioms form the foundation upon which more complex mathematical structures are built.
-
Consistency and Logic: The fact that these simple equations yield consistent and predictable results highlights the inherent consistency and logical structure of mathematics. This consistency is what makes mathematics a powerful tool for understanding the world around us.
The Role of Zero in Advanced Mathematics
Beyond basic arithmetic, zero plays a critical role in numerous advanced mathematical areas:
-
Calculus: Zero is central to concepts like limits and derivatives, which form the foundation of calculus. Understanding the behavior of functions as they approach zero is crucial for solving many problems in physics, engineering, and other fields.
-
Set Theory: In set theory, the empty set (a set containing no elements) is often represented by {} or Ø, essentially representing zero in a set context. Understanding the empty set is crucial for various aspects of set theory and its applications in computer science and other fields.
-
Number Systems: The development of zero significantly impacted our number systems, allowing for the representation of larger numbers and more complex mathematical operations. Different number systems (binary, hexadecimal, etc.) also rely on the concept of zero to distinguish between values.
-
Abstract Algebra: Zero's properties as the additive identity and the role it plays in various algebraic structures are deeply explored in abstract algebra. This branch of mathematics examines algebraic systems with axioms that generalize the properties of familiar number systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is division by zero undefined?
A: Division by zero is undefined because it leads to contradictions within the mathematical system. If we allow division by zero, it would violate fundamental rules of arithmetic and lead to inconsistencies in various mathematical operations.
Q: What is the significance of the commutative property?
A: The commutative property simplifies calculations and allows for flexibility in solving equations. It also plays a crucial role in higher-level mathematics, such as abstract algebra.
Q: Is zero a number or just a placeholder?
A: Zero is a number, and it's a very important one at that! While it acts as a placeholder in our number system, it also has specific mathematical properties, notably as the additive identity and its significant role in multiplication.
Q: How is zero used in real-world applications?
A: Zero is fundamental to countless real-world applications, from computer programming and scientific calculations to accounting and financial modeling. Its use is pervasive in modern society.
Conclusion: The Unassuming Power of Simplicity
The series 3 x 2, 2 x 3, and 0 might seem deceptively simple. However, a deeper exploration reveals the rich tapestry of mathematical concepts they represent. From the commutative property of multiplication to the unique significance of zero, each element unveils fundamental principles underlying the entire structure of mathematics. Understanding these seemingly basic ideas is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation and appreciating the power and beauty of this essential discipline. The seemingly simple expressions illustrate the elegance and power of mathematical abstraction and the critical role that seemingly simple concepts, like zero, play in shaping our understanding of the world. They remind us that even the most basic elements can hold profound significance when explored with curiosity and careful consideration.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3x 2 2x 3 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.