4 15 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 11, 2025 · 5 min read
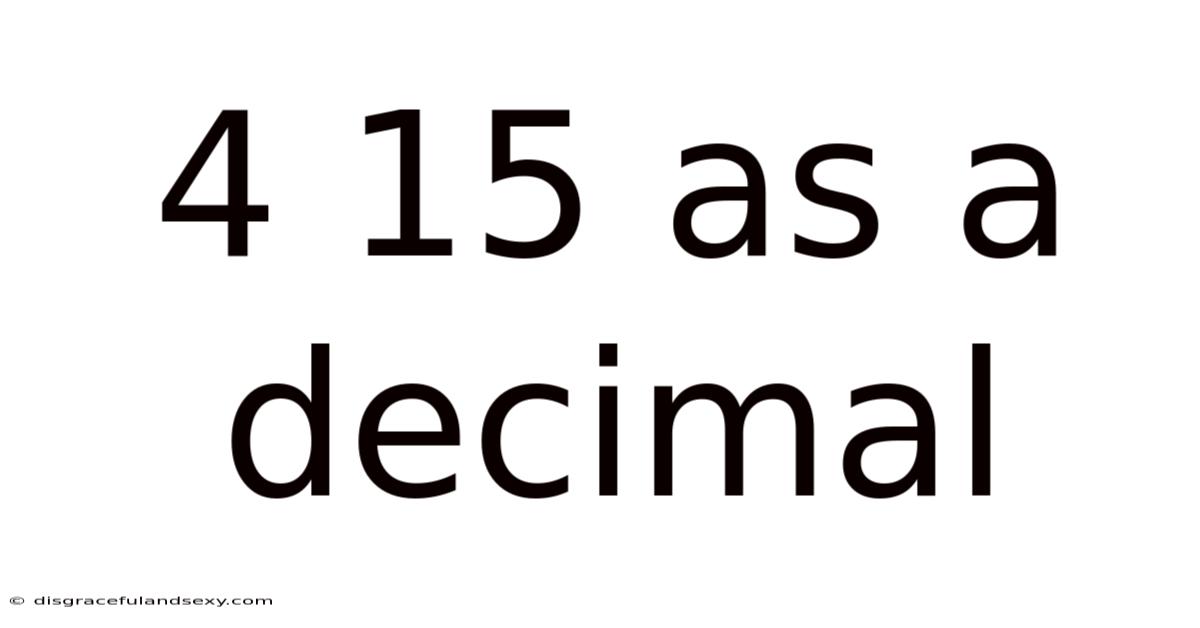
Table of Contents
4/15 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide to Fraction Conversion
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to advanced scientific computations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the conversion of the fraction 4/15 into its decimal equivalent, providing a step-by-step explanation, exploring different methods, and addressing common questions. We will also examine the underlying principles and explore the practical significance of such conversions.
Introduction: Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before diving into the conversion of 4/15, let's briefly review the concepts of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). A decimal is a way of expressing a number using a base-ten system, where digits to the right of the decimal point represent fractions with denominators of powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.).
The core concept behind converting fractions to decimals is to find an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10. This allows us to directly express the fraction as a decimal. However, not all fractions can be easily converted to a terminating decimal (a decimal that ends). Some fractions result in repeating decimals (decimals with a pattern of digits that repeat infinitely).
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting a fraction to a decimal is through long division. We divide the numerator (4) by the denominator (15).
-
Set up the division: Write 4 as the dividend and 15 as the divisor. Since 4 is smaller than 15, we add a decimal point to 4 and add zeros as needed.
-
Perform the division:
15 goes into 40 two times (2 x 15 = 30). Subtract 30 from 40, leaving a remainder of 10.
Bring down a zero. 15 goes into 100 six times (6 x 15 = 90). Subtract 90 from 100, leaving a remainder of 10.
Notice the remainder is 10 again. This indicates a repeating decimal.
-
Identify the repeating pattern: The remainder of 10 repeats, leading to a repeating pattern of 6 in the quotient.
-
Express the decimal: The decimal representation of 4/15 is 0.26666... This is often written as 0.26̅, where the bar indicates the repeating digit.
Method 2: Equivalent Fractions with Powers of 10
While long division is always reliable, some fractions can be more easily converted by finding an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). Unfortunately, 15 doesn't directly simplify to a power of 10. Its prime factorization is 3 x 5. To obtain a power of 10, we'd need factors of 2 and 5. Since we have a factor of 5 but not 2, we cannot use this method directly for 4/15. This highlights that long division is the more universally applicable approach for fraction-to-decimal conversions.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
Modern calculators provide a convenient way to convert fractions to decimals. Simply enter 4 ÷ 15 and the calculator will display the decimal equivalent: 0.266666... (or a similar representation depending on the calculator's precision). While calculators offer speed and efficiency, understanding the underlying mathematical principles remains crucial for a deeper comprehension.
The Significance of Repeating Decimals
The result, 0.26̅, is a repeating decimal. This means the digit 6 repeats infinitely. Not all fractions result in repeating decimals; some result in terminating decimals (decimals that end). Terminating decimals occur when the denominator of the fraction, in its simplest form, contains only factors of 2 and 5. Since 15 has a factor of 3, it results in a repeating decimal.
Practical Applications of Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
The ability to convert fractions to decimals is essential in many real-world scenarios:
- Financial Calculations: Dealing with percentages, interest rates, and discounts often involves converting fractions to decimals for accurate calculations.
- Measurement and Engineering: Precision in measurements and engineering designs frequently requires converting fractional units (e.g., inches) into decimal equivalents.
- Scientific Computations: Many scientific formulas and equations require decimal representations of fractions for accurate calculations.
- Data Analysis and Statistics: Converting fractions to decimals is crucial for various statistical analyses and data representations.
Understanding the Concept of Recurring Decimals
The recurring decimal 0.26̅ represents the infinite sum:
0.2 + 0.06 + 0.006 + 0.0006 + ...
This is a geometric series with a first term (a) of 0.06 and a common ratio (r) of 0.1. The sum of an infinite geometric series is given by the formula: S = a / (1 - r), provided |r| < 1. In this case:
S = 0.06 / (1 - 0.1) = 0.06 / 0.9 = 2/30 = 1/15
Adding the 0.2, we get 0.2 + 1/15 = 3/15 + 1/15 = 4/15
This demonstrates the equivalence between the fraction 4/15 and its decimal representation 0.26̅.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why does 4/15 result in a repeating decimal?
A1: Because the denominator 15, when simplified, contains factors other than 2 and 5 (it contains a factor of 3). Fractions with denominators containing only factors of 2 and 5 always result in terminating decimals.
Q2: How can I round a repeating decimal?
A2: Rounding depends on the desired level of precision. You can round to a specific number of decimal places (e.g., rounding 0.26̅ to 0.27). The context of the application determines the appropriate level of rounding.
Q3: Are there other methods to convert fractions to decimals besides long division?
A3: Yes, using a calculator is a common alternative. In certain cases, finding an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 is possible, but this isn't always feasible.
Q4: What is the difference between a terminating and a repeating decimal?
A4: A terminating decimal ends after a finite number of digits (e.g., 0.75). A repeating decimal continues indefinitely with a recurring pattern of digits (e.g., 0.333...).
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
Converting fractions to decimals is a valuable skill with widespread applications. Understanding the underlying principles, whether using long division, equivalent fractions, or a calculator, enhances mathematical proficiency. The conversion of 4/15 to its decimal equivalent, 0.26̅, showcases the concept of repeating decimals and their significance in various fields. Mastering this skill lays a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving. Remember to always consider the context and choose the most appropriate method and level of precision when working with decimals.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 15 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.