48/5 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
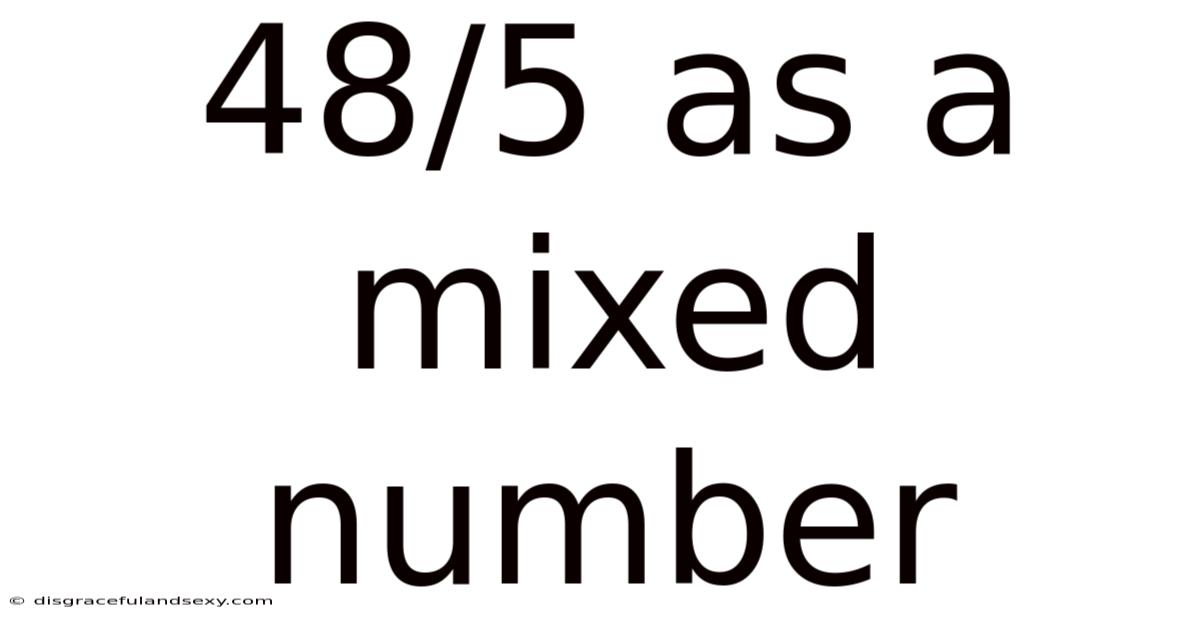
Table of Contents
Understanding 48/5 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting improper fractions, like 48/5, into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in arithmetic. This guide will walk you through the process of converting 48/5 into a mixed number, explaining the underlying concepts and providing examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore the practical applications of mixed numbers and answer frequently asked questions. This comprehensive approach ensures you not only learn how to do the conversion but also why it's important and how it works.
Introduction to Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before diving into the conversion of 48/5, let's clarify the terminology. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). Examples include 7/4, 11/3, and, of course, our focus today, 48/5. An improper fraction represents a value greater than or equal to one.
A mixed number, on the other hand, combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator smaller than its denominator (e.g., 3/4, 1/2, 2/5). Mixed numbers offer a more intuitive way to represent values greater than one, making them easier to visualize and understand in everyday contexts. For instance, 2 3/4 is clearer than 11/4, even though they represent the same quantity.
Converting 48/5 to a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion of an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, and the remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains the same.
Let's break down the conversion of 48/5:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: We divide 48 by 5.
48 ÷ 5 = 9 with a remainder of 3
-
Identify the whole number: The quotient (the result of the division) is 9. This becomes the whole number part of our mixed number.
-
Identify the numerator of the fraction: The remainder is 3. This becomes the numerator of the fractional part of our mixed number.
-
Retain the denominator: The denominator remains the same as the original improper fraction, which is 5.
-
Combine the whole number and the fraction: Combining the whole number and the fraction, we get the mixed number: 9 3/5
Therefore, 48/5 expressed as a mixed number is 9 3/5.
Visual Representation: Understanding the Concept
Imagine you have 48 cookies, and you want to divide them equally among 5 friends. Each friend would receive 9 cookies (45 cookies in total: 45/5 = 9). You would have 3 cookies left over (48 - 45 = 3). So each friend gets 9 whole cookies, and there are 3 cookies remaining. This perfectly illustrates the mixed number 9 3/5. The whole number (9) represents the whole number of cookies each friend receives, while the fraction (3/5) represents the leftover cookies.
The Importance of Mixed Numbers in Everyday Life
Mixed numbers are frequently used in various everyday situations:
-
Measurement: When measuring lengths, weights, or volumes, mixed numbers are commonly used. For example, a piece of wood might be 5 1/2 feet long, or a recipe might call for 2 1/4 cups of flour.
-
Time: Time is often expressed using mixed numbers. For instance, you might say a movie lasted 1 hour and 45 minutes, which can be represented as 1 3/4 hours (since there are 60 minutes in an hour, and 45 minutes is 3/4 of an hour).
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes frequently require fractional amounts of ingredients, and often these are presented as mixed numbers for easy understanding.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in construction and engineering, making mixed numbers an essential tool for calculations and plans.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand how to convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction. This is done using the following steps:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: In our example, 9 (whole number) * 5 (denominator) = 45.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result from step 1 to the numerator: 45 + 3 (numerator) = 48.
-
Retain the denominator: The denominator remains unchanged: 5.
-
Combine into a fraction: This gives us the improper fraction: 48/5. This confirms our earlier conversion.
Further Examples: Practice Makes Perfect
Let's solidify our understanding with a few more examples:
-
Convert 27/4 to a mixed number: 27 ÷ 4 = 6 with a remainder of 3. Therefore, 27/4 = 6 3/4.
-
Convert 35/6 to a mixed number: 35 ÷ 6 = 5 with a remainder of 5. Therefore, 35/6 = 5 5/6.
-
Convert 100/7 to a mixed number: 100 ÷ 7 = 14 with a remainder of 2. Therefore, 100/7 = 14 2/7.
These examples showcase the consistent application of the division process to convert improper fractions into mixed numbers.
Mathematical Explanation: Why This Works
The method of dividing the numerator by the denominator to convert an improper fraction to a mixed number is based on the fundamental concept of division and remainders. The division represents how many times the denominator goes into the numerator completely (the whole number). The remainder represents the portion that is left over, forming the fractional part.
This method is consistent with the principles of fraction arithmetic and provides a systematic approach to expressing a value greater than one in a more easily interpretable format.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if the remainder is zero after division?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 20/5 = 4. There's no fractional part.
Q: Can I convert any improper fraction to a mixed number?
A: Yes, any improper fraction can be converted to a mixed number using the described method.
Q: Are there different methods to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: While the division method is the most common and straightforward, alternative methods might involve using visual aids or manipulatives for better understanding, especially for younger learners. However, the fundamental principle remains the same: dividing the numerator by the denominator.
Q: Why is it important to learn this conversion?
A: This conversion skill is essential for simplifying mathematical expressions, solving problems involving measurements, and comprehending values represented in a mixed number format. It lays the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion of Improper Fractions
Converting improper fractions like 48/5 to mixed numbers (9 3/5) is a crucial skill with practical applications across various aspects of life. This guide has provided a step-by-step approach, illustrated the concept with visual examples, and explored the mathematical rationale behind the conversion process. By understanding both the 'how' and the 'why', you'll not only master the conversion but also appreciate its importance in daily life and advanced mathematical studies. Remember that practice is key to solidifying this fundamental mathematical skill. Continue working through examples, and you will become proficient in converting improper fractions to mixed numbers effortlessly.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 48/5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.