4x 2 X 1 0
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
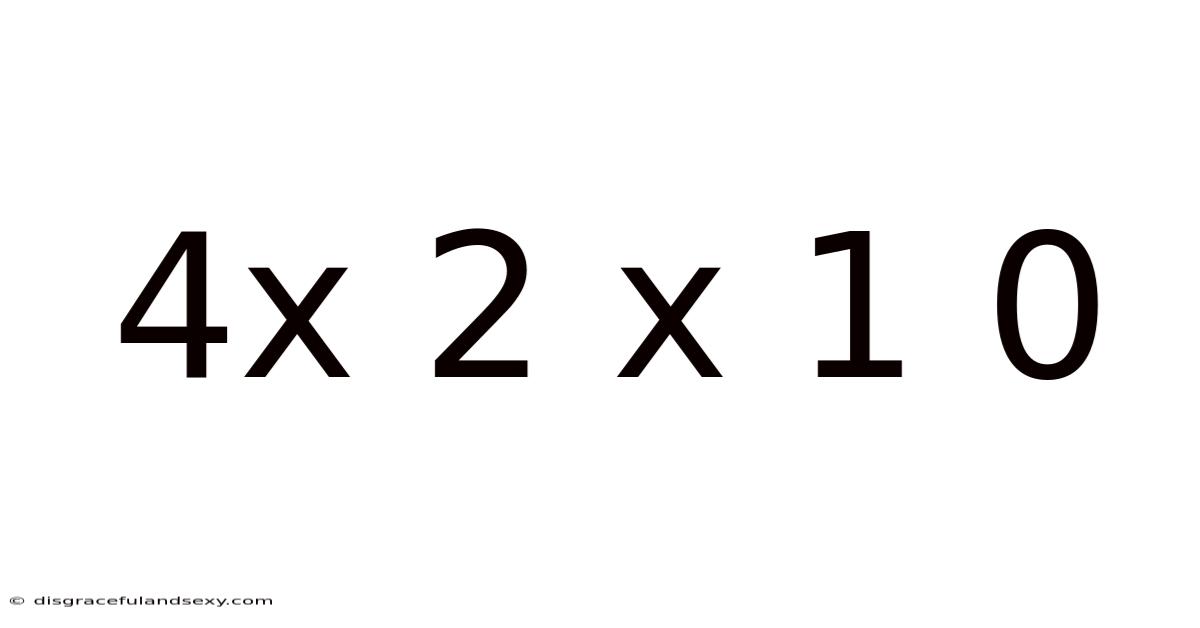
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery of 4 x 2 x 1 x 0: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and the Zero Property
This article explores the seemingly simple yet profoundly important mathematical concept illustrated by the expression 4 x 2 x 1 x 0. We'll unravel the mystery behind this equation, delve into the fundamental principles of multiplication, particularly the role of zero, and illuminate its implications across various mathematical fields. Understanding this seemingly basic equation is crucial for building a strong foundation in arithmetic and higher-level mathematics.
Introduction: Understanding the Fundamentals of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, represents repeated addition. When we say 4 x 2, we're essentially adding four twos together: 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8. This simple concept forms the bedrock of more complex calculations. The numbers involved in multiplication are known as factors, and the result is called the product. In our example, 4 and 2 are the factors, and 8 is the product.
This understanding helps us visualize multiplication, especially when dealing with small numbers. However, as we progress to larger numbers and more complex equations, a deeper understanding of the underlying principles becomes essential. This is particularly true when zero is involved.
The Zero Property of Multiplication: The Key to Understanding 4 x 2 x 1 x 0
The crucial element in the expression 4 x 2 x 1 x 0 is the presence of zero. The Zero Property of Multiplication states that any number multiplied by zero equals zero. This seemingly simple rule has profound consequences for all mathematical operations. Let's break down why this is the case:
-
Visual Representation: Imagine you have four groups of two apples each. That's 4 x 2 = 8 apples. Now, imagine you have four groups, but each group contains zero apples. No matter how many groups you have, you still have zero apples in total. This visually demonstrates the principle: 4 x 0 = 0.
-
Repeated Addition Perspective: Recall that multiplication is repeated addition. If we consider 4 x 0, we're adding four zeros together: 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 0. The result is inevitably zero.
-
Mathematical Proof (Abstract Approach): A more formal mathematical proof would involve using the distributive property and axioms of arithmetic. While beyond the scope of this introductory explanation, the essence remains consistent: the product will always be zero when any factor is zero.
Step-by-Step Calculation of 4 x 2 x 1 x 0
Now, let's tackle the equation 4 x 2 x 1 x 0 systematically:
-
Step 1: 4 x 2 = 8: We begin by multiplying the first two factors, 4 and 2.
-
Step 2: 8 x 1 = 8: Next, we multiply the result (8) by the third factor, 1. Multiplying by 1 leaves the number unchanged (the multiplicative identity).
-
Step 3: 8 x 0 = 0: Finally, we multiply the result (8) by the last factor, 0. According to the Zero Property of Multiplication, any number multiplied by zero equals zero. Therefore, the final product is 0.
Therefore, the solution to 4 x 2 x 1 x 0 is 0.
The Significance of the Zero Property in Larger Contexts
The Zero Property of Multiplication isn't just a simple rule; it's a fundamental concept that underpins many advanced mathematical concepts. Here are some examples:
-
Algebra: In algebraic equations, the Zero Property is frequently used to solve for unknown variables. For instance, if you have the equation 5x = 0, you know immediately that x must be 0.
-
Calculus: In calculus, the concept of limits often involves approaching zero, and the Zero Property plays a crucial role in evaluating these limits.
-
Linear Algebra: In linear algebra, the zero vector (a vector with all components equal to zero) has significant properties stemming directly from the Zero Property of Multiplication.
-
Probability and Statistics: In probability, the probability of an impossible event is defined as zero. This ties directly into multiplicative properties when considering the probabilities of multiple independent events.
-
Computer Science: In computer programming, the Zero Property is foundational in Boolean logic and conditional statements, where a zero often represents a false condition.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions surround the Zero Property of Multiplication. Let's address some of them:
-
"Multiplication always makes things bigger": This is incorrect. While multiplying by numbers greater than 1 generally increases the magnitude, multiplying by numbers between 0 and 1 results in a smaller product, and multiplying by 0 always results in 0.
-
Ignoring Zero: Students might sometimes overlook the zero in a multiplication problem, leading to an incorrect answer. It's crucial to remember that even a single zero factor will always yield a zero product.
-
Confusion with Addition: Students might confuse the Zero Property of Multiplication with the Zero Property of Addition (adding zero doesn't change the value). While related, they are distinct properties applicable to different operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What happens if there are multiple zeros in a multiplication problem?
A1: The result will still be zero. Regardless of the number of other factors, the presence of even one zero will make the entire product zero. For example, 5 x 10 x 0 x 20 x 100 = 0.
Q2: Is there any exception to the Zero Property of Multiplication?
A2: No, there are no exceptions to the Zero Property of Multiplication within the standard number systems (real numbers, complex numbers, etc.). It's a fundamental and universally accepted mathematical principle.
Q3: How can I explain the Zero Property to a younger child?
A3: Use visual aids like toys or candies. Explain that if you have several groups of items, but each group is empty (zero items), then you have zero items in total.
Q4: Why is the Zero Property important in real-world applications?
A4: It's crucial in many areas, including finance (calculating zero balances), engineering (checking for null values in calculations), and computer programming (handling conditions where a value might be absent or equal to zero).
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of a Simple Equation
The seemingly simple equation 4 x 2 x 1 x 0 = 0 embodies a fundamental principle that is far-reaching in its implications. Understanding the Zero Property of Multiplication is not just about solving a single equation; it's about grasping a foundational concept that underpins much of mathematics and its applications across various fields. This deep understanding allows for more confident problem-solving, stronger analytical skills, and a more robust foundation for future mathematical exploration. The seemingly simple act of multiplying by zero carries immense weight in the world of numbers, reinforcing the power and elegance of mathematical principles. Remember this core principle: the presence of zero as a factor guarantees a product of zero, a rule that remains steadfast and essential across all mathematical domains.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4x 2 X 1 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.