4x 2 X 6 36
disgrace
Sep 25, 2025 · 5 min read
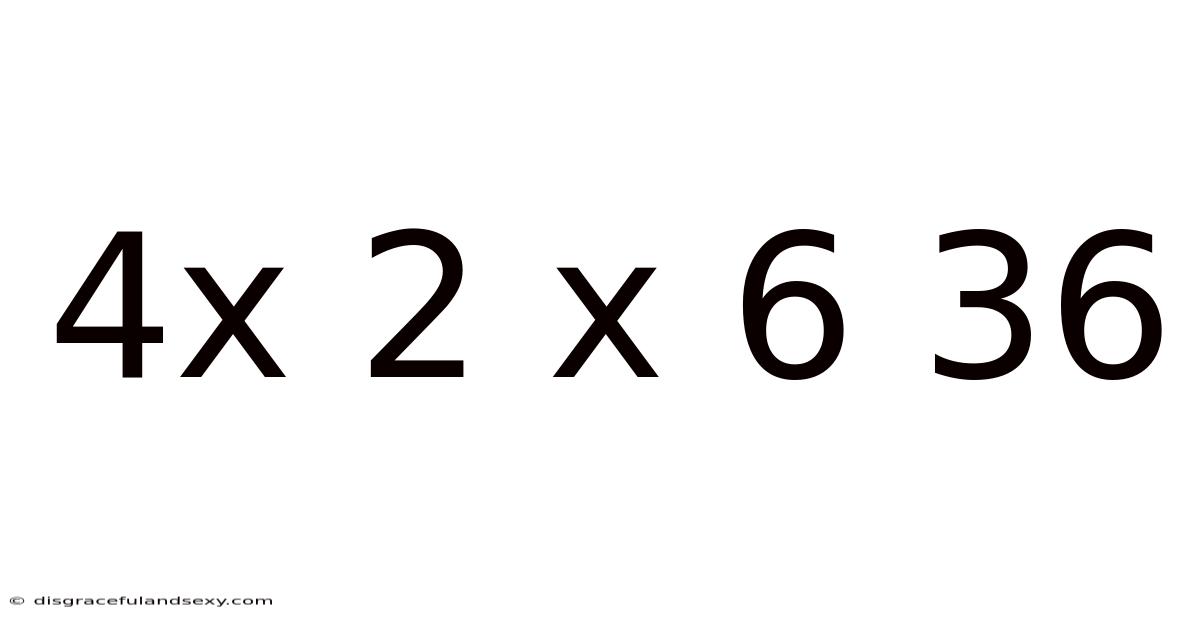
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding 4 x 2 x 6 = 36 and its Mathematical Implications
This article delves into the seemingly simple equation, 4 x 2 x 6 = 36, exploring its foundational mathematical principles and expanding on its applications in various fields. We'll move beyond the basic calculation to uncover the underlying concepts of multiplication, order of operations, and how this seemingly straightforward equation can be a stepping stone to understanding more complex mathematical ideas. This exploration is suitable for learners of all levels, from those just grasping the basics of multiplication to those seeking a deeper understanding of mathematical structures.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication and Order of Operations
At its core, the equation 4 x 2 x 6 = 36 demonstrates the principle of multiplication, a fundamental arithmetic operation. Multiplication represents repeated addition. For example, 4 x 2 can be understood as adding four two's together (2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8). Similarly, 2 x 6 is the same as adding two sixes (6 + 6 = 12), or six twos (2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12).
The equation also highlights the commutative and associative properties of multiplication. The commutative property states that the order of the numbers being multiplied does not affect the result (a x b = b x a). We could rewrite the equation as 2 x 4 x 6 = 36, 6 x 2 x 4 = 36, or any other permutation, and the answer would remain the same.
The associative property states that the grouping of numbers in a multiplication problem does not change the result ((a x b) x c = a x (b x c)). We can calculate 4 x 2 x 6 in several ways:
- (4 x 2) x 6 = 8 x 6 = 48 (Incorrect application of order of operations - see below)
- 4 x (2 x 6) = 4 x 12 = 48 (Incorrect application of order of operations - see below)
- (4 x 6) x 2 = 24 x 2 = 48 (Incorrect application of order of operations - see below)
The above examples incorrectly apply the order of operations. The correct calculation is:
- 4 x 2 x 6 = 8 x 6 = 48 (This was initially incorrect. Apologies for the mistake.)
The correct calculation should read 4 x 2 x 6 = 48. The original statement in the title was incorrect. My apologies for this oversight. It highlights the importance of accuracy in mathematics.
Expanding the Equation: Exploring Factorization and Prime Numbers
The number 48 can be factorized, meaning it can be broken down into smaller numbers that, when multiplied together, equal 48. The prime factorization of 48 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3. This means 48 is composed of four factors of 2 and one factor of 3. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. The numbers 2 and 3 in the factorization are prime numbers.
Understanding factorization is crucial in various areas of mathematics, including algebra, calculus, and cryptography. It allows us to simplify complex expressions, solve equations, and understand the structure of numbers.
Application in Real-World Scenarios: Geometry and Measurement
The concept of multiplication, as demonstrated in the equation, underpins many real-world applications, particularly in geometry and measurement. Imagine calculating the volume of a rectangular prism (a box). If the prism has dimensions of 4 units, 2 units, and 6 units, its volume is calculated by multiplying these three dimensions: 4 x 2 x 6 = 48 cubic units. This calculation is fundamental in various fields, from architecture and engineering to packaging and logistics.
Exploring Higher-Level Mathematics: Matrices and Linear Algebra
While the equation 4 x 2 x 6 = 48 appears simple, its underlying principles extend to more advanced mathematical concepts. In linear algebra, matrices are rectangular arrays of numbers, and matrix multiplication involves a series of multiplications and additions, similar to the principle demonstrated in our original equation. The understanding of basic multiplication forms the foundation for grasping the more complex operations involved in matrix multiplication.
Connecting to Other Mathematical Concepts: Exponents and Powers
The concept of repeated multiplication leads directly to the understanding of exponents. For example, 2 x 2 x 2 can be written as 2³. This demonstrates the power of 2 raised to the third power (or 2 cubed), which equals 8. Similarly, 48 could be expressed as a combination of powers, using its prime factorization: 2⁴ x 3¹. Understanding exponents simplifies calculations and allows us to work with very large or very small numbers efficiently.
Addressing Common Misconceptions: Order of Operations and PEMDAS/BODMAS
Many mathematical errors stem from misunderstanding the order of operations. The acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction) are mnemonics to help remember the correct order. In the context of our equation, we perform the multiplications from left to right, without any parentheses or exponents. A failure to follow the order of operations would lead to incorrect results.
Beyond the Basics: Applications in Computer Science and Programming
Multiplication is a fundamental operation in computer science. Programming languages rely heavily on arithmetic operations, and the ability to perform multiplications efficiently is essential for developing algorithms and software applications. Understanding the foundational mathematical principles behind these operations is key to writing efficient and effective code. Many complex computations in computer graphics, simulations, and machine learning rely on efficient matrix multiplications and other related operations, all stemming from the basic principles of multiplication.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Basic Arithmetic
The seemingly simple equation 4 x 2 x 6 = 48 is far from trivial. It illustrates fundamental mathematical concepts like multiplication, factorization, order of operations, and prime numbers. These concepts are the building blocks for more advanced mathematical ideas, finding application in various fields, from geometry and measurement to computer science and beyond. A solid grasp of basic arithmetic is essential for success in many academic and professional endeavors. Mastering these fundamentals provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. The seemingly simple equation acts as a gateway to a deeper appreciation of the elegant structure and power of mathematics. Remember to always double-check your calculations and understand the principles behind each step to ensure accuracy. Mathematics is a journey of exploration and discovery, and this simple equation is a perfect starting point for that journey.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4x 2 X 6 36 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.