4x2 + 12x + 9
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
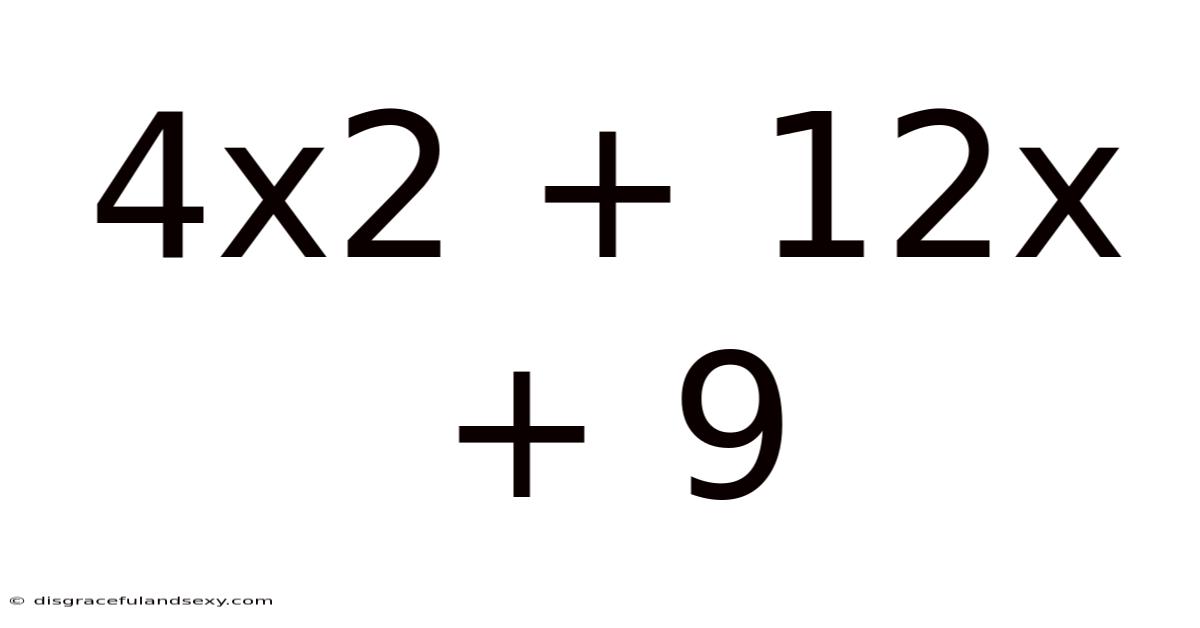
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into the Quadratic Expression 4x² + 12x + 9
This article explores the quadratic expression 4x² + 12x + 9, examining its properties, methods of solving it, and its applications in various mathematical contexts. Understanding this seemingly simple expression provides a solid foundation for grasping more complex algebraic concepts. We'll cover everything from factoring and the quadratic formula to its graphical representation and real-world applications. Prepare to delve into the fascinating world of quadratics!
Introduction: Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. Our focus, 4x² + 12x + 9, perfectly fits this mold, with a = 4, b = 12, and c = 9. Understanding quadratic expressions is crucial in algebra, calculus, and various branches of physics and engineering.
Method 1: Factoring the Quadratic Expression
Factoring is a powerful technique to simplify and solve quadratic expressions. It involves rewriting the expression as a product of two or more simpler expressions. The goal is to find two binomials whose product equals the original quadratic. For 4x² + 12x + 9, we look for two numbers that add up to 12 (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 36 (the product of a and c, 4 * 9). These numbers are 6 and 6. Therefore, we can factor the expression as follows:
4x² + 12x + 9 = (2x + 3)(2x + 3) = (2x + 3)²
This reveals that 4x² + 12x + 9 is a perfect square trinomial, meaning it's the square of a binomial. This simplifies many subsequent calculations and analyses.
Why is factoring important? Factoring allows us to find the roots or zeros of the quadratic equation (when set equal to zero). The roots are the values of x that make the equation true. In this case, setting (2x + 3)² = 0, we find that the only root is x = -3/2. This means the parabola represented by the quadratic equation touches the x-axis at only one point.
Method 2: Using the Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal method for solving quadratic equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Plugging in the values from our expression (a = 4, b = 12, c = 9), we get:
x = [-12 ± √(12² - 4 * 4 * 9)] / (2 * 4) x = [-12 ± √(144 - 144)] / 8 x = [-12 ± √0] / 8 x = -12 / 8 x = -3/2
This confirms our earlier finding that the only root is x = -3/2. The quadratic formula is particularly useful when factoring is difficult or impossible.
The Discriminant: Unveiling the Nature of the Roots
The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula, b² - 4ac, is called the discriminant. It provides valuable information about the nature of the roots of the quadratic equation:
- If the discriminant is positive (b² - 4ac > 0): The quadratic equation has two distinct real roots. The parabola intersects the x-axis at two different points.
- If the discriminant is zero (b² - 4ac = 0): The quadratic equation has one real root (a repeated root). The parabola touches the x-axis at exactly one point, as we saw with our example.
- If the discriminant is negative (b² - 4ac < 0): The quadratic equation has no real roots. The parabola does not intersect the x-axis. The roots are complex numbers (involving the imaginary unit i).
In our case, the discriminant is 0, indicating a single real root.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Quadratic
The quadratic expression 4x² + 12x + 9 represents a parabola. Since the coefficient of x² (a = 4) is positive, the parabola opens upwards. The vertex of the parabola, which is the lowest point, can be found using the formula:
x = -b / 2a = -12 / (2 * 4) = -3/2
Substituting this value of x back into the original expression gives the y-coordinate of the vertex:
y = 4(-3/2)² + 12(-3/2) + 9 = 0
Therefore, the vertex of the parabola is at (-3/2, 0). This confirms that the parabola touches the x-axis at only one point, which is the vertex itself.
Applications of Quadratic Expressions
Quadratic equations and expressions appear frequently in various fields:
- Physics: Calculating projectile motion, analyzing the trajectory of objects under gravity.
- Engineering: Designing bridges, parabolic antennas, and other structures.
- Economics: Modeling cost functions, revenue functions, and profit maximization.
- Computer Graphics: Creating curves and shapes.
Completing the Square: Another Approach to Solving
Completing the square is an algebraic technique used to rewrite a quadratic expression in a form that reveals its vertex more easily. The process involves manipulating the expression to create a perfect square trinomial. For 4x² + 12x + 9:
- Factor out the coefficient of x² from the x² and x terms: 4(x² + 3x) + 9
- Take half of the coefficient of x (3), square it (9/4), and add and subtract it inside the parentheses: 4(x² + 3x + 9/4 - 9/4) + 9
- Rewrite the perfect square trinomial: 4((x + 3/2)² - 9/4) + 9
- Simplify: 4(x + 3/2)² - 9 + 9 = 4(x + 3/2)²
This shows that the vertex form of the quadratic is 4(x + 3/2)², which clearly indicates the vertex at (-3/2, 0).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between a quadratic expression and a quadratic equation?
- A: A quadratic expression is simply a polynomial of degree two (e.g., 4x² + 12x + 9). A quadratic equation is a quadratic expression set equal to zero (e.g., 4x² + 12x + 9 = 0).
-
Q: Can a quadratic equation have more than two roots?
- A: No, a quadratic equation can have at most two roots (real or complex).
-
Q: What is the significance of the vertex of a parabola?
- A: The vertex represents the minimum or maximum value of the quadratic function. In our case, it represents the minimum value (since the parabola opens upwards).
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of 4x² + 12x + 9
This comprehensive exploration of 4x² + 12x + 9 has demonstrated various methods for analyzing and solving this seemingly simple quadratic expression. From factoring and the quadratic formula to completing the square and graphical representation, we've uncovered its fundamental properties and highlighted its significance within a broader mathematical context. Understanding quadratic expressions is a cornerstone of algebraic proficiency, paving the way for tackling more complex mathematical challenges in various fields of study and application. Remember, the journey of learning is continuous, and mastering fundamental concepts like this opens doors to a world of exciting mathematical discoveries.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4x2 + 12x + 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.