5 2 In Simplest Form
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
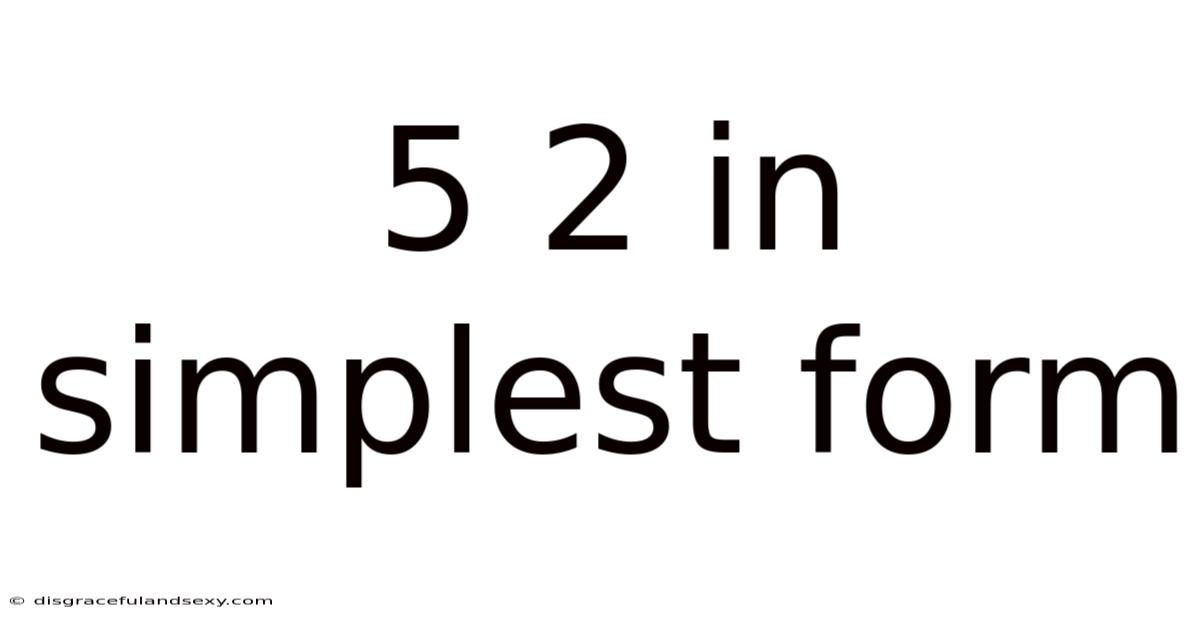
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Simplicity of 5/2: A Deep Dive into Fractions
Fractions, those seemingly simple numerical expressions, often hold a surprising depth of mathematical meaning. Understanding fractions is fundamental to grasping more advanced mathematical concepts. This article delves into the seemingly straightforward fraction 5/2, exploring its simplest form, various representations, and applications within different mathematical contexts. We'll uncover why understanding fractions like 5/2 is crucial for success in mathematics and beyond. Let's embark on this journey to demystify this fundamental building block of arithmetic.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Refresher
Before we dissect 5/2, let's briefly revisit the core components of a fraction. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key elements:
- Numerator: The top number (in 5/2, it's 5). It indicates how many parts we have.
- Denominator: The bottom number (in 5/2, it's 2). It indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
Therefore, 5/2 signifies that we have 5 parts of a whole that's been divided into 2 equal parts.
5/2 in its Simplest Form: Irreducible Fractions
The simplest form of a fraction, also known as an irreducible fraction, is when the numerator and denominator share no common factors other than 1. This means the fraction cannot be simplified further by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
Is 5/2 in its simplest form? Let's analyze.
The factors of 5 are 1 and 5. The factors of 2 are 1 and 2.
The only common factor between 5 and 2 is 1. Therefore, 5/2 is already in its simplest form. We cannot reduce it any further.
Representing 5/2: Multiple Perspectives
While 5/2 is in its simplest fractional form, it can be represented in several other ways:
-
Improper Fraction: 5/2 is an improper fraction because the numerator (5) is larger than the denominator (2). Improper fractions represent values greater than 1.
-
Mixed Number: We can convert 5/2 into a mixed number, which combines a whole number and a proper fraction. To do this, we perform division: 5 divided by 2 is 2 with a remainder of 1. Therefore, 5/2 is equal to 2 1/2. This means we have two whole units and one-half of another unit.
-
Decimal: We can also express 5/2 as a decimal. Dividing 5 by 2 gives us 2.5.
-
Percentage: To convert 5/2 to a percentage, we first express it as a decimal (2.5) and then multiply by 100: 2.5 * 100 = 250%. This means 5/2 represents 250% of a whole.
Illustrating 5/2: Visual Representations
Visual aids are incredibly helpful in understanding fractions. Imagine a pizza cut into two equal slices. 5/2 represents having two whole pizzas and an additional half-pizza. This visual representation reinforces the concept of the mixed number 2 1/2. Similarly, using bars or shapes divided into two parts can effectively illustrate this fraction.
Applications of 5/2 in Real-World Scenarios
The fraction 5/2, or its equivalents (2.5, 2 1/2, 250%), appears frequently in everyday situations:
-
Measurement: Imagine measuring ingredients for a recipe. If a recipe calls for 2.5 cups of flour, it's essentially 5/2 cups.
-
Money: If you have $2.50, that's equivalent to 5/2 dollars.
-
Time: 2.5 hours is the same as 5/2 hours – or 2 hours and 30 minutes.
-
Geometry: Calculations involving lengths, areas, or volumes often involve fractions like 5/2.
Mathematical Operations with 5/2
Understanding how to perform mathematical operations with 5/2 is crucial. Let's examine some examples:
-
Addition: To add 5/2 and another fraction (e.g., 3/4), we need a common denominator. The least common multiple of 2 and 4 is 4. Therefore, we rewrite 5/2 as 10/4 and add it to 3/4: 10/4 + 3/4 = 13/4.
-
Subtraction: Subtracting fractions follows a similar approach, requiring a common denominator.
-
Multiplication: Multiplying fractions is straightforward: (5/2) * (3/4) = (53) / (24) = 15/8.
-
Division: Dividing fractions involves inverting the second fraction and multiplying: (5/2) / (3/4) = (5/2) * (4/3) = 20/6 = 10/3.
Beyond the Basics: 5/2 in Advanced Mathematics
While seemingly simple, 5/2 finds applications in more advanced mathematical contexts:
-
Algebra: Solving algebraic equations might involve fractions like 5/2 as coefficients or constants.
-
Calculus: Derivatives and integrals frequently involve fractional coefficients.
-
Linear Algebra: Matrices and vectors can include fractional components, including 5/2.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can 5/2 be expressed as a whole number?
A: No, 5/2 represents a value between two whole numbers (2 and 3). It's an improper fraction, resulting in a mixed number (2 1/2) or a decimal (2.5).
Q: What is the reciprocal of 5/2?
A: The reciprocal of a fraction is obtained by switching the numerator and the denominator. Therefore, the reciprocal of 5/2 is 2/5.
Q: How do I convert 5/2 to a percentage?
A: Convert 5/2 to a decimal (2.5) and then multiply by 100%. This results in 250%.
Q: Why is understanding fractions important?
A: Fractions are foundational to arithmetic and form the basis for understanding more complex mathematical concepts in algebra, geometry, calculus, and beyond. They're essential for various real-world applications, from cooking to finance.
Conclusion: Mastering the Simplicity of 5/2
The seemingly simple fraction 5/2 offers a rich landscape of mathematical exploration. By understanding its simplest form, multiple representations, and applications in various mathematical contexts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the fundamentals of arithmetic. Mastering fractions like 5/2 is not just about memorizing procedures; it's about developing a strong foundation that will empower you to confidently tackle more complex mathematical challenges. The ability to seamlessly translate between fractions, mixed numbers, decimals, and percentages is a valuable skill that transcends the confines of the classroom and extends to practical applications in everyday life. So embrace the power of fractions – the journey of understanding them is a rewarding one.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 2 In Simplest Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.