5 2 N 1 2n
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
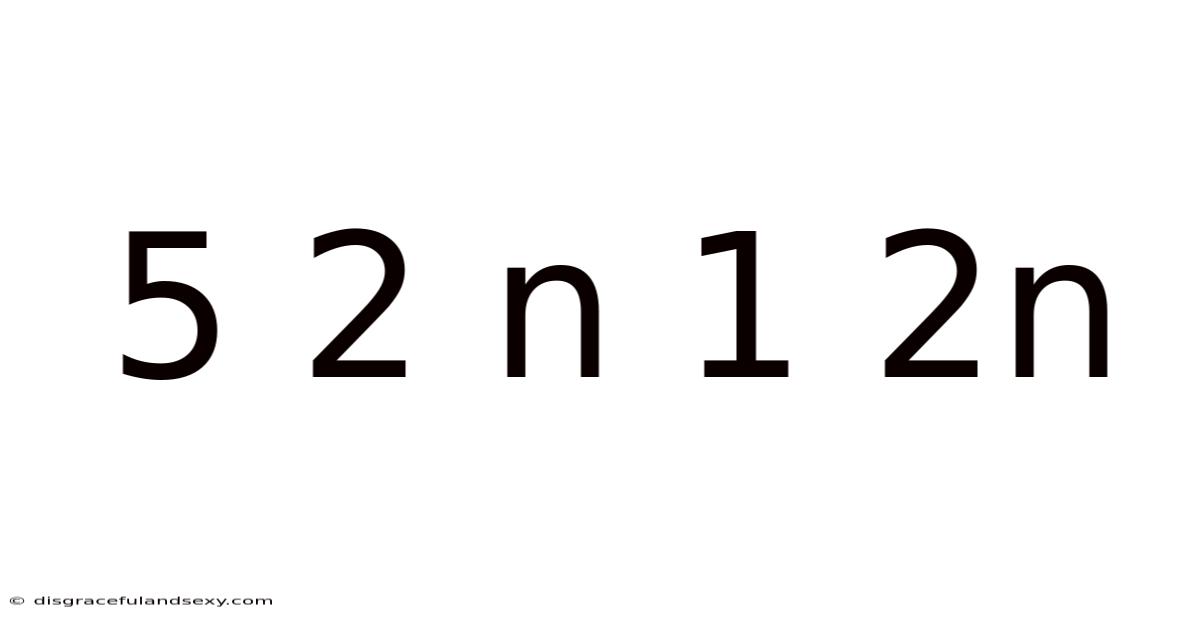
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery of 5, 2, n, 1, 2n: A Deep Dive into Sequence, Series, and Pattern Recognition
This article delves into the intriguing sequence 5, 2, n, 1, 2n, exploring its potential patterns, underlying mathematical principles, and possible solutions for the unknown variable 'n'. We'll uncover the logic behind the sequence, examining various approaches to pattern recognition and demonstrating how mathematical reasoning can unlock the secrets hidden within seemingly random numbers. This exploration will be particularly beneficial for students learning about sequences, series, and problem-solving in mathematics.
Understanding Sequences and Series
Before we tackle the specific sequence 5, 2, n, 1, 2n, let's establish a foundational understanding of sequences and series. A sequence is simply an ordered list of numbers, often following a specific rule or pattern. Examples include arithmetic sequences (where the difference between consecutive terms is constant) and geometric sequences (where the ratio between consecutive terms is constant). A series is the sum of the terms in a sequence.
Our challenge lies in identifying the pattern within the sequence 5, 2, n, 1, 2n. Since we don't have a readily apparent arithmetic or geometric progression, we must explore other potential relationships between the terms. This often involves looking for differences between consecutive terms, ratios between terms, or even more complex relationships.
Approaches to Solving for 'n'
There's no single definitive solution for 'n' without additional context or information. The sequence is intentionally ambiguous, designed to challenge our pattern recognition skills. Let's explore several potential approaches and reasoning paths:
1. Difference Analysis:
Let's examine the differences between consecutive terms:
- 5 - 2 = 3
- 2 - n = 2 - n
- n - 1 = n - 1
- 1 - 2n = 1 - 2n
This approach doesn't immediately reveal a consistent pattern. The differences themselves form a new sequence (3, 2-n, n-1, 1-2n), which is not readily interpretable.
2. Ratio Analysis:
Similar to the difference analysis, let's examine the ratios between consecutive terms:
- 5/2 = 2.5
- 2/n = 2/n
- n/1 = n
- 1/(2n) = 1/(2n)
Again, no clear pattern emerges from the ratios. The resulting sequence of ratios (2.5, 2/n, n, 1/(2n)) doesn't suggest a simple mathematical relationship.
3. Exploring Quadratic Relationships:
It's possible that the relationship between terms is not linear but quadratic or even higher order. We might explore fitting a quadratic equation to the known terms (5, 2, 1) to predict the value of 'n' and 2n. However, this requires making assumptions and might not yield a unique solution. The validity of such an approach depends heavily on the underlying pattern, which remains undefined.
4. Considering Alternate Number Systems or Transformations:
We could explore whether the sequence might be meaningful in a different number system (e.g., binary, hexadecimal) or if some mathematical transformation (e.g., logarithmic, exponential) applied to the terms would reveal a pattern. This avenue requires a strong intuition and familiarity with various mathematical concepts.
5. The Role of Context:
The most crucial aspect often overlooked is the context surrounding the sequence. Where did this sequence originate? Is it part of a larger problem or puzzle? Knowing the source or context can provide invaluable clues to understanding its underlying logic. The sequence might represent a coded message, a specific mathematical property, or a step in a more extensive process. Without context, the solutions remain speculative.
Illustrative Example: Introducing a Hypothetical Context
Let's imagine a scenario where the sequence represents the number of steps in a recursive algorithm. Each term (5, 2, n, 1, 2n) represents the number of computational steps at each iteration. If we assume a pattern where the number of steps decreases and then increases, we might speculate:
- Iteration 1: 5 steps
- Iteration 2: 2 steps
- Iteration 3: n steps (potentially a smaller number, like 1)
- Iteration 4: 1 step (minimum number of steps)
- Iteration 5: 2n steps (an increase from the previous step).
In this hypothetical context, a reasonable assumption might be that n = 1. This would create a sequence: 5, 2, 1, 1, 2. The pattern is now more apparent, showing a decrease followed by a minimum and then an increase. This exemplifies the importance of context in solving such problems.
Advanced Techniques: Generating Functions and Recurrence Relations
For more complex sequences, advanced mathematical tools can be employed. Generating functions, for instance, can provide a compact representation of a sequence, enabling us to analyze its properties more efficiently. Alternatively, a recurrence relation might exist, defining each term as a function of preceding terms. However, these approaches require a good understanding of advanced mathematical concepts and are often not necessary for simpler sequences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there only one solution for 'n'?
A: No, without additional information or context, there isn't a unique solution for 'n'. The sequence is underdetermined; several values for 'n' could potentially fit, depending on the underlying, yet unknown, pattern or relationship between the numbers.
Q: What if the sequence continues beyond 2n?
A: The continuation of the sequence would provide more data points, potentially allowing for a clearer identification of the pattern and a more definitive solution for 'n'. More data leads to better pattern recognition.
Q: Are there any online tools that can help solve this type of problem?
A: While some online tools can identify patterns in simple sequences, the ambiguity of this sequence makes it challenging for such tools. The focus should be on understanding the underlying mathematical principles rather than relying solely on computational assistance.
Conclusion
The sequence 5, 2, n, 1, 2n serves as a valuable exercise in pattern recognition and problem-solving. It highlights the importance of considering various approaches, such as difference and ratio analysis, as well as exploring the potential for more complex relationships or the impact of context. While a unique solution for 'n' remains elusive without further information, this exploration underscores the critical thinking skills needed in mathematics and the creative approaches needed to decode seemingly random numerical arrangements. The ambiguity of this sequence is its strength; it teaches us the value of thorough investigation and the limits of relying solely on algorithmic solutions. The solution, if it exists, is intrinsically linked to the unspoken context and the hidden rules that govern its generation. The journey of exploring this sequence is, therefore, more insightful than arriving at a definitive numerical answer.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 2 N 1 2n . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.