5 6 Divided By 8
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
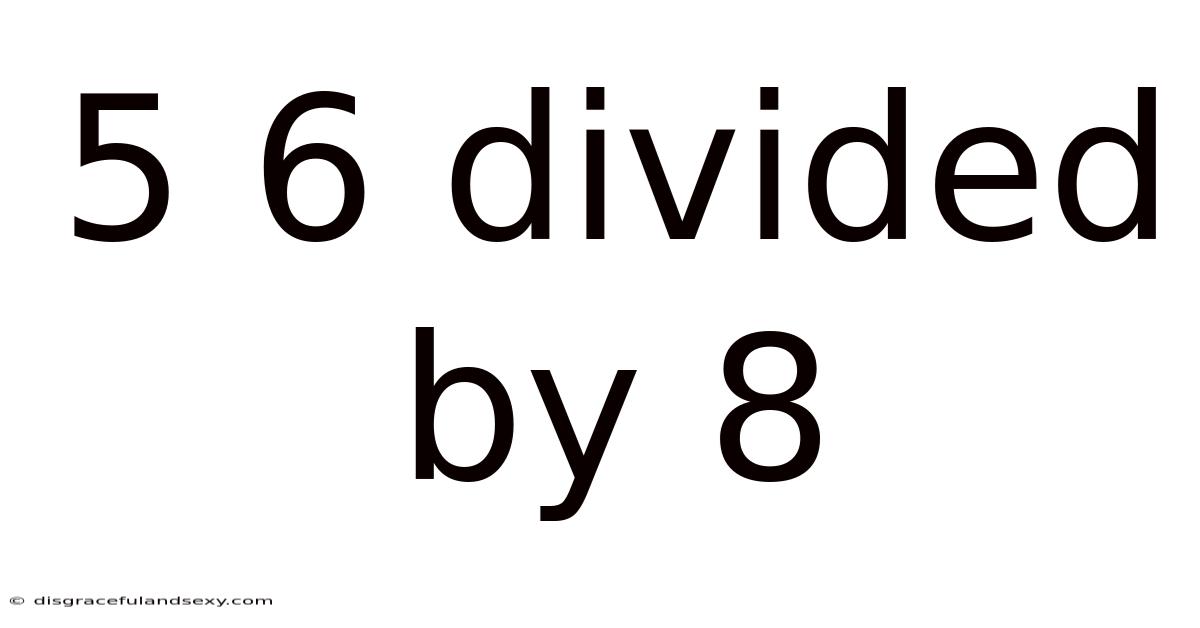
Table of Contents
Deconstructing Division: A Deep Dive into 5 6/8
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical problem of dividing 5 6/8. While the initial calculation might appear straightforward, delving deeper reveals opportunities to understand fundamental concepts in fractions, mixed numbers, and division, making it an excellent learning experience for students and adults alike. We'll break down the process step-by-step, explore different approaches, and discuss the underlying mathematical principles involved. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear, concise, and engaging explanation, suitable for various learning levels.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before tackling the division problem, let's review the components of the mixed number 5 6/8. A mixed number combines a whole number (5) and a proper fraction (6/8). A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than the denominator (bottom number). Conversely, an improper fraction has a numerator equal to or greater than the denominator.
To perform division effectively, it's often easier to convert the mixed number into an improper fraction. This is done by multiplying the whole number by the denominator and adding the numerator, then placing the result over the original denominator.
In our example:
5 6/8 = (5 * 8 + 6) / 8 = (40 + 6) / 8 = 46/8
Now we have an improper fraction representing the same quantity as the mixed number. This form is generally more convenient for division operations.
Method 1: Dividing the Improper Fraction
Our problem is now 46/8 divided by 8. When dividing fractions, we can rewrite the problem as multiplication by the reciprocal of the divisor. The reciprocal of a number is simply 1 divided by that number. The reciprocal of 8 (or 8/1) is 1/8.
Therefore, our problem becomes:
46/8 ÷ 8 = 46/8 * 1/8 = 46/64
This fraction can be simplified by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and the denominator. The GCD of 46 and 64 is 2. Dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2 gives us:
46/64 = 23/32
Therefore, 5 6/8 divided by 8 is equal to 23/32.
Method 2: Dividing the Whole Number and Fraction Separately
Alternatively, we can approach the problem by dividing the whole number and fractional parts separately. This method provides a different perspective on the process and can be helpful for understanding the underlying mechanics.
First, divide the whole number:
5 ÷ 8 = 5/8
Next, divide the fractional part:
6/8 ÷ 8 = 6/8 * 1/8 = 6/64 = 3/32
Now, add the results together:
5/8 + 3/32 = (5 * 4)/32 + 3/32 = 20/32 + 3/32 = 23/32
Again, we arrive at the same result: 23/32. This method emphasizes that division can be applied to each component of a mixed number.
Method 3: Converting to Decimals
Another approach involves converting the mixed number into a decimal and then performing the division.
First, convert 5 6/8 to a decimal:
6/8 = 0.75
5 6/8 = 5 + 0.75 = 5.75
Now, divide by 8:
5.75 ÷ 8 = 0.71875
This decimal representation offers another way to express the answer. Note that this is an equivalent result to 23/32, but represented in a different format. The choice of fraction or decimal often depends on the context of the problem.
Illustrative Examples and Applications
The principles illustrated by dividing 5 6/8 have broad applications in various real-world scenarios. Consider these examples:
-
Sharing Resources: Imagine you have 5 6/8 pizzas to share equally among 8 people. Each person would receive 23/32 of a pizza.
-
Measuring Ingredients: In baking, you might need to divide a quantity of an ingredient, expressed as a mixed number, by a specific factor.
-
Calculating Averages: In statistical analysis, you may encounter the need to divide a quantity expressed as a mixed number to calculate an average.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use a calculator for this type of problem?
A: Yes, most calculators can handle mixed numbers and fractions. However, understanding the underlying process is crucial for developing a strong foundation in mathematics. Using a calculator without understanding the principles defeats the educational purpose.
Q: Why is simplifying the fraction important?
A: Simplifying a fraction reduces it to its lowest terms, making it easier to understand and work with. It provides a more concise and efficient representation of the quantity.
Q: What if the divisor wasn't a whole number, but another fraction or mixed number?
A: The same principles apply. You would convert all mixed numbers into improper fractions and then multiply by the reciprocal of the divisor.
Q: Are there other methods for solving this type of division problem?
A: While the methods described above are the most common and straightforward, other approaches exist, especially for more complex fractions. Long division methods can also be applied after converting to decimals.
Conclusion
Dividing 5 6/8 by 8, though seemingly simple at first glance, offers a rich learning opportunity. By exploring different methods – converting to an improper fraction, dividing whole and fractional parts separately, or converting to decimals – we reinforce fundamental concepts in fractions, mixed numbers, and division. The process of simplification highlights the importance of concise mathematical representation. This comprehensive explanation aims to not only provide the answer but also to foster a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles and their practical applications in various contexts. The ability to confidently tackle such problems builds a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember, the key to mastering mathematics lies in understanding the why behind the how.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 6 Divided By 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.