5x 2 22x 8 Factor
disgrace
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
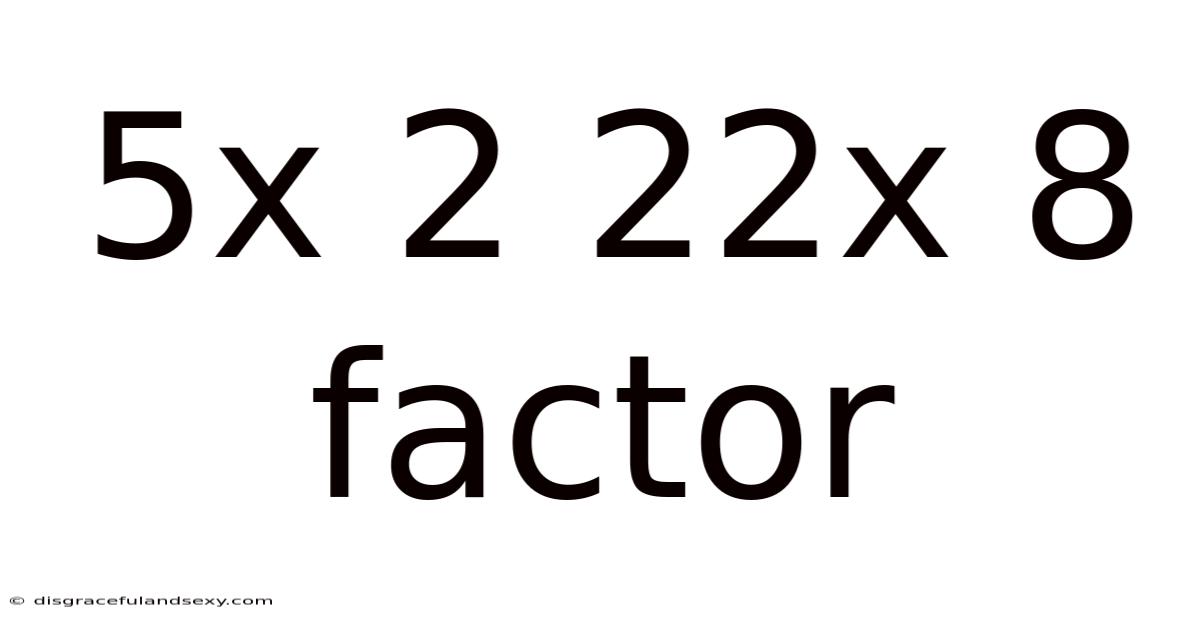
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries: A Deep Dive into the Factors of 5 x 2 and 22 x 8
Understanding factors is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various calculations and problem-solving scenarios. This article will thoroughly explore the factors of 5 x 2 and 22 x 8, providing a step-by-step breakdown, scientific explanations, and frequently asked questions to solidify your comprehension. We'll move beyond simple calculations to understand the underlying principles and their broader mathematical implications.
Introduction: What are Factors?
Before we dive into the specifics of 5 x 2 and 22 x 8, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. In mathematics, a factor is a number that divides another number completely without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly. Finding factors is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding the fundamental building blocks of numbers.
1. Analyzing the Factors of 5 x 2 = 10
Let's begin with the simpler multiplication: 5 x 2 = 10. To find the factors of 10, we need to identify all the numbers that divide 10 without leaving a remainder. We can systematically approach this:
- 1: 10 divided by 1 equals 10.
- 2: 10 divided by 2 equals 5.
- 5: 10 divided by 5 equals 2.
- 10: 10 divided by 10 equals 1.
Therefore, the factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10. Notice that the factors always come in pairs (except for perfect squares, where the square root is paired with itself).
2. Analyzing the Factors of 22 x 8 = 176
Now, let's tackle the slightly more complex multiplication: 22 x 8 = 176. Finding the factors of 176 requires a more methodical approach. One way is to systematically check each number starting from 1:
- 1: 176 divided by 1 equals 176.
- 2: 176 divided by 2 equals 88.
- 4: 176 divided by 4 equals 44.
- 8: 176 divided by 8 equals 22.
- 11: 176 divided by 11 equals 16.
- 16: 176 divided by 16 equals 11.
- 22: 176 divided by 22 equals 8.
- 44: 176 divided by 44 equals 4.
- 88: 176 divided by 88 equals 2.
- 176: 176 divided by 176 equals 1.
Therefore, the factors of 176 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 11, 16, 22, 44, 88, and 176.
A Deeper Dive: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a powerful technique to find all the factors of a number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization expresses a number as the product of its prime factors.
Let's apply prime factorization to both numbers:
1. Prime Factorization of 10:
10 can be expressed as 2 x 5. Both 2 and 5 are prime numbers. This means the prime factorization of 10 is 2 x 5.
2. Prime Factorization of 176:
The prime factorization of 176 is a bit more involved:
- 176 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2: 176 = 2 x 88
- 88 is also divisible by 2: 88 = 2 x 44
- 44 is divisible by 2: 44 = 2 x 22
- 22 is divisible by 2: 22 = 2 x 11
- 11 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 176 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 11, or 2⁴ x 11.
Knowing the prime factorization allows us to easily find all the factors. We can combine the prime factors in various ways to generate all possible factors. For example, for 176:
- 2¹ = 2
- 2² = 4
- 2³ = 8
- 2⁴ = 16
- 11¹ = 11
- 2¹ x 11¹ = 22
- 2² x 11¹ = 44
- 2³ x 11¹ = 88
- 2⁴ x 11¹ = 176
And so on... This systematic approach ensures we don't miss any factors.
Mathematical Significance and Applications
Understanding factors has far-reaching implications in various mathematical areas:
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): Finding the GCF of two or more numbers helps in simplifying fractions and solving algebraic problems. The GCF is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more given numbers. This concept is crucial when working with fractions and solving problems involving cyclical events.
-
Algebra: Factoring algebraic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, enabling us to solve equations and simplify complex expressions. The principles of factoring numbers directly translate to factoring algebraic terms.
-
Number Theory: Factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. Concepts like prime factorization and the distribution of prime numbers are crucial research areas in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between a factor and a multiple?
A factor divides a number completely, while a multiple is a number obtained by multiplying a given number by another integer. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48, and so on.
Q2: How can I easily find the factors of larger numbers?
For larger numbers, systematic approaches like prime factorization or using factor trees are more efficient than trial and error. Online calculators and software can also assist with finding factors of very large numbers.
Q3: Are there any tricks to quickly identify if a number is divisible by certain factors?
Yes, there are divisibility rules:
- Divisibility by 2: Even numbers are divisible by 2.
- Divisibility by 3: If the sum of the digits is divisible by 3, the number is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: Numbers ending in 0 or 5 are divisible by 5.
- Divisibility by 10: Numbers ending in 0 are divisible by 10.
- Divisibility by 11: Alternately add and subtract digits. If the result is divisible by 11, the number is divisible by 11.
Q4: Why is prime factorization important?
Prime factorization provides a unique representation of a number, revealing its fundamental building blocks. This is crucial for many advanced mathematical concepts and algorithms.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
Understanding factors is not just about performing calculations; it's about grasping the fundamental structure of numbers. This article has provided a comprehensive exploration of the factors of 5 x 2 and 22 x 8, delving into prime factorization and highlighting the broader mathematical significance of this concept. By mastering these fundamental principles, you build a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical studies and problem-solving skills. Remember, practice is key! The more you work with numbers and their factors, the more intuitive and efficient your understanding will become.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5x 2 22x 8 Factor . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.