6 25 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
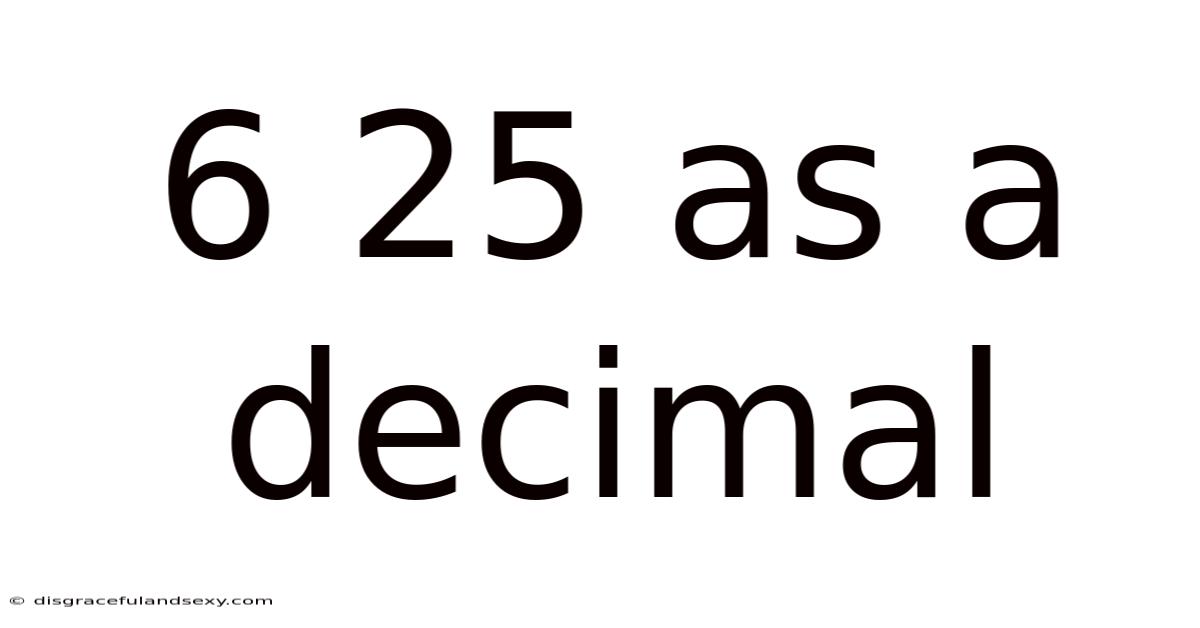
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mystery: 6 25 as a Decimal
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to advanced scientific computations. This article delves into the conversion of the mixed number 6 25 to its decimal equivalent, explaining the process step-by-step, exploring the underlying mathematical principles, and answering frequently asked questions. By the end, you'll not only know the decimal representation of 6 25 but also grasp the broader concept of fraction-to-decimal conversion.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before jumping into the conversion, let's briefly review the terminology. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 6 25. This represents 6 whole units plus an additional 25 of a unit. The fraction 25 itself consists of a numerator (2) and a denominator (5). The denominator indicates how many equal parts a whole unit is divided into, while the numerator specifies how many of those parts are considered.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal, Then Adding the Whole Number
This is arguably the most straightforward method. We'll first convert the fractional part (25) into a decimal and then add the whole number (6).
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
To convert the fraction 25 to a decimal, we simply perform the division: 2 ÷ 5.
2 ÷ 5 = 0.4
Step 2: Add the Whole Number
Now, add the whole number part (6) to the decimal equivalent of the fraction (0.4):
6 + 0.4 = 6.4
Therefore, 6 25 as a decimal is 6.4.
Method 2: Converting the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction, Then to a Decimal
This method involves an extra step but provides a deeper understanding of the relationship between fractions and decimals.
Step 1: Convert the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction
An improper fraction has a numerator larger than or equal to its denominator. To convert 6 25 to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number (6) by the denominator (5): 6 x 5 = 30
- Add the numerator (2) to the result: 30 + 2 = 32
- Keep the same denominator (5): The improper fraction is 325
Step 2: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Now, divide the numerator (32) by the denominator (5):
32 ÷ 5 = 6.4
Again, we arrive at the decimal equivalent of 6.4.
The Underlying Mathematical Principle: Division as the Core Operation
The core principle behind converting any fraction to a decimal is division. The fraction bar (/) signifies division. Whether you're working with a simple fraction like 12 or a more complex mixed number like 6 25, the process always involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. This division represents the process of splitting the whole into equal parts and determining the quantity of those parts represented by the fraction. The decimal representation then provides a convenient alternative way to express that quantity.
Extending the Concept: Converting Other Fractions to Decimals
The methods described above can be applied to convert any fraction, whether proper or improper, to its decimal equivalent. For instance:
- 1/4: 1 ÷ 4 = 0.25
- 3/8: 3 ÷ 8 = 0.375
- 7/2: 7 ÷ 2 = 3.5
- 11/5: 11 ÷ 5 = 2.2
The process remains consistent: divide the numerator by the denominator. If the division results in a remainder that continues indefinitely (e.g., 1/3 = 0.333...), the decimal is called a repeating decimal, often represented with a bar over the repeating digits (0.3̅).
Dealing with Terminating and Repeating Decimals
When converting fractions to decimals, you might encounter two types of decimal representations:
-
Terminating Decimals: These decimals have a finite number of digits after the decimal point (e.g., 0.25, 0.375, 6.4). These often result from fractions where the denominator can be expressed as a power of 10 (e.g., 25 = 10/4) or where the denominator's only prime factors are 2 and/or 5.
-
Repeating Decimals: These decimals have an infinite number of digits after the decimal point, with a pattern of digits that repeats indefinitely (e.g., 1/3 = 0.3̅, 1/7 = 0.142857̅). These typically occur when the denominator contains prime factors other than 2 and 5.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversions
Converting fractions to decimals is essential in numerous real-world situations:
- Finance: Calculating interest, discounts, and percentages.
- Engineering: Measuring dimensions and tolerances.
- Science: Recording experimental data and performing calculations.
- Everyday life: Dividing quantities, calculating tips, and understanding proportions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the fraction is already a decimal?
A1: If the fraction is already expressed as a decimal (e.g., 0.75), no conversion is necessary.
Q2: Can I use a calculator for these conversions?
A2: Absolutely! Calculators are a great tool for performing the division required for these conversions.
Q3: What if the denominator is zero?
A3: Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. A fraction with a denominator of zero is not a valid mathematical expression.
Q4: How do I handle very large fractions?
A4: Even for large fractions, the principle remains the same: divide the numerator by the denominator. You might need a calculator or computer for larger numbers.
Q5: Are there other methods for converting fractions to decimals besides division?
A5: While division is the most direct method, there are alternative approaches involving manipulating the fraction to express it with a denominator that is a power of 10. However, these methods often require a good understanding of fraction simplification and equivalent fractions.
Conclusion: Mastering Decimal Conversions
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental mathematical operation with widespread applications. This article has explored two distinct methods for converting the mixed number 6 25 to its decimal equivalent (6.4), explained the underlying principles of division, and addressed common questions. Mastering this skill will strengthen your mathematical foundation and improve your problem-solving capabilities in various contexts. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering any mathematical skill, so keep practicing and don't hesitate to revisit these concepts as needed. The understanding gained here will serve as a solid base for more advanced mathematical explorations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6 25 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.