6 2x 5 X 4
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
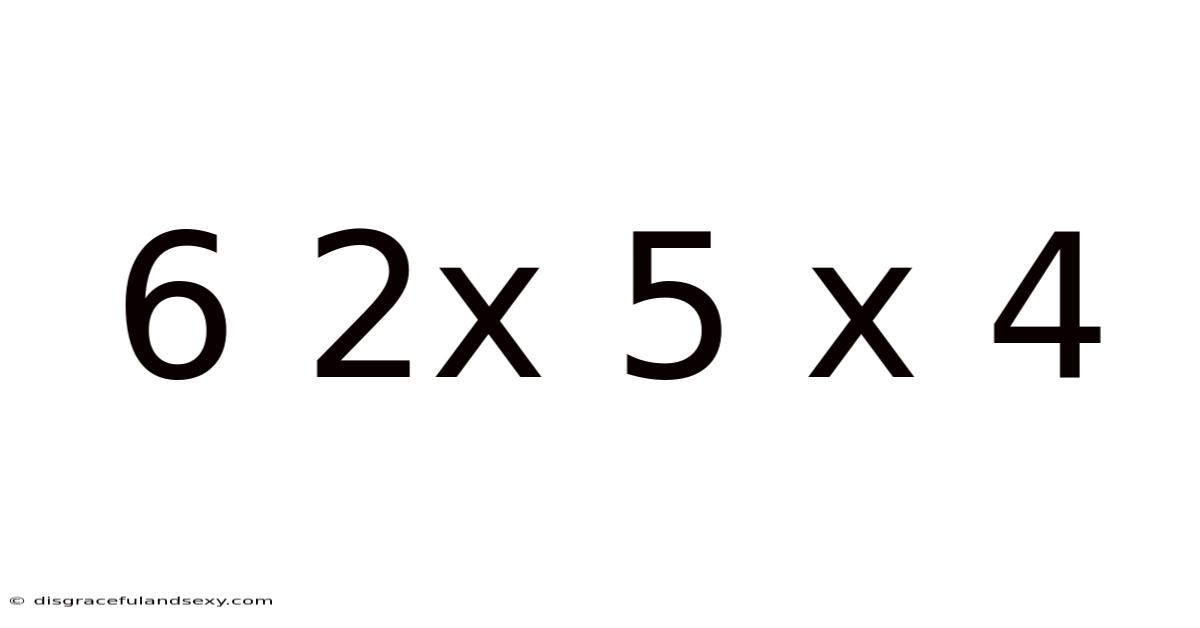
Table of Contents
Decoding 6 x 2 x 5 x 4: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "6 x 2 x 5 x 4," delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying principles of multiplication, its various applications in different fields, and its significance in developing a strong mathematical foundation. We'll unravel the mystery behind this equation, looking at different approaches to solving it, exploring the properties of multiplication, and showcasing its real-world relevance.
Introduction: Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, "6 x 2 x 5 x 4" represents a multiplication problem. Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation that essentially involves repeated addition. Think of it as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. For example, 6 x 2 means adding 6 to itself twice (6 + 6 = 12). This seemingly simple concept forms the bedrock of numerous complex mathematical operations and applications. This particular problem, however, presents us with a chain of multiplications, requiring us to understand the order of operations and the associative property of multiplication.
Solving 6 x 2 x 5 x 4: Different Approaches
There are several ways to approach solving this problem. The most straightforward method is to perform the multiplications sequentially:
- 6 x 2 = 12
- 12 x 5 = 60
- 60 x 4 = 240
Therefore, the answer to 6 x 2 x 5 x 4 is 240.
However, the associative property of multiplication allows us to change the grouping of numbers without affecting the result. This means we can rearrange the order of the multiplication to simplify the calculation. For example:
- (6 x 2) x (5 x 4) = 12 x 20 = 240 This method makes the calculation easier by working with smaller, more manageable numbers.
- (6 x 5) x (2 x 4) = 30 x 8 = 240 This approach highlights how we can strategically group numbers to simplify the calculations.
These alternative methods illustrate the flexibility and efficiency that can be gained by understanding the properties of multiplication. Choosing the most efficient method often depends on the specific numbers involved and individual preference.
The Commutative and Associative Properties of Multiplication
The ease with which we can rearrange the numbers in "6 x 2 x 5 x 4" is due to two important properties:
-
Commutative Property: This property states that the order of the numbers in a multiplication problem does not affect the result. For example, 2 x 6 is the same as 6 x 2. This applies to all the numbers in our equation, allowing for flexible arrangement.
-
Associative Property: This property states that the grouping of numbers in a multiplication problem does not affect the result. We can group the numbers in any way we want using parentheses, as demonstrated in the alternative solving methods above.
Understanding these properties is crucial not only for solving simple multiplication problems but also for more advanced mathematical concepts like algebra and calculus.
Real-World Applications: Where Multiplication Matters
Multiplication is far from a purely theoretical exercise; it's a fundamental tool applied across numerous fields:
-
Everyday Calculations: Calculating the total cost of multiple items, determining the area of a rectangular space, figuring out the total distance traveled, and even splitting a bill among friends all involve multiplication.
-
Engineering and Architecture: Engineers and architects utilize multiplication extensively in designing structures, calculating material quantities, determining forces and stresses, and scaling drawings. Accurate multiplication is crucial for structural integrity and safety.
-
Finance and Business: Calculating profits, losses, interest, taxes, and investments all rely heavily on multiplication. Businesses use it for inventory management, pricing strategies, and forecasting.
-
Computer Science: Multiplication is fundamental to computer algorithms, particularly in areas like graphics processing, cryptography, and data analysis. Efficient multiplication algorithms are crucial for maximizing computing power.
-
Science: Scientists employ multiplication in various experiments, data analysis, and modeling. From calculating the speed of an object to determining the concentration of a solution, multiplication plays a vital role.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding Our Understanding
While the equation "6 x 2 x 5 x 4" might seem elementary, it serves as a springboard for exploring deeper mathematical concepts:
-
Prime Factorization: We can break down each number into its prime factors. 6 = 2 x 3, so the equation becomes (2 x 3) x 2 x 5 x (2 x 2) = 2<sup>4</sup> x 3 x 5. This prime factorization method helps in understanding the building blocks of numbers and is essential for concepts like greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM).
-
Exponential Notation: The prime factorization demonstrates how exponential notation simplifies expressions with repeated factors. The 2<sup>4</sup> represents 2 multiplied by itself four times. This notation is crucial for dealing with large numbers and advanced mathematical problems.
Exploring Related Concepts: Division and Fractions
Multiplication has a close relationship with division. Division is essentially the inverse operation of multiplication. If we know that 6 x 2 x 5 x 4 = 240, then we can use division to find any of the original numbers if we know the product and the remaining numbers. For example, 240 / 6 / 5 / 4 = 2.
Fractions are closely related to multiplication and division. Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators together and the denominators together. Understanding fractions is essential for solving a wide array of mathematical problems and real-world scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS)?
The order of operations dictates the sequence in which mathematical operations should be performed. PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction) ensures consistent results. In our example, only multiplication is involved, so the order doesn't significantly matter due to the commutative and associative properties.
Q2: Can I use a calculator to solve this problem?
Yes, absolutely! Calculators are valuable tools for performing calculations quickly and accurately, especially for more complex problems.
Q3: Are there any tricks or shortcuts to solve multiplication problems?
Yes, various multiplication tricks and mental math techniques exist to speed up calculations. For example, multiplying by 5 is the same as multiplying by 10 and dividing by 2. Learning these shortcuts enhances mathematical fluency.
Q4: How does understanding this basic multiplication problem help me with more advanced math?
Mastering fundamental concepts like multiplication builds a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts such as algebra, calculus, and statistics. A solid understanding of basic arithmetic operations is essential for success in higher-level mathematics.
Conclusion: The Power of Fundamentals
The simple equation "6 x 2 x 5 x 4" might seem insignificant at first glance. However, through a detailed analysis, we've explored fundamental mathematical concepts, highlighted the practical applications of multiplication in diverse fields, and touched upon more advanced mathematical ideas. This seemingly basic problem reveals the immense power and broad utility of multiplication, underscoring the importance of mastering fundamental mathematical skills. The ability to confidently solve this type of problem is a cornerstone of numeracy and a stepping stone towards a deeper understanding of the mathematical world. Furthermore, the flexible approaches to solving this simple equation illuminate the beauty and elegance inherent within mathematical principles. It's not just about finding the answer (240); it's about understanding why that answer is correct and appreciating the underlying mathematical structure. This understanding forms the foundation for tackling more complex challenges, empowering individuals to confidently approach mathematical problems in various aspects of their lives.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6 2x 5 X 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.