6 X 1 5x 4
disgrace
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
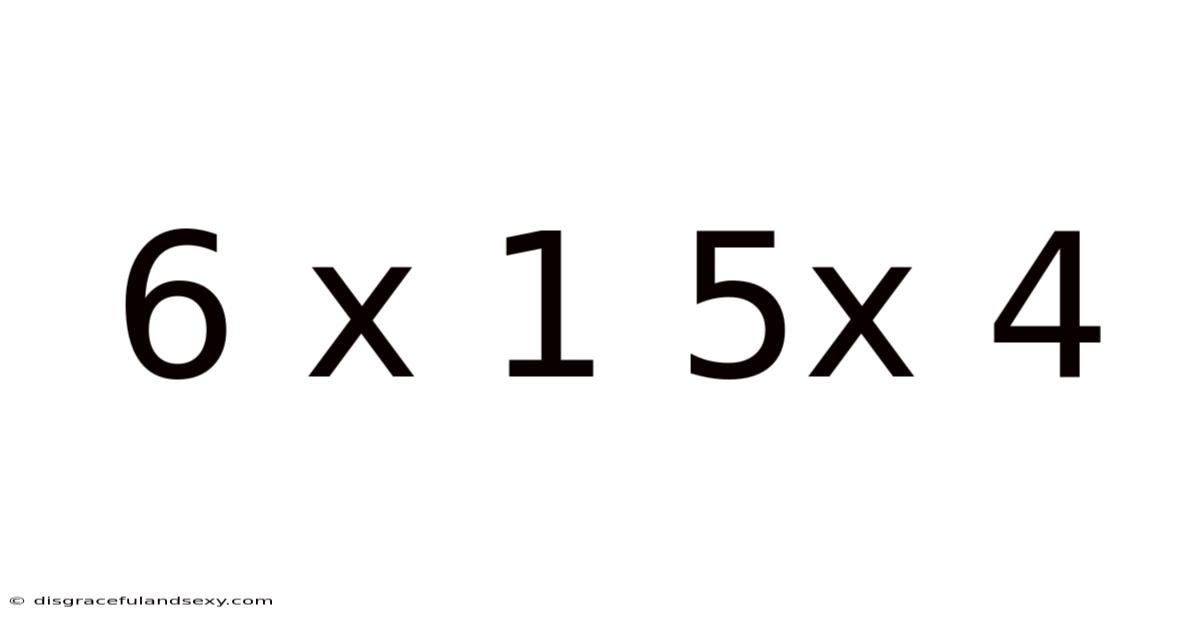
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Exploring the Mathematical and Practical Implications of "6 x 1" and "5 x 4"
The seemingly simple expressions "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" hold far more depth than their initial appearance suggests. While a quick calculation reveals their answers – 6 and 20 respectively – delving deeper unveils significant concepts in mathematics, its applications in various fields, and the broader implications of understanding fundamental arithmetic operations. This article will explore these expressions, examining their mathematical foundations, practical uses, and contextual relevance, providing a comprehensive understanding for learners of all levels.
I. Introduction: Understanding Multiplication as Repeated Addition
Before diving into the specifics of "6 x 1" and "5 x 4," let's establish a foundational understanding of multiplication. At its core, multiplication is a shorthand method for repeated addition. For instance, "6 x 1" can be understood as adding the number 1 six times: 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6. Similarly, "5 x 4" represents adding the number 4 five times: 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 20. This conceptual understanding is crucial, especially for younger learners, as it bridges the gap between addition and multiplication, solidifying the basic principles of arithmetic.
II. Analyzing "6 x 1": The Identity Property of Multiplication
The expression "6 x 1" highlights a fundamental property in mathematics: the identity property of multiplication. This property states that any number multiplied by 1 equals itself. In essence, multiplying a number by 1 leaves the number unchanged. This principle is universally applicable across all numbers, whether positive, negative, whole, fractions, or decimals. Understanding this property simplifies numerous calculations and is essential for more advanced mathematical concepts. The intuitive understanding of "6 x 1 = 6" lays the groundwork for more complex algebraic manipulations.
III. Exploring "5 x 4": Commutative and Distributive Properties
The expression "5 x 4" allows us to explore other important mathematical properties. Firstly, it demonstrates the commutative property of multiplication. This property states that the order of the numbers being multiplied does not affect the result. Therefore, 5 x 4 is equal to 4 x 5, both resulting in 20. This seemingly simple property has profound implications in more complex calculations, allowing for flexibility and simplification.
Furthermore, "5 x 4" can be used to illustrate the distributive property of multiplication. This property states that multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying the number by each addend individually and then adding the products. For example, we can express 5 x 4 as 5 x (2 + 2) = (5 x 2) + (5 x 2) = 10 + 10 = 20. This property is invaluable in simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations.
IV. Practical Applications: From Everyday Life to Advanced Mathematics
The seemingly simple calculations of "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" have far-reaching practical applications across numerous fields.
-
Everyday Calculations: These fundamental operations are crucial for everyday tasks, from calculating the total cost of items (e.g., 5 items at $4 each) to determining the number of items needed (e.g., 6 sets of 1 item each). The ability to perform these calculations quickly and accurately is a foundational life skill.
-
Geometry and Measurement: These principles underpin geometric calculations. Determining the area of a rectangle, for instance, involves multiplying its length and width. Understanding multiplication is therefore essential for various aspects of geometry and measurement, from calculating the area of a room to designing complex structures.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Multiplication is fundamental to various statistical calculations. Calculating averages, percentages, and probabilities often involve multiplication operations. A strong understanding of multiplication is therefore essential for analyzing data and making informed decisions based on statistical information.
-
Advanced Mathematics: These basic operations form the building blocks for more complex mathematical concepts. Algebra, calculus, and linear algebra all rely on a strong foundation in arithmetic, with multiplication being a cornerstone. Understanding these basic principles is therefore essential for progressing to more advanced mathematical studies.
-
Computer Science and Programming: Multiplication is a fundamental operation in computer programming. Many algorithms and computations rely on efficient multiplication procedures. In computer graphics, for instance, transformations and scaling operations often involve repeated multiplications.
V. Beyond the Numbers: Developing Critical Thinking Skills
The exploration of "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" extends beyond mere calculation; it promotes the development of crucial critical thinking skills. By analyzing these expressions, students learn to:
-
Identify Patterns and Relationships: Recognizing patterns like the identity and commutative properties allows for the development of abstract thinking skills and the ability to identify similar patterns in other mathematical contexts.
-
Problem-Solving: Applying these concepts to solve practical problems builds problem-solving skills and reinforces the relevance of mathematical principles in real-world situations.
-
Logical Reasoning: Understanding and explaining the underlying principles of multiplication fosters logical reasoning and the ability to justify mathematical conclusions.
-
Abstract Thinking: Moving beyond the concrete examples of "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" and applying the underlying principles to more abstract mathematical concepts strengthens abstract thinking abilities.
VI. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the significance of the number 1 in multiplication?
A1: The number 1 is the multiplicative identity. Multiplying any number by 1 results in the original number. This property is essential for various mathematical operations and simplifications.
Q2: Are there any exceptions to the commutative property of multiplication?
A2: No, the commutative property holds true for all real numbers. The order of multiplication does not affect the result.
Q3: How does understanding "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" help with more complex math?
A3: These basic calculations establish a foundational understanding of multiplication and its properties, which are crucial for more advanced concepts like algebra, calculus, and linear algebra. They provide the building blocks for more complex mathematical operations.
Q4: Why is it important to understand the distributive property?
A4: The distributive property simplifies complex expressions, making them easier to solve. It is used extensively in algebra and other branches of mathematics.
VII. Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Fundamental Arithmetic
While seemingly simple, the expressions "6 x 1" and "5 x 4" represent far more than basic arithmetic. They serve as gateways to understanding fundamental mathematical principles, exploring crucial properties like the identity, commutative, and distributive properties. These principles aren't confined to the classroom; they are essential for everyday life, various professions, and the pursuit of more advanced mathematical studies. Understanding these seemingly simple calculations is not just about getting the right answer; it's about building a strong foundation in mathematics and developing crucial critical thinking skills that will serve learners throughout their lives. The journey from understanding "6 x 1 = 6" and "5 x 4 = 20" is a journey into the fascinating world of numbers, logic, and the power of mathematical thinking. The more we explore these fundamental concepts, the more we unlock the power and beauty inherent in mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6 X 1 5x 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.