64/5 As A Mixed Number
disgrace
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
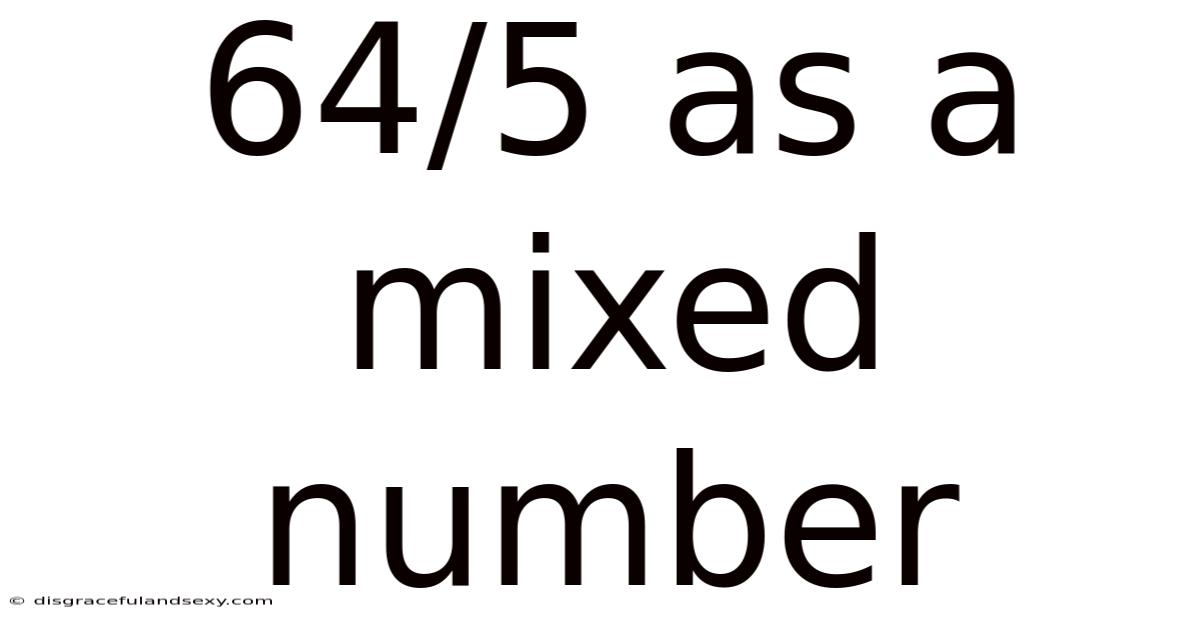
Table of Contents
Understanding 64/5 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Many mathematical concepts can seem daunting at first, but with a little patience and the right approach, they become surprisingly straightforward. This article will delve into the process of converting an improper fraction like 64/5 into a mixed number. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide step-by-step instructions, and answer frequently asked questions. By the end, you'll not only understand how to convert 64/5 but also gain a deeper understanding of fractions and mixed numbers.
What are Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers?
Before we tackle the conversion of 64/5, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms involved.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). Examples include 7/4, 11/5, and of course, 64/5. Essentially, it represents a value greater than or equal to one whole.
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator smaller than the denominator. Examples include 1 ¾, 2 ⅓, and 3 ⅛. Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to represent values greater than one.
Converting 64/5 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
The conversion of an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The result will give you the whole number part of your mixed number, and the remainder will form the fractional part. Let's break it down for 64/5:
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Divide 64 (the numerator) by 5 (the denominator): 64 ÷ 5 = 12 with a remainder of 4.
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and the Remainder
From Step 1, we get:
- Whole Number: 12 (This is the quotient from the division.)
- Remainder: 4 (This is the number left over after the division.)
Step 3: Construct the Mixed Number
The whole number becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. The remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part, and the original denominator remains the same. Therefore, 64/5 as a mixed number is 12 ⅘.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 64 identical objects, and you want to group them into sets of 5. You can form 12 complete sets of 5, leaving 4 objects ungrouped. This visually represents the 12 whole sets (the whole number) and the remaining 4 objects (the numerator of the fraction), all still grouped by a set size of 5 (the denominator).
The Mathematical Explanation
The conversion process is based on the fundamental principle of fraction representation. The improper fraction 64/5 can be rewritten as the sum of several fractions:
64/5 = 5/5 + 5/5 + 5/5 + ... + 5/5 + 4/5
Since 5/5 equals 1, we can simplify this to:
64/5 = 1 + 1 + 1 + ... + 1 + 4/5
There are twelve 1s (because 64 ÷ 5 = 12 with a remainder), so we have:
64/5 = 12 + 4/5 = 12 ⅘
Working with Other Improper Fractions
The method described above applies to any improper fraction. Let's consider a few examples:
-
17/3: 17 ÷ 3 = 5 with a remainder of 2. Therefore, 17/3 = 5 ⅔
-
29/6: 29 ÷ 6 = 4 with a remainder of 5. Therefore, 29/6 = 4 ⅝
-
35/4: 35 ÷ 4 = 8 with a remainder of 3. Therefore, 35/4 = 8 ¾
Converting Mixed Numbers back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand the reverse process: converting a mixed number back to an improper fraction. This involves these steps:
-
Multiply the whole number by the denominator: For 12 ⅘, this is 12 x 5 = 60.
-
Add the numerator: Add the result from step 1 to the numerator of the fraction: 60 + 4 = 64.
-
Keep the same denominator: The denominator remains 5.
Therefore, 12 ⅘ becomes 64/5.
Applications of Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Improper fractions and mixed numbers are essential in various real-world applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require fractional amounts of ingredients. Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers ensures accurate measurements.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in construction and engineering, and fractions are commonly used in blueprints and calculations.
-
Data Analysis: Representing data as fractions and mixed numbers can help in visualizing and interpreting results.
-
Everyday Life: Dividing a pizza, sharing snacks, or calculating distances often involves the use of fractions and mixed numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the remainder is 0?
A1: If the remainder is 0, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 20/5 = 4 (because 20 ÷ 5 = 4 with no remainder).
Q2: Can I simplify the fractional part of the mixed number?
A2: Yes, always simplify the fractional part of the mixed number if possible. For instance, if you have 15 ⁶/₁₂, you should simplify the fraction to 15 ½.
Q3: Why are mixed numbers useful?
A3: Mixed numbers offer a more intuitive representation of quantities larger than one. They are easier to visualize and understand in everyday contexts compared to improper fractions.
Q4: Are there different methods to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A4: While the long division method is the most common and widely understood, other methods exist, including using equivalent fractions or visual aids. However, the long division method provides a systematic and consistent approach for all improper fractions.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 64/5 to a mixed number (12 ⅘) is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process involves dividing the numerator by the denominator, identifying the whole number and the remainder, and constructing the mixed number accordingly. Understanding this concept is vital for numerous applications, from solving everyday problems to tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you work with improper fractions and mixed numbers, the more comfortable and confident you'll become in converting between them.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 64/5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.