6x 2 5x 6 Factored
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
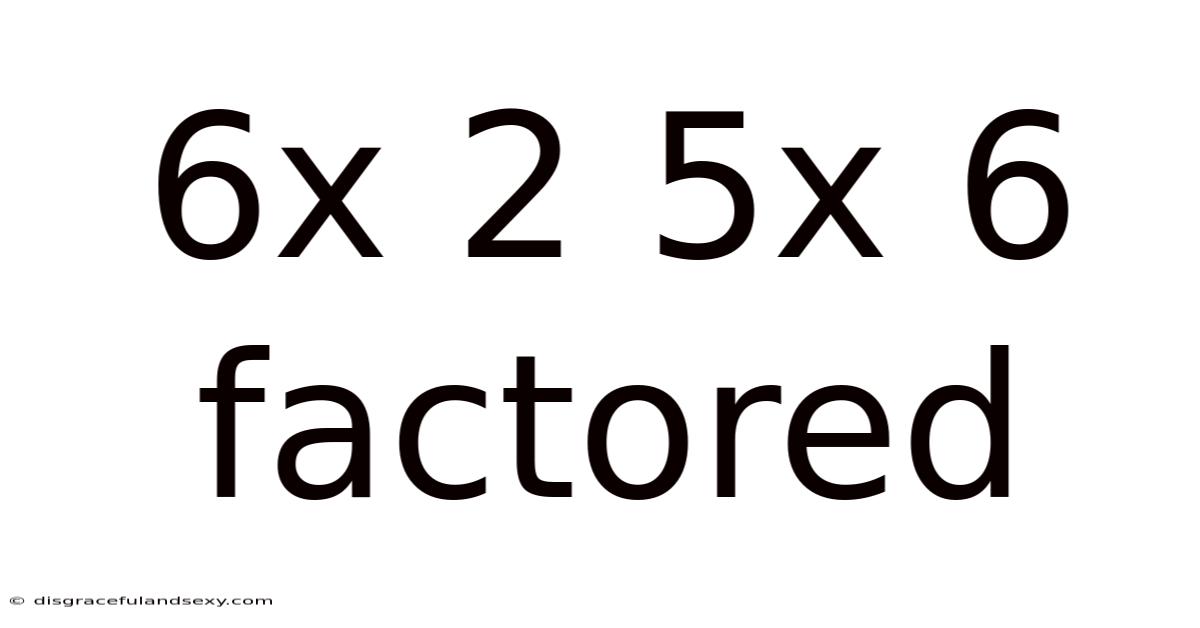
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: Factoring 6x² + 5x + 6
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding many mathematical concepts. This article delves into the process of factoring the quadratic expression 6x² + 5x + 6, exploring different approaches and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. While this specific quadratic may initially seem challenging, mastering the techniques outlined here will equip you to tackle similar problems with confidence. We'll explore both the practical steps and the mathematical reasoning behind them, making this a valuable resource for students of all levels.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
Before we dive into factoring 6x² + 5x + 6, let's refresh our understanding of quadratic expressions. A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually 'x') is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants. In our case, a = 6, b = 5, and c = 6.
Factoring a quadratic expression means rewriting it as a product of two linear expressions. This is essentially reversing the process of expanding brackets using the distributive property (often referred to as FOIL - First, Outer, Inner, Last). The goal is to find two binomials whose product equals the original quadratic.
Attempting Traditional Factoring Methods
The most common method for factoring quadratics involves finding two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'ac' (the product of the coefficients of x² and the constant term). Let's apply this to our expression:
- Find the product 'ac': 6 * 6 = 36
- Find two numbers that add to 'b' (5) and multiply to 36: This is where we encounter a challenge. There are no two integers that satisfy both conditions. The pairs of factors of 36 are (1, 36), (2, 18), (3, 12), (4, 9), (6, 6). None of these pairs add up to 5.
This indicates that the quadratic expression 6x² + 5x + 6 cannot be factored using simple integer coefficients. This doesn't mean it's unfactorable; it just means the factors are not as straightforward as those we usually encounter in introductory algebra.
Exploring the Quadratic Formula
When simple factoring methods fail, we can turn to the quadratic formula, a powerful tool for finding the roots (or zeros) of any quadratic equation. The roots are the values of x that make the quadratic expression equal to zero. The quadratic formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Let's apply this to our expression:
- a = 6
- b = 5
- c = 6
Substituting these values into the quadratic formula, we get:
x = [-5 ± √(5² - 4 * 6 * 6)] / (2 * 6) x = [-5 ± √(25 - 144)] / 12 x = [-5 ± √(-119)] / 12
Notice that we have a negative number under the square root (√-119). This indicates that the roots of the quadratic equation 6x² + 5x + 6 = 0 are complex numbers, involving the imaginary unit i (where i² = -1).
Understanding Complex Numbers and Factoring
The presence of complex roots means that the quadratic expression cannot be factored into two linear expressions with real coefficients. The factors will involve complex numbers. To express the factored form, we can use the roots we found using the quadratic formula. Let's denote the roots as x₁ and x₂:
x₁ = [-5 + √(-119)] / 12 x₂ = [-5 - √(-119)] / 12
The factored form of the quadratic can then be expressed as:
6(x - x₁)(x - x₂)
This is the fully factored form, although it might seem less intuitive due to the involvement of complex numbers. Substituting the expressions for x₁ and x₂ would provide the complete, albeit somewhat cumbersome, factored form.
Why is this Quadratic Difficult to Factor? The Discriminant
The key to understanding why 6x² + 5x + 6 is difficult to factor lies in the discriminant, the expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac). In this case, the discriminant is -119.
- Positive Discriminant: If b² - 4ac > 0, the quadratic has two distinct real roots, and it can be factored into two linear expressions with real coefficients.
- Zero Discriminant: If b² - 4ac = 0, the quadratic has one real root (a repeated root), and it can be factored as a perfect square.
- Negative Discriminant: If b² - 4ac < 0, as in our case, the quadratic has two complex conjugate roots, and it cannot be factored into linear expressions with real coefficients. The factors will involve complex numbers.
The negative discriminant tells us that the parabola represented by the quadratic expression 6x² + 5x + 6 does not intersect the x-axis. This is a graphical interpretation of the absence of real roots.
Alternative Approaches and Further Exploration
While the quadratic formula provides the definitive answer, other methods can offer additional insights. These might include:
-
Completing the Square: This technique involves manipulating the quadratic expression to create a perfect square trinomial, which can then be factored easily. While possible, it's often more cumbersome than the quadratic formula for this specific expression.
-
Graphical Analysis: Graphing the quadratic function y = 6x² + 5x + 6 will visually demonstrate that the parabola lies entirely above the x-axis, confirming the absence of real roots.
-
Numerical Methods: For practical applications, if you needed to find approximate values of x where the expression is close to zero, numerical methods (like the Newton-Raphson method) could be employed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is it important to learn how to factor quadratic expressions?
A: Factoring is a fundamental algebraic skill used in solving quadratic equations, simplifying rational expressions, and many other advanced mathematical concepts. It's a building block for higher-level mathematics.
Q: Are there any "tricks" to quickly factor quadratics?
A: While there are some shortcuts for certain types of quadratics (like perfect square trinomials), no single "trick" works for all cases. Practice and understanding the underlying principles are crucial.
Q: What if I get a fraction or decimal as a root when using the quadratic formula?
A: That's perfectly acceptable. Roots can be rational or irrational numbers. The quadratic formula is designed to work for all types of quadratic equations.
Q: Can a quadratic expression have more than two factors?
A: No, a quadratic expression (of degree 2) can have at most two linear factors.
Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression 6x² + 5x + 6 reveals a deeper understanding of quadratic equations and the properties of their roots. While it cannot be factored simply using integer coefficients due to its negative discriminant, understanding the quadratic formula and its relationship to the discriminant provides a complete and accurate solution. The resulting factors involve complex numbers, highlighting the broader scope of number systems in algebra. Mastering the techniques described here is crucial for success in algebra and beyond, and don't be discouraged by expressions that initially seem difficult – with the right tools and understanding, even complex problems can be solved.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6x 2 5x 6 Factored . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.