6x 2 X 2 0
disgrace
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
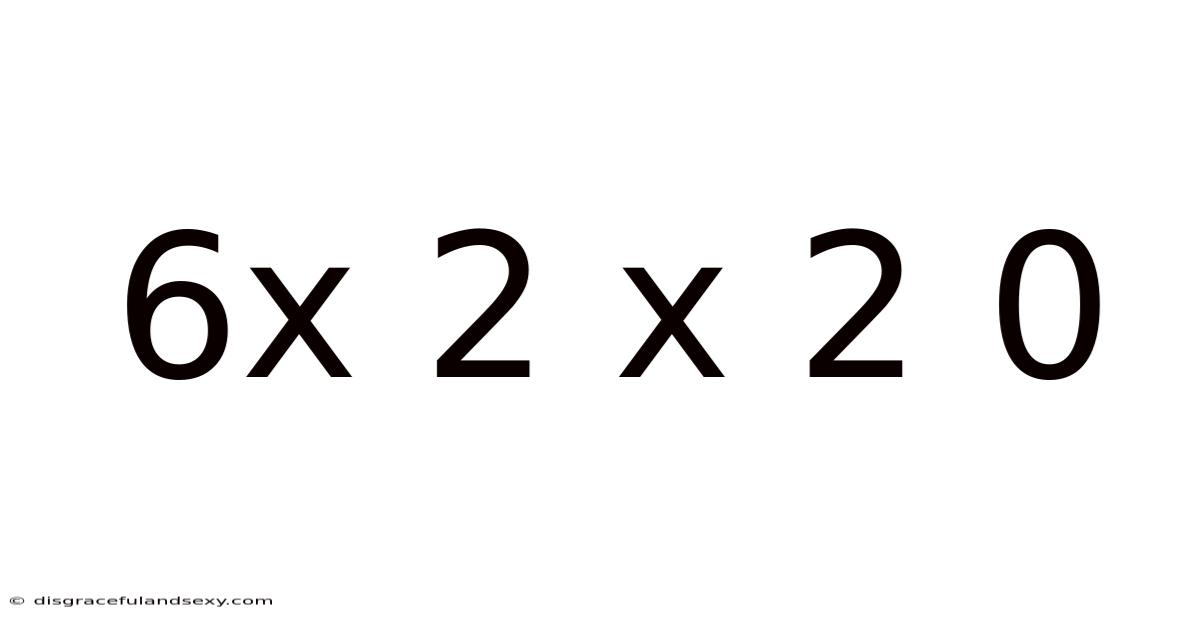
Table of Contents
Decoding 6x2x20: A Deep Dive into the Mathematics and Beyond
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "6 x 2 x 20," delving beyond the basic calculation to uncover its underlying principles, potential interpretations, and applications in various fields. We will examine the fundamental operations involved, explore the concept of order of operations, and consider how this expression can be used as a foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts. This exploration will also touch upon the significance of numbers and their symbolic representation across cultures and history.
The Basic Calculation: Understanding Multiplication
At its core, "6 x 2 x 20" is a multiplication problem. Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation representing repeated addition. In this case, we are repeatedly adding the number 6, 2 times, and then multiplying the result by 20. The simplest approach is to perform the multiplications sequentially:
- Step 1: 6 x 2 = 12
- Step 2: 12 x 20 = 240
Therefore, the solution to 6 x 2 x 20 is 240. This simple calculation forms the bedrock of our further exploration.
The Importance of Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS)
While the order in this particular example doesn't alter the outcome, it's crucial to understand the order of operations, often remembered by the acronyms PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction). These acronyms emphasize that multiplication and division are performed before addition and subtraction. In expressions with parentheses or exponents, those operations take precedence. The consistent application of these rules ensures that mathematical expressions are interpreted and solved uniformly, regardless of who is performing the calculation.
Understanding the order of operations is essential for tackling more complex mathematical problems. Without it, ambiguity arises, leading to different and incorrect answers. For example, consider the expression 6 + 2 x 20. If we perform the addition first, we get (6 + 2) x 20 = 160. However, following PEMDAS/BODMAS, we perform the multiplication first: 6 + (2 x 20) = 46. The correct answer is 46, demonstrating the importance of adhering to the established order of operations.
Factorization and Prime Numbers: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The expression 6 x 2 x 20 can be further analyzed by considering the prime factorization of each number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7). Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime number components.
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 2 = 2
- 20 = 2 x 2 x 5
Therefore, the prime factorization of 6 x 2 x 20 is 2 x 3 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 5, which simplifies to 2<sup>4</sup> x 3 x 5. This process reveals the fundamental building blocks of the number 240, highlighting the interconnectedness of numbers through their prime components. This concept is crucial in various areas of mathematics, including number theory and cryptography.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
While seemingly simple, the concept of multiplication, as demonstrated by 6 x 2 x 20, finds numerous applications in everyday life and various professional fields:
- Business and Finance: Calculating total costs, profits, or sales based on unit price and quantity. For instance, if a company sells 6 items at $20 each, and has 2 different types of items, the total revenue would involve calculations similar to our example.
- Engineering and Construction: Determining quantities of materials needed for a project. This might involve calculating the number of bricks needed for a wall, the volume of concrete, or the length of wire required for an electrical system.
- Data Analysis and Statistics: Multiplication is fundamental in various statistical calculations, such as determining averages, calculating probabilities, and scaling data sets.
- Computer Science: Multiplication plays a vital role in many algorithms and computational tasks, including image processing, graphics rendering, and data encryption.
These are just a few examples. The ability to perform and understand basic arithmetic operations like multiplication is a cornerstone of success in numerous fields.
Beyond the Numbers: Symbolic and Cultural Interpretations
Numbers, including those in our expression (6, 2, 20, and 240), often hold symbolic and cultural significance. Different cultures may associate specific numbers with particular concepts, beliefs, or events. For example:
- The Number 6: In some cultures, 6 is associated with harmony, balance, and perfection. In Christianity, it represents creation (6 days of creation).
- The Number 2: Often represents duality, partnership, and balance. It’s frequently seen as a symbol of opposing forces.
- The Number 20: Holds significance in various contexts, including ancient Mayan calendar systems.
- The Number 240: While not as prominently symbolic as the others, it can be interpreted within the context of the original expression, linking it to the combined meanings of its constituent numbers.
Understanding the symbolic implications of numbers adds a layer of depth to mathematical exploration, highlighting the rich interplay between mathematics and culture.
Expanding the Concept: Exploring Further Mathematical Concepts
The seemingly straightforward expression "6 x 2 x 20" can serve as a stepping stone to understand more advanced mathematical ideas:
- Algebra: This expression could be represented algebraically using variables, allowing for more generalized calculations and problem-solving. For instance, we could use variables like a, b, and c to represent 6, 2, and 20 respectively, resulting in the algebraic expression a x b x c.
- Geometry: This expression could be used to calculate areas or volumes. For instance, imagine a rectangular prism with dimensions 6, 2, and 20 units. The volume would be 240 cubic units.
- Calculus: While seemingly unrelated, the principles underlying multiplication and the concept of limits are fundamental to calculus, a branch of mathematics dealing with continuous change.
By viewing this simple expression as a building block, one can bridge the gap to more complex and abstract mathematical concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What is the result of 6 x 2 x 20?
- A: The result is 240.
-
Q: What if the numbers were arranged differently? Would the answer change?
- A: No, the order of multiplication does not change the result (due to the commutative property of multiplication).
-
Q: How can I solve this problem without a calculator?
- A: You can perform the multiplication step-by-step: first 6 x 2 = 12, then 12 x 20 = 240. Alternatively, you could use mental math techniques to simplify the calculation.
-
Q: What is the significance of the prime factorization of 240?
- A: The prime factorization (2<sup>4</sup> x 3 x 5) reveals the fundamental building blocks of the number 240, providing insights into its structure and relationships with other numbers.
-
Q: Are there any real-world applications beyond those mentioned?
- A: Yes, countless real-world scenarios utilize multiplication. Examples include calculating dosages of medication, determining the amount of fuel needed for a journey, and even managing personal finances.
Conclusion: The Power of Simple Mathematics
The expression "6 x 2 x 20," while seemingly simple, provides a rich starting point for exploring fundamental mathematical concepts, real-world applications, and the deeper symbolic meanings associated with numbers. From the basic calculation to the broader implications in various fields and cultural contexts, this seemingly straightforward problem reveals the power and versatility of even the most basic mathematical operations. The ability to perform this simple calculation and understand its underlying principles forms a crucial foundation for success in numerous academic and professional endeavors. This article hopefully highlights not just the "how" but also the "why" behind basic arithmetic, encouraging further exploration and deeper understanding of the world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6x 2 X 2 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.