7 4 As A Decimal
disgrace
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
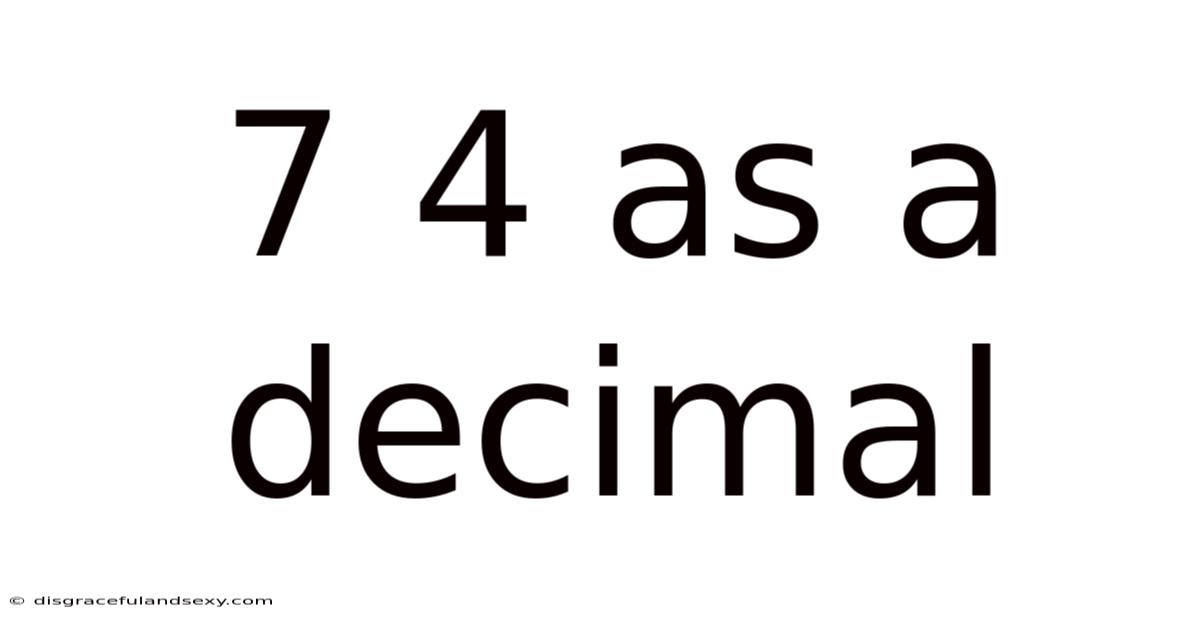
Table of Contents
Decoding 7/4 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will explore the conversion of the fraction 7/4 into its decimal representation, providing a step-by-step approach, explaining the underlying principles, and addressing frequently asked questions. We'll delve into various methods, ensuring a thorough understanding for learners of all levels. This will cover not only the simple conversion but also the broader context of fractions and decimals, making this a valuable resource for anyone seeking to master these essential concepts.
Introduction: Fractions and Decimals
Before diving into the specific conversion of 7/4, let's refresh our understanding of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). For example, in the fraction 7/4, 7 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. A decimal, on the other hand, represents a number using base-10 notation, with a decimal point separating the whole number part from the fractional part. Understanding the relationship between fractions and decimals is crucial for various mathematical operations.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method to convert a fraction to a decimal is through long division. We divide the numerator (7) by the denominator (4).
-
Set up the division: Write 7 as the dividend and 4 as the divisor. You can set this up as 7 ÷ 4 or using the long division format.
-
Perform the division: 4 goes into 7 one time (4 x 1 = 4). Subtract 4 from 7, leaving a remainder of 3.
-
Add a decimal point and a zero: Bring down a zero to the remainder, making it 30.
-
Continue the division: 4 goes into 30 seven times (4 x 7 = 28). Subtract 28 from 30, leaving a remainder of 2.
-
Add another zero: Bring down another zero, making it 20.
-
Final division: 4 goes into 20 five times (4 x 5 = 20). The remainder is 0.
Therefore, 7/4 = 1.75
Method 2: Understanding Improper Fractions
The fraction 7/4 is an improper fraction, meaning the numerator (7) is larger than the denominator (4). Improper fractions can be easily converted to mixed numbers. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction.
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: 7 ÷ 4 = 1 with a remainder of 3.
-
Write the mixed number: The whole number is the quotient (1), and the fraction is the remainder (3) over the denominator (4). This gives us 1 3/4.
-
Convert the proper fraction to a decimal: Now, we convert the proper fraction 3/4 to a decimal using long division (as shown in Method 1) or by recognizing that 3/4 is equivalent to 0.75.
-
Combine the whole number and the decimal: 1 + 0.75 = 1.75
This method highlights the versatility of representing fractions in different formats, all leading to the same decimal equivalent.
Method 3: Using Equivalent Fractions
While less direct than long division, understanding equivalent fractions can be helpful. We can express 7/4 using an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). This directly gives us the decimal representation. However, in this case, finding a power of 10 denominator isn't as straightforward. While you could express 7/4 as 175/100, this method doesn't provide a systematic approach for all fractions. The long division method is generally more robust and applicable to a wider range of fractions.
Mathematical Explanation: Why This Works
The conversion from a fraction to a decimal fundamentally relies on the concept of division. A fraction represents a division problem. The numerator is divided by the denominator. The decimal representation expresses this division result using base-10 notation. The long division process systematically performs this division, providing the decimal equivalent digit by digit. When the remainder becomes zero, the division is complete, and we have the exact decimal representation. If the remainder never becomes zero, it indicates a repeating or non-terminating decimal.
Real-World Applications of Decimal Conversions
Converting fractions to decimals is essential in many real-world situations:
- Finance: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and proportions often involve converting fractions to decimals.
- Measurement: Converting measurements from fractions of an inch or centimeter to decimal values is common in engineering, construction, and manufacturing.
- Science: Data analysis and scientific calculations frequently utilize decimals.
- Computing: Computers work with binary numbers (base-2), but many computations require conversion to and from decimal representations.
Understanding this process enables you to tackle these real-world problems effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the fraction results in a repeating decimal?
Some fractions, when converted to decimals, result in repeating decimals (e.g., 1/3 = 0.333...). In these cases, you can represent the repeating part using a bar notation (e.g., 0.3̅) or round the decimal to a desired number of decimal places.
Q2: Can I use a calculator to convert fractions to decimals?
Yes, most calculators have a fraction-to-decimal conversion function. Simply enter the fraction and press the appropriate button. However, understanding the underlying process is crucial for developing mathematical intuition and problem-solving skills.
Q3: Is there a difference between using a mixed number and an improper fraction for conversion?
No, the final decimal result will be the same whether you start with an improper fraction (7/4) or its equivalent mixed number (1 3/4). The choice depends on personal preference and the context of the problem. However, using the improper fraction often simplifies the long division process.
Q4: What if the denominator is a large number?
Even with large denominators, the long division method remains the most reliable approach. While it might take more steps, the process remains consistent. Consider using a calculator for efficiency, but remember the foundational principles.
Q5: Are there any shortcuts for converting specific fractions to decimals?
Some common fractions have easily memorized decimal equivalents (e.g., 1/2 = 0.5, 1/4 = 0.25, 3/4 = 0.75). Recognizing these common fractions can speed up calculations, but the long division method serves as a universal approach.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction to Decimal Conversions
Converting 7/4 to its decimal equivalent, 1.75, is a foundational concept in mathematics. Understanding this process, through methods such as long division and working with improper fractions and mixed numbers, empowers you to tackle more complex mathematical problems. This understanding extends beyond simple conversions, providing a solid base for future mathematical endeavors. The ability to confidently translate between fractions and decimals is a valuable skill applicable across numerous fields, strengthening your overall mathematical proficiency. By mastering this skill, you build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and real-world problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 4 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.