7 X 4 X 3
disgrace
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
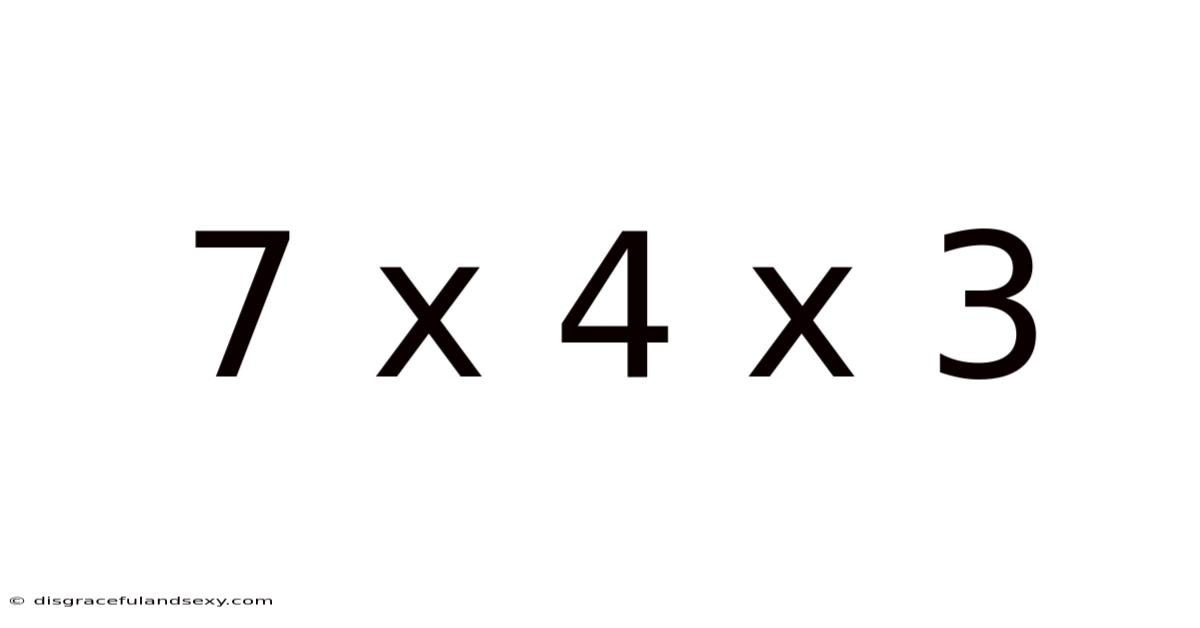
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of 7 x 4 x 3: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and Beyond
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "7 x 4 x 3," delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying principles of multiplication, its practical applications, and its connections to broader mathematical concepts. We'll explore different methods of calculation, discuss the commutative and associative properties, and even touch upon the historical context of multiplication. This comprehensive guide is designed for anyone, from elementary school students grasping the basics to those seeking a deeper understanding of mathematical foundations.
I. Introduction: More Than Just a Calculation
At first glance, 7 x 4 x 3 appears to be a straightforward multiplication problem. The answer, 84, is easily obtained with a calculator or through manual calculation. However, this seemingly simple equation provides a fantastic opportunity to explore fundamental mathematical concepts and their applications in various fields. This article aims to dissect this problem, revealing the richness hidden within its seemingly simple structure. We will examine different approaches to solving the problem, explore the properties of multiplication, and highlight its relevance in diverse contexts, from everyday life to advanced mathematics.
II. Calculating 7 x 4 x 3: Different Approaches
There are several ways to calculate 7 x 4 x 3, highlighting the flexibility of mathematics.
-
Method 1: Sequential Multiplication: The most straightforward method is to perform the multiplications sequentially. First, calculate 7 x 4 = 28, and then multiply the result by 3: 28 x 3 = 84.
-
Method 2: Changing the Order (Commutative Property): Multiplication is commutative, meaning the order of the numbers doesn't affect the result. We can rearrange the numbers to simplify the calculation. For example, we could calculate 4 x 3 = 12 first, and then multiply by 7: 12 x 7 = 84. This method often makes mental calculation easier.
-
Method 3: Grouping (Associative Property): Multiplication is also associative, allowing us to group the numbers differently. We can calculate (7 x 4) x 3 or 7 x (4 x 3) without altering the outcome. This property is crucial in more complex calculations.
-
Method 4: Using Distributive Property: While less efficient for this specific problem, the distributive property can be applied in more complex scenarios. For instance, if we were to calculate 7 x (4 + 3), we could distribute the 7 to both terms inside the parenthesis: (7 x 4) + (7 x 3) = 28 + 21 = 49. This is not directly applicable to 7 x 4 x 3, but demonstrates a related concept.
III. The Commutative and Associative Properties: Cornerstones of Multiplication
The successful application of Methods 2 and 3 above hinges on two crucial properties:
-
Commutative Property: This property states that for any two numbers a and b, a x b = b x a. This means that we can swap the order of numbers being multiplied without changing the product. This seems simple, but it's a fundamental concept that simplifies many calculations and underlies more advanced mathematical theorems.
-
Associative Property: This property states that for any three numbers a, b, and c, (a x b) x c = a x (b x c). This allows us to group the numbers being multiplied in any way without affecting the final result. This property is particularly useful when dealing with multiple factors, making calculations more manageable.
IV. Applications of Multiplication: From Everyday Life to Advanced Mathematics
The seemingly simple operation of 7 x 4 x 3 has far-reaching applications:
-
Everyday Calculations: Imagine you need to buy 7 packs of pencils, each containing 4 boxes, and each box holding 3 pencils. 7 x 4 x 3 immediately tells you the total number of pencils (84). This is a common application in inventory management, pricing, or any situation involving multiple quantities.
-
Geometry and Volume: Consider a rectangular prism (a box) with dimensions 7 units, 4 units, and 3 units. The volume of this prism is calculated by multiplying these three dimensions: 7 x 4 x 3 = 84 cubic units. Understanding multiplication is essential for calculating areas, volumes, and other geometrical properties.
-
Algebra and Beyond: Multiplication forms the basis of many algebraic concepts. It's fundamental to solving equations, understanding polynomials, and exploring advanced mathematical topics like linear algebra and calculus.
-
Computer Science: Multiplication is a core operation in computer programming, utilized in countless algorithms and computations, from simple calculations to complex simulations.
-
Physics and Engineering: Many physical phenomena are described using mathematical models that rely heavily on multiplication. Force, energy, and momentum calculations all involve multiplicative relationships.
V. The Historical Context of Multiplication
The concept of multiplication, while seemingly simple today, has a rich history. Early civilizations developed different methods for multiplication, often relying on visual aids or specific techniques. The development of efficient multiplication algorithms has been a crucial step in the advancement of mathematics and technology. The understanding and utilization of the commutative and associative properties, while now seemingly obvious, represent significant milestones in mathematical understanding.
VI. Expanding on the Problem: Exploring Related Concepts
The problem 7 x 4 x 3 opens doors to explore several interconnected mathematical concepts:
-
Factors and Multiples: The numbers 7, 4, and 3 are factors of 84. Conversely, 84 is a multiple of 7, 4, and 3. Exploring factors and multiples is important for understanding number theory and simplifying fractions.
-
Prime Factorization: We can break down 84 into its prime factors: 2 x 2 x 3 x 7. This factorization is unique to every number and is essential in various mathematical fields.
-
Exponents: We can express 84 using exponents, although it's not as directly related as prime factorization. For example, 84 can be represented as 2² x 3 x 7.
-
Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): While not directly relevant to this simple equation, understanding the order of operations (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) is crucial for solving more complex mathematical expressions.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the easiest way to calculate 7 x 4 x 3?
- A: The easiest way depends on your preference and mathematical skills. Many find calculating 4 x 3 = 12 first, then 12 x 7 = 84, to be simpler.
-
Q: Why is the order of multiplication not important in this problem?
- A: Because multiplication is commutative and associative. This means you can change the order of the numbers or group them differently without altering the product.
-
Q: What are some real-world applications of this calculation?
- A: Many scenarios in daily life involve multiplying multiple quantities. This includes calculating the total cost of multiple items, the volume of objects, or the number of items in a collection.
-
Q: How does this relate to more advanced math?
- A: Multiplication is the foundation of many advanced mathematical concepts, including algebra, calculus, and linear algebra. Understanding fundamental principles like the commutative and associative properties is crucial for tackling more complex problems.
VIII. Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of a Simple Equation
While seemingly simple, the equation 7 x 4 x 3 offers a gateway to a much wider understanding of mathematics. It showcases the power of fundamental principles like the commutative and associative properties, demonstrates the versatility of multiplication in various applications, and provides a stepping stone to explore more complex mathematical concepts. By understanding the intricacies of this seemingly basic calculation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematics in our world. It’s not just about getting the answer (84); it's about understanding why the answer is 84 and the implications of that understanding. This exploration highlights the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and encourages a deeper engagement with the beauty and utility of numbers.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 X 4 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.