7 X 5 X 2
disgrace
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
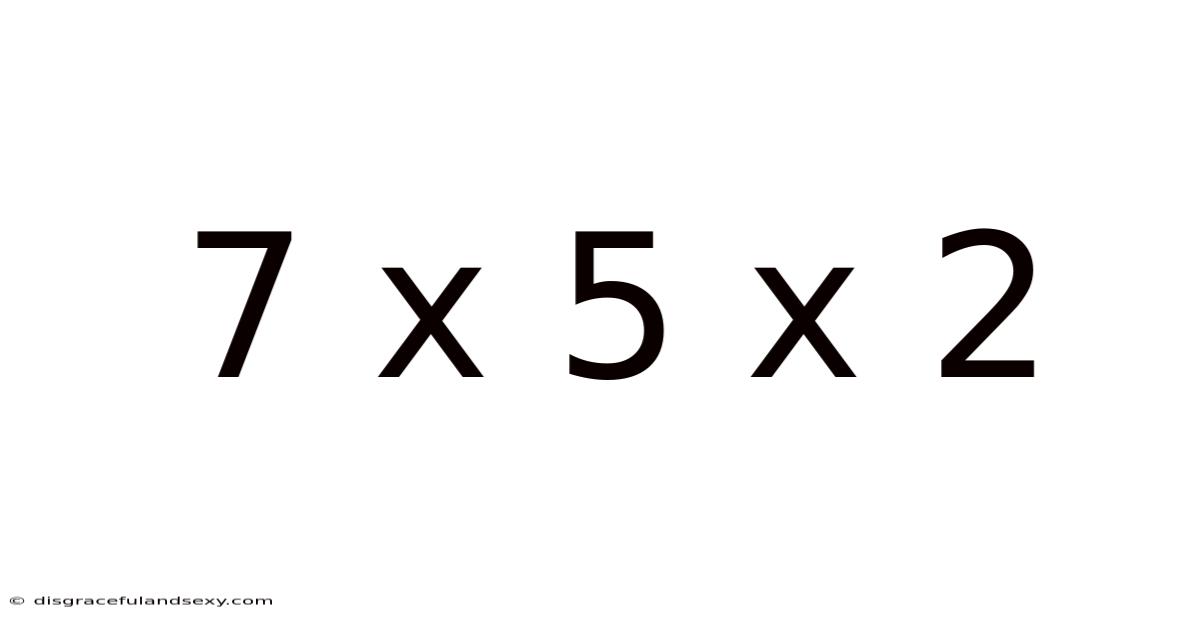
Table of Contents
Decoding 7 x 5 x 2: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical expression "7 x 5 x 2," delving far beyond the basic arithmetic solution. We'll examine the fundamental principles of multiplication, its practical applications across various fields, and even touch upon the fascinating philosophical implications of this seemingly straightforward calculation. Understanding this seemingly simple equation unlocks a world of mathematical understanding, highlighting the power and elegance of mathematics in our daily lives.
Introduction: The Building Blocks of Multiplication
At its core, 7 x 5 x 2 is a multiplication problem. Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation representing repeated addition. Think of it as adding the number 7, five times, and then doubling the result. This concept, while simple in its essence, forms the cornerstone of more complex mathematical concepts. The order of operations doesn't matter in this instance (due to the commutative and associative properties of multiplication), meaning we can calculate this in several ways: (7 x 5) x 2, 7 x (5 x 2), or any other combination. The answer remains consistent: 70. This seemingly simple fact highlights the power and consistency within the mathematical framework.
Step-by-Step Calculation: Different Approaches
Let's break down the calculation in a few different ways, illustrating the flexibility of multiplication:
Method 1: Sequential Multiplication
- 7 x 5 = 35: First, we multiply 7 by 5. This can be visualized as seven rows of five objects each.
- 35 x 2 = 70: Next, we multiply the result (35) by 2. This is equivalent to doubling 35.
Method 2: Rearranging the Factors
- 5 x 2 = 10: We can begin by multiplying 5 and 2, resulting in 10.
- 7 x 10 = 70: Then, we multiply 7 by 10, which is a simpler calculation than 35 x 2 for many.
This demonstrates the commutative property of multiplication: the order of the numbers doesn't affect the final product (a x b = b x a). It also demonstrates the associative property: the grouping of the numbers doesn't matter ((a x b) x c = a x (b x c)). These properties are fundamental to algebraic manipulation and problem-solving.
The Practical Applications of Multiplication: Beyond the Classroom
The seemingly simple equation 7 x 5 x 2 has far-reaching practical applications across numerous fields:
-
Everyday Life: Imagine you're buying groceries. You need 7 packs of apples, each containing 5 apples, and you decide to buy two such sets. 7 x 5 x 2 instantly tells you the total number of apples: 70. This simple calculation extends to various purchasing scenarios, budgeting, and everyday accounting.
-
Engineering and Construction: In construction, calculating the volume of a rectangular object often requires multiplication. For example, imagine a room that is 7 meters long, 5 meters wide, and 2 meters high. 7 x 5 x 2 gives us the volume of 70 cubic meters. This is crucial for material estimations, cost calculations, and efficient resource allocation in construction projects. Similar calculations are used in other engineering fields.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: In data analysis, multiplication is used extensively for scaling data, calculating averages, and performing statistical analysis. Understanding multiplicative relationships is critical for interpreting data and drawing accurate conclusions.
-
Computer Science and Programming: Multiplication is a fundamental operation in computer programming, used in various algorithms, data structures, and calculations. From basic arithmetic to complex simulations, multiplication underpins much of the computational work done by computers.
-
Finance and Economics: Calculating compound interest, determining investment returns, or forecasting economic growth often involves repeated multiplication. A solid understanding of multiplication is essential for anyone working in finance or economics.
Exploring the Mathematical Concepts: Beyond the Basics
Let's delve deeper into some relevant mathematical concepts related to our equation:
-
Prime Factorization: The numbers 7, 5, and 2 are all prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. The prime factorization of 70 (7 x 5 x 2) is a unique representation of this number as a product of its prime factors. This concept is fundamental in number theory and cryptography.
-
Factors and Multiples: The numbers 7, 5, 2, 10, 14, 35, and 70 are all factors of 70. Conversely, 70 is a multiple of 7, 5, 2, 10, 14, and 35. Understanding factors and multiples is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding divisibility rules.
-
Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): While the order of operations doesn't change the result in this specific calculation because it only involves multiplication, understanding PEMDAS/BODMAS (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) is vital for solving more complex mathematical expressions involving different operations.
-
Algebraic Representation: Our equation can be represented algebraically as x = 7 * y * z, where x = 70, y = 5, and z = 2. This illustrates how simple arithmetic lays the foundation for algebraic concepts and problem-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What if the order of numbers was different? The commutative and associative properties of multiplication ensure that the result remains the same regardless of the order of the numbers.
-
How can I visualize 7 x 5 x 2? You can visualize this as a rectangular prism with dimensions 7 units by 5 units by 2 units. The total number of unit cubes within this prism is 70.
-
Are there any real-world examples beyond the ones mentioned? Countless real-world scenarios utilize this type of multiplication. Consider calculating the total cost of multiple items with the same price, determining the number of seats in a rectangular auditorium, or even calculating the area of a rectangular plot of land.
-
How does this relate to more advanced mathematics? This simple equation serves as a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts such as linear algebra, calculus, and number theory. Understanding the fundamentals is crucial for tackling more complex problems.
Conclusion: The Significance of Simplicity
The seemingly simple equation 7 x 5 x 2 provides a gateway to understanding a wealth of mathematical concepts and their practical applications. From everyday calculations to sophisticated scientific analyses, multiplication forms the cornerstone of many crucial processes. By grasping the fundamental principles involved in this simple equation, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the power and elegance of mathematics, recognizing its pervasive role in shaping our world. The ability to perform this calculation efficiently is not merely about finding the answer (70); it's about developing a foundational understanding of mathematical principles that extend far beyond this single problem. This seemingly simple equation serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of mastering fundamental skills and appreciating their far-reaching consequences. The beauty of mathematics often lies in its simplicity and the surprising depth it reveals upon closer examination.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 7 X 5 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.